Why in the news?
Recently, MyGov platform completed 10 years.
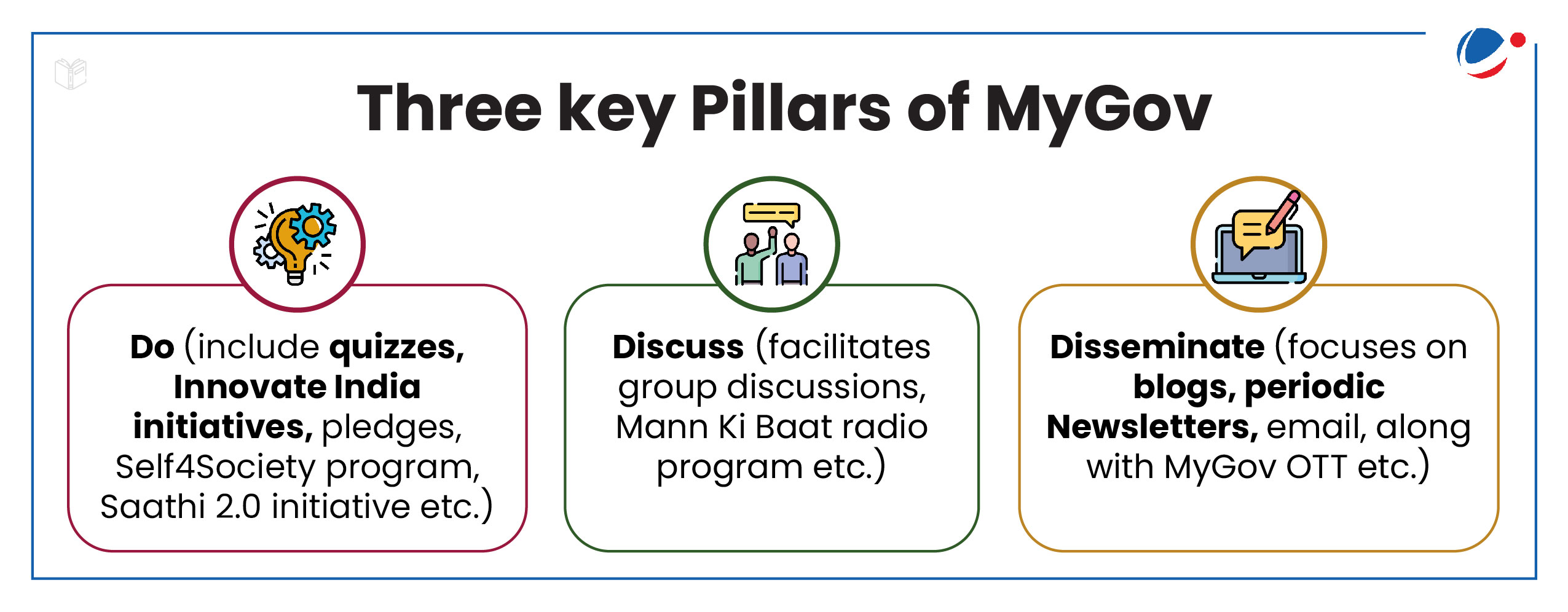
About MyGov Platform
- Launched by Prime Minister, MyGov is a Citizen Engagement Platform which collaborates with multiple Government bodies/ Ministries to engage with citizens for policy formulation and seeks opinion of people on issues of public interest and welfare.
- In short, it empowers people to connect with Government and contribute towards good governance.
- Since 2014, it has evolved into a robust platform with over 4.72 crore registered users, known as MyGov Saathis.
Major MyGov Campaigns
- LiFE Campaign: To engage individuals in addressing environmental degradation and climate change, emphasizing impact of individual and community actions on global challenge.
- Stay Safe Online: Launched by MeitY during India's G20 presidency to educate citizens, including specially-abled individuals, about online risks, safety measures, and cyber hygiene to enhance overall cyber safety.
- Swachh Bharat Survekshan: Through interactive activities and social media engagement, it fosters active public participation in creating a cleaner and healthier India.
- Millet-SuperFood: To highlight nutritional advantages of millets and understand their role in preventing lifestyle diseases.
How Citizen Participation helps in Good Governance?
- Accountability and Transparency: Citizens hold government officials accountable by providing feedback, reporting issues, and demanding action, which encourages transparency and openness in government decisions.
- For instance, RTI empowers citizens by providing them information to hold government officials and agencies accountable for their actions.
- Service delivery: Through active participation in policymaking, citizens ensure their needs and interests are considered in decision-making process, enhancing delivery of public services and policy outcomes.
- For instance, community participation in evaluation of Delhi government's Mohalla Clinics improved access to quality healthcare.
- Fosters Inclusivity: Engaging citizens in governance develops a sense of belongingness and ensures that diverse voices, including marginalized groups are heard, promoting equity and social justice.
- For instance, MGNREGA Social audit helps in prioritisation of voices of the poor and marginalised.
- Trust-building: Active citizen participation programs foster trust in government institutions, reinforcing democratic principles and promote cooperative relationship between state and society.
- Example, Gram Sabhas fosters community trust at the grassroot level.
- Innovation: Citizen participation can bring new perspectives, innovative ideas and solutions to address issues strengthening governance structure.
- For instance, Mysuru- based firm has been granted a patent for their innovative solution to use plastic waste to make environment friendly interlock tiles or pavers that are stronger than cement.
Challenges associated with Citizen Participation in Good Governance
- Lack of Commitment: Engagement in policymaking requires time and resources, which are often limited, restricting the continuous participation of citizens.
- Limited engagement: Many citizens lack required knowledge and understanding of government processes, laws, and their rights, hindering their effective participation.
- Further, complex procedures and red tape can make it difficult for citizens to participate.
- Administrative challenges: Governments may lack capacity to manage large-scale participation, including processing feedback, organizing events etc. further hampering active participation.
- Limited trust in government: Public trust in government is often low due to unfulfilled promises, perceived corruption and nepotism, and failure to consider community input on development priorities, impeding their participation.
- Social factors: Lack of equal access, ability to participate, due to socio-economic conditions, cultural norms and traditions such as patriarchy, may limit participation of women and other marginalized groups in governance.

Way ahead
- Accessibility: Release government data in a structured and accessible format and ensure that citizens have easy access to government information e.g. strengthening RTI Act to enhance transparency.
- Awareness: Incorporate governance and civic education into school curriculum, organizing workshops to educate citizens on their rights, importance of their participation, and how they can effectively engage in governance processes.
- Digital Platforms: Strengthening digital infrastructure, creating user-friendly e-governance platforms where citizens can access information, and provide feedback to facilitate citizen's participation.
- Inclusive Policy-Making: Organize regular public consultations, hearings on key policy decisions, ensuring representation from diverse communities to strengthen governance processes. E.g. strengthening public hearing component of Environmental Impact Assessment.
- Grievance Redressal: Strengthen and streamline grievance redressal mechanisms, ensuring that citizen complaints are addressed promptly to build trust in governance system. Further, strengthening feedback systems to enhance policy implementation.







