Why in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy for "Fostering High-Performance Biomanufacturing".
More on the News
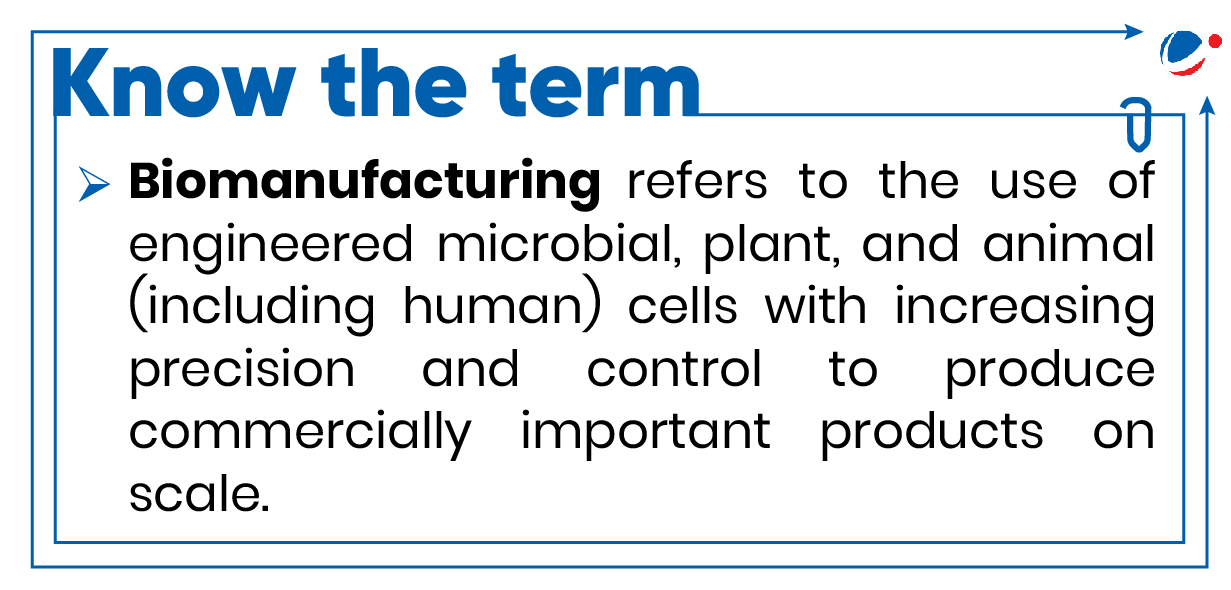
- BioE3 Policy will scale up efforts in high-performance biomanufacturing with a stated ambition of achieving a US $300 billion bioeconomy by 2030.
- Bioeconomy has grown from US $10 billion in 2014 to over US $130 billion in 2024.
- The Policy will steer India on the path of accelerated 'Green Growth' by promoting 'Circular Bioeconomy'.
- According to FAO, Bioeconomy is "the production, use and conservation of biological resources, including related knowledge, science, technology, and innovation to provide information, products, processes and services to all economic sectors.
- Examples: Sustainable agriculture, sustainable fishing, forestry and aquaculture, food and feed manufacturing, Bio-based products (e.g., bioplastics, biodegradable clothing).
About BioE3 Policy (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment)
- Aim: To set forth a framework that ensures the adoption of cutting-edge advanced technologies, align innovative research aimed at revolutionizing biomanufacturing processes.
- Implementation: Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
- Salient Features:
- It includes innovation-driven support to R&D and entrepreneurship across thematic sectors.
- Through this Policy, the government will delineate an ambitious vision to achieve technology leadership and tackle major challenges with focused mission in six thematic sectors:
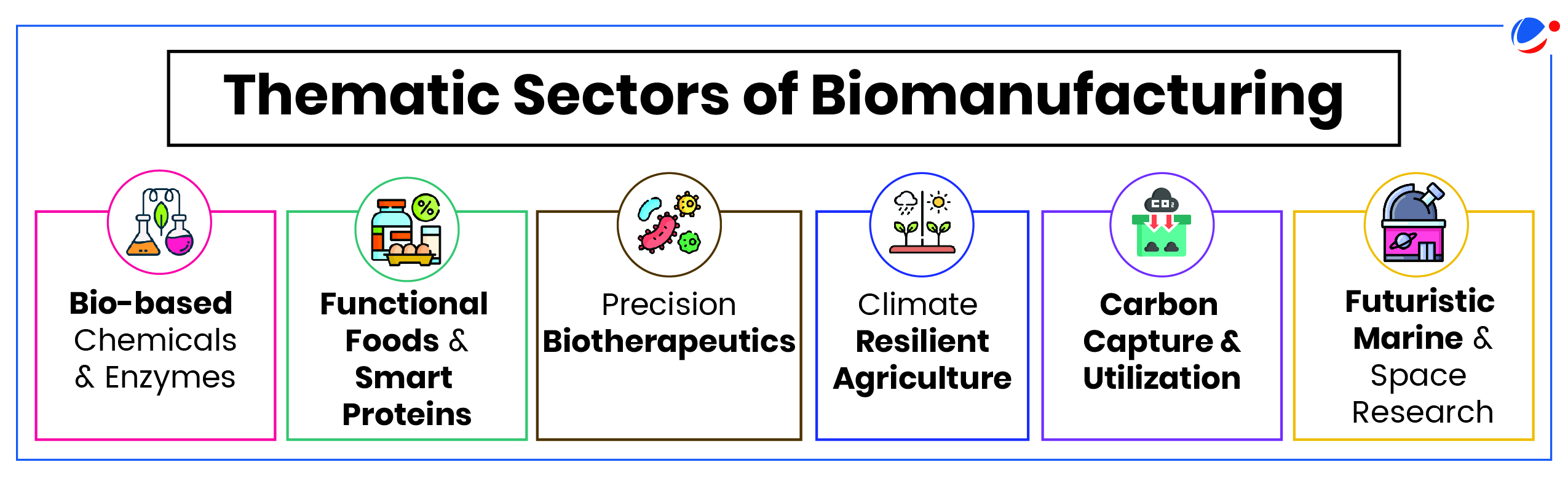
- The research and translational activities under these verticals will be catalyzed by:
- Bio-Artificial Intelligence (AI) Hubs: Integrating AI with biological data like genomics, proteomics, and medical imaging will enhance understanding of biological systems, improve disease diagnosis and treatment.
- These hubs in agriculture sector can provide data analytics to improve farming practices.
- Biomanufacturing Hubs: These hubs will comprise common usage of pilot and pre-commercial manufacturing facilities for researchers, startups and SMEs to support early-stage manufacturing.
- Regulations and Global Standards: This Policy will enhance inter-ministerial co-ordination to ensure seamless integration of biosafety and biosecurity considerations.
- Data Governance Framework: Through this framework discoveries, inventions, and other knowledge arising thereof, will be made freely available to the wider scientific community, while allowing for protection of intellectual property.
- Bio-Artificial Intelligence (AI) Hubs: Integrating AI with biological data like genomics, proteomics, and medical imaging will enhance understanding of biological systems, improve disease diagnosis and treatment.
Need for BioE3 Policy
- Sustainability: Need for innovation in biotransformation of chemical processes is critical for achieving sustainability goals.
- This policy will play a catalytic role in sustainable bio-based production of high-value specialty chemicals, enzymes and biopolymers.
- Cater Nutrition Challenge: There is a growing demand for food as India will likely comprise of around 1.67 billion citizens in 2050 for whom adequate and nutritional food intake would be a key concern.
- The Policy will facilitate production of smart proteins and functional foods with low carbon footprint using synthetic biology, and metabolic engineering tools.
- Growth of Cell and Gene therapy: By 2027, the cell and gene therapy market are forecasted to be over $22 billion (~₹1846 billion).
- This Policy will intensify engagement of India in futuristic biotherapeutics technologies and personalized medicine such as cell and gene therapy, mRNA therapeutics, and monoclonal antibodies.
- Food security: Need to promote soil microbiome-based research in India including soil microbiome/genome analysis, selection process for superior microbial phenotypes etc.
- This Policy will enable fundamental goal of food security through innovations for climate smart agriculture for production of improved crop varieties.
- Climate Change Mitigation: India aiming for 45% reduction in emission intensity by 2030 and is taking steps towards achieving Net Zero by 2070.
- The Policy will facilitate to have focus on achieving de-carbonization through microbial conversion of captured CO2 into industrially relevant compounds.
- Space-Missions: Need for development of safe, nutritious meals for future long-duration space missions, considering the challenges in product quality & safety, shelf life, and packaging waste.
- Microbial biomanufacturing has the potential to provide integrated solutions for remote or austere locations.
- Skill Gaps: There is a shortage of trained professionals with expertise in cutting-edge areas like synthetic biology, bioinformatics, and bioprocess engineering.
- Bio-hubs under policy will act as training centres to ensure generation of skilled manpower in the evolving field of biomanufacturing.

Way Forward
- Adopt circular bioeconomy: The principles of the circular economy (reuse, repair and recycle) are a fundamental part of the bioeconomy. Through reuse, repair and recycling, the total amount of waste and its impact can be reduced.
- Learning from the USA: Like the $2 billion investment made for startups in USA for transitioning into large-scale manufacturing.
- Single window clearance: Implement a single window clearance system for all selected Biomanufacturers.
- STEM talent: Retain 25% of global Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) talent within India for sustained growth.
- International Collaborations: Many nations like the USA, Japan, Australia, Finland and European countries, have put forward their policies, strategies and roadmaps to set up a robust framework for biomanufacturing.







