Why in News?
The Indian Chamber of Commerce launched the All India Initiative on Creative Economy (AIICE) with an aim to "tap into the vast potential of India's creative industries".
Creative Economy or Orange Economy:
- It is an evolving concept based on creative assets potentially generating economic growth and development.
- Essentially it is knowledge-based economic activities upon which 'creative industries' are based.
- Creative industries are cycles of creation, production and distribution of goods and services that use creativity and intellectual capital as primary inputs (See infographic)
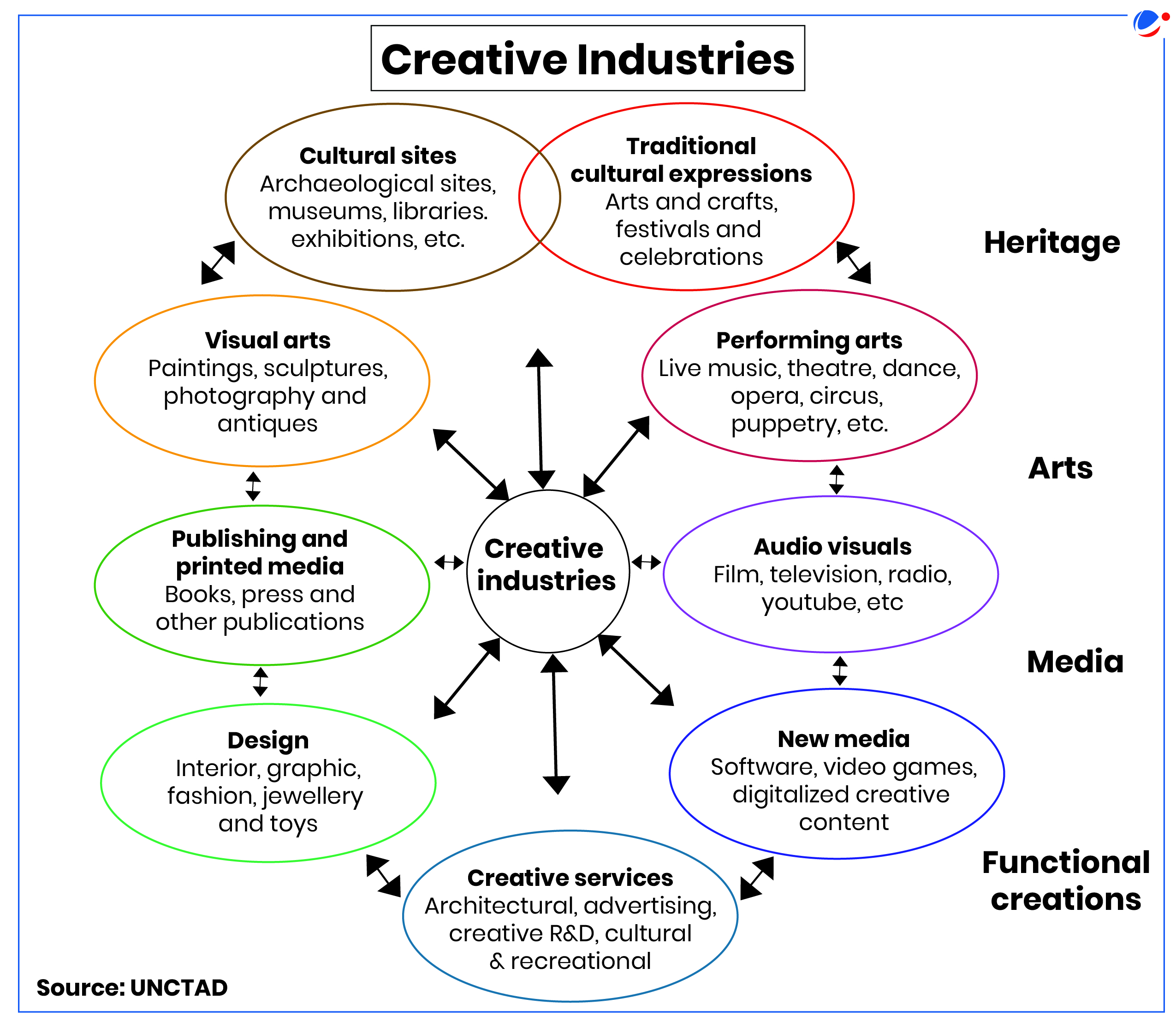
Characteristics of Creative Economy
- Knowledge-based economic activities: based on knowledge that is either formally acquired through education and training or inherited (informal skill transfer that has been preserved over generations).
- Original idea and imagination: involve generation and exploitation of intellectual property.
- Non-repetitive and adaptive to technological change and mechanization: This feature is especially important in India where 69% of jobs will be threatened due to automation by 2040.
- Economic and culture value chain: An individual's original idea, is developed into a cultural product through production and distribution.
Significance of Creative Economy
- Economic aspects:
- Create linkages and Spill-over Effects: Can lead to an increase in demand for goods and services from other sectors, such as hospitality and tourism industry.
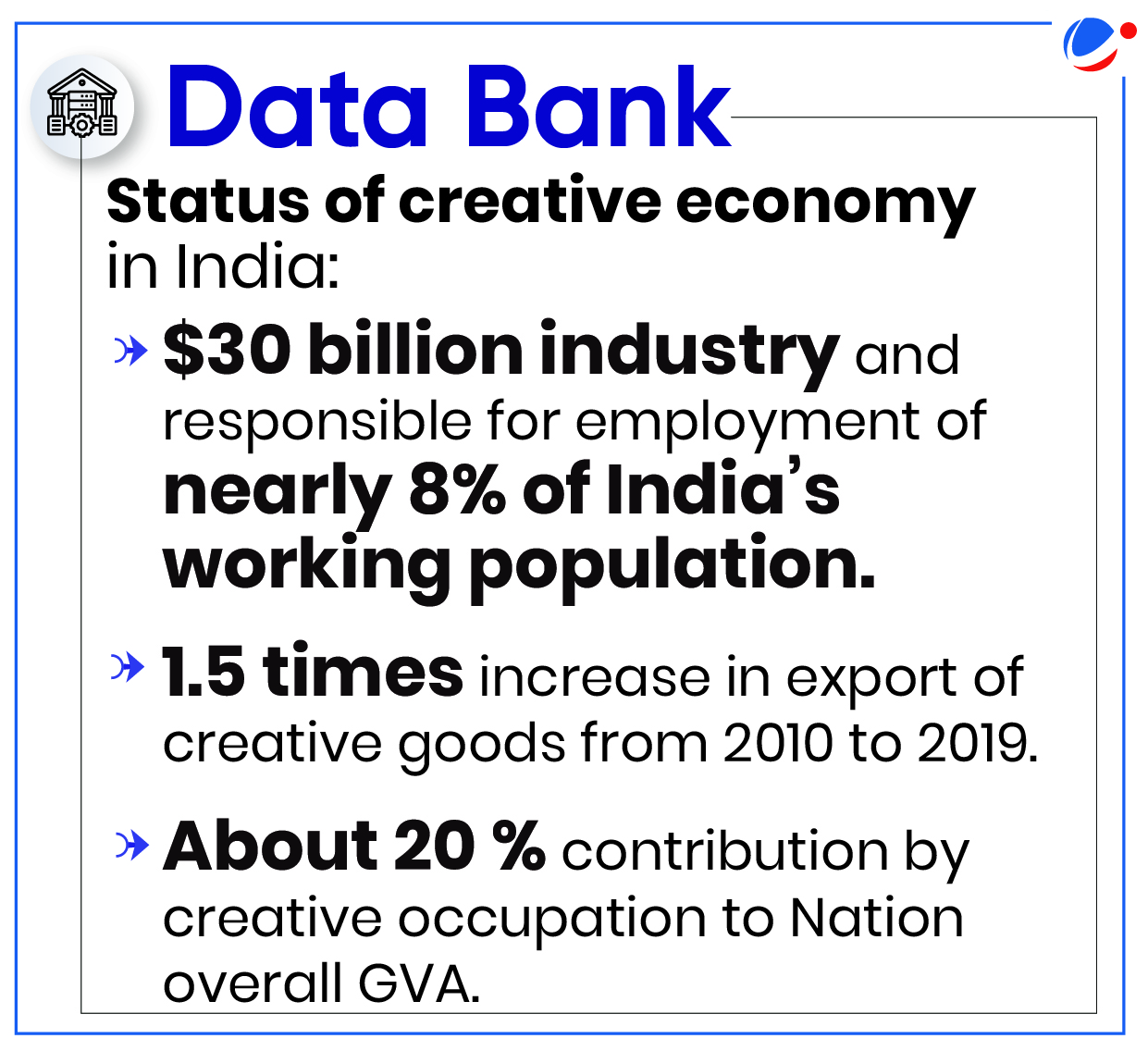
- According to UN estimates, creative economy industries generate annual revenues of over $2 trillion and account for nearly 50 million jobs worldwide
- Social aspects: 23% of people employed in creative industries are between 15 and 29 (more than in any other sectors), while women hold 45% of creative occupations worldwide.
- Skill Development and Education: The rise of edutainment in India, where education is combined with entertainment through digital platforms, has transformed traditional learning methods.
- Diplomacy and Soft Power: Cultural exchange promotes mutual understanding and opens up avenues for diplomatic engagement.
- E.g. Indian cuisine has become an integral part of India's soft power.
- Sustainable Development: Creative industries are mostly environmentally friendly since primary input for creative activities is creativity rather than natural resources as in case of mining, agriculture etc.
Hurdles hindering growth of creative economy
- Digitalization challenges: Like digital divide, cyber security concerns, literacy as digital ecosystem plays a crucial role in creative industry. E.g. accessing online platform, digital art galleries, etc.
- Rural Internet subscriber are about 41% of overall internet subscriber while having higher population.
- Rural Urban Divide: A sizeable 67.07% of all creative workers in India are in the urban areas.
- India's IPR regime: E.g. in India, it takes about 58 months on average to dispose of a patent application as compared to about 20 months in China and 23 months in US.
- Inherent issues of the sector: Such as fragmentation of creative industries, ineffective market access and distribution, and lack of transparency in the selection process, etc.
- Inadequate recognition and lack of awareness: about local culture and arts in India.
- Traditional career preferences: Societal pressure in India to pursue conventional career paths like engineering, medicine, etc.
- Creative professions are seen as risky and unstable in Indian society.

Way Forward
- Increasing Recognition of Indian Culture Globally: Promote Indian cultural and creative goods and services through organization of events, trade fairs, and international festivals. E.g. Ministry of Culture's Global Engagement scheme.
- Improving Access to Finance: Credit guarantees schemes and crowd funding for financing entrepreneurs and MSMEs in creative sector.
- Adopt global best practices such as "Crowdfunding4Culture" portal of European Commission.
- Reforming Intellectual Property Rights Framework: Addressing issues of copyrights, intellectual property protection and safeguard the interests of creators and innovators.
- Establishing Creative Districts/Hubs: On the lines of creative district models in Thailand.
- Integrated Policymaking Institution: Forming a Specialized institution for Creative Industries on the lines of UK (Creative Industries Council).
- Human Capital Development: Instilling digital skills, such as digital marketing and graphic design in young workers.
- Launching Pilot Project to promote entrepreneurship including creative entrepreneurship as an alternate career choice by providing end-to-end entrepreneurship education.
- Artificial intelligence governance and policy frameworks: Policies should consider the digital divides and aim to close the digital, knowledge, physical and digital infrastructure gap.







