Why in the News?
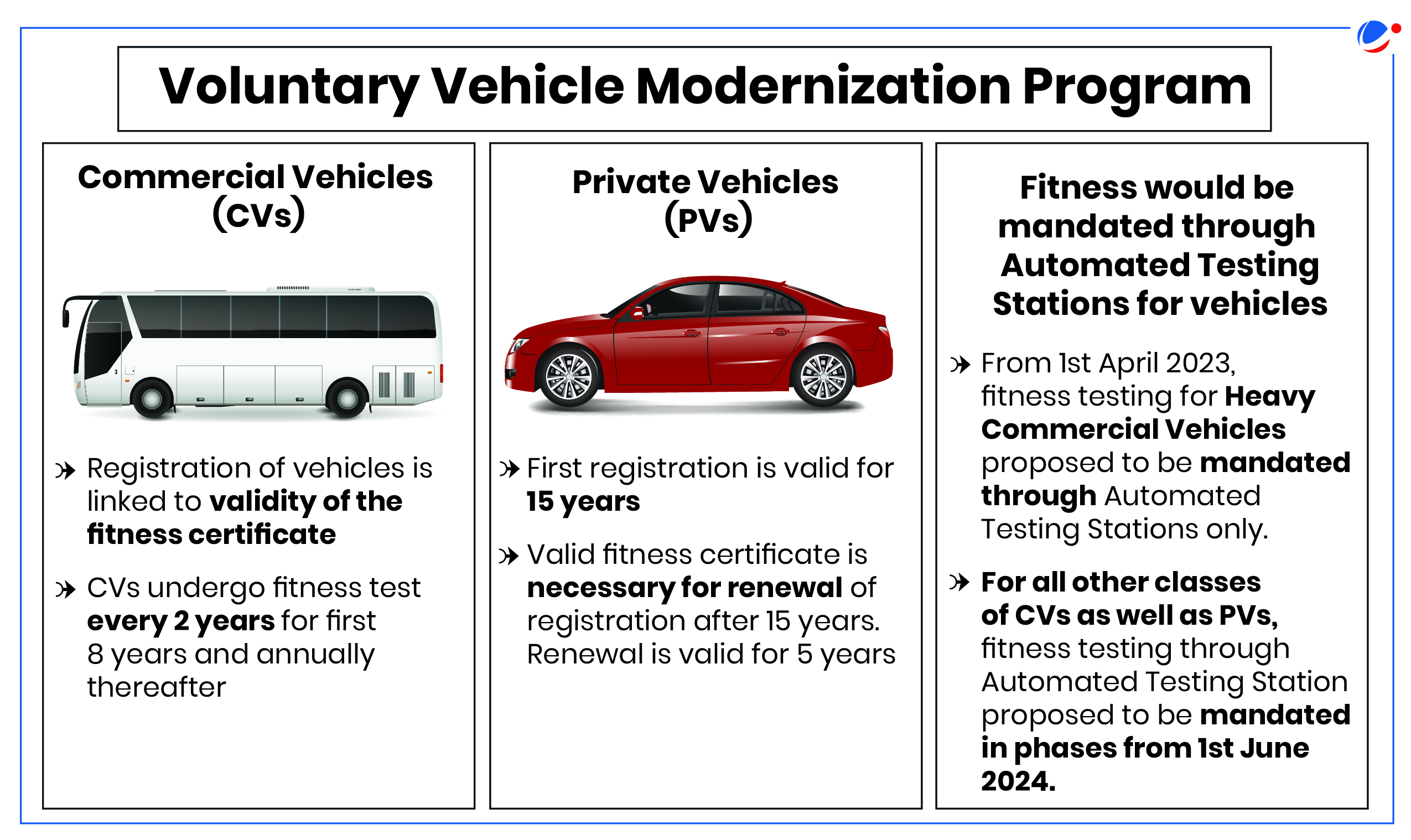
Recently, Union Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) launched the Voluntary Vehicle Modernization Program or Vehicle Scrapping Policy.
More on the News
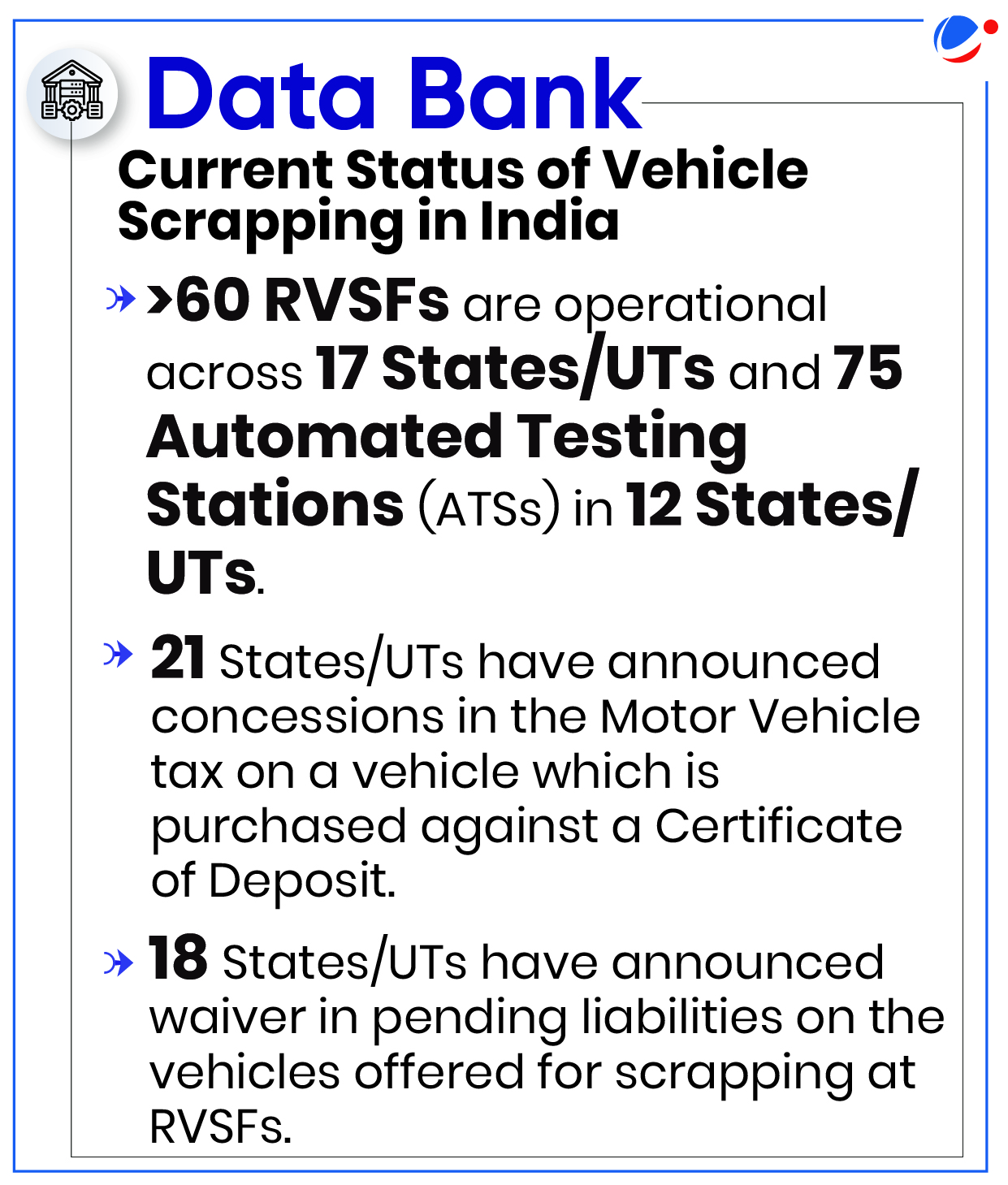
- Program aims to create an ecosystem for phasing out unfit polluting vehicles across the country through a network of Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSFs) and Automated Testing Stations (ATSs).
- Under this, multiple commercial and passenger vehicle manufacturers would offer discounts for a period of two years and one year respectively against a Scrappage Certificate.
- Previously, Union Government announced Vehicle Scrapping Policy in 2021 to gradually phase out the vehicles which are more than 15-20 years old to reduce air pollution, improve road safety, and boost vehicle sales.
Key Highlights of the Voluntary Vehicle Modernization Program
- Circular Economy: It aims to create a circular economy in the automotive sector by promoting recycling and reducing raw material consumption.
- Vehicles that fail the fitness test will be scrapped, and owners will receive a Certificate of Deposit (Scrappage Certificate) as proof, which can be used to avail of discounts on purchasing new vehicles.
- Incentives for Scrapping:
- Manufacturers have announced various incentives to encourage vehicle scrapping:
- Commercial Vehicle Manufacturers offer discounts up to 3% of the ex-showroom price.
- Passenger Vehicle Manufacturers offer discounts of 1.5% of the ex-showroom price.
- These discounts are over and above the scrap value provided by RVSFs and government incentives like Motor Vehicle Tax concessions and waivers on registration fees.
- Manufacturers have announced various incentives to encourage vehicle scrapping:
Significance of Scrapping of Old Vehicles
- Environmental: Older vehicles typically have outdated technology and poor fuel efficiency, which leads to higher emissions of pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM).
- Scrapping them reduces air pollution, helping to combat climate change and improve urban air quality.
- Economic: It will also encourage people to purchase new vehicles, thereby stimulating demand in the automobile industry.
- Circular economy: Scrapping of old vehicles allows for the recovery of valuable materials like steel, aluminum, copper, rubber, etc., reducing the need for mining and manufacturing raw materials.
- Road safety: Removing older vehicle, which lack modern safety features, from the roads increases the overall safety of transportation systems by reducing the likelihood of accidents caused by faulty vehicles.
- Regulatory compliance: By scrapping older vehicles, India's vehicle fleet can better comply with the revised emission standards under the BS-VI norms.
Challenges for effective Vehicle scrapping in India
- Inadequate infrastructure: Absence of a well-established network of authorized recycling centers and dominance of unorganized sector, where scrapping is often carried out in environmentally unsafe conditions, leading to health hazards and improper waste management.
- Poor integration with circular economy: Absence of clear recycling supply chains where materials from scrapped vehicles are effectively recycled into the production of new vehicle and other goods result in inefficiencies and hinder effective price-realization.
- Awareness and participation: Many vehicle owners are unaware of the environmental and economic benefits of scrapping their old vehicles, sentimental attachment of owners to their old vehicles, etc., restricts voluntary vehicle scrapping.
- Economic constraints: Perceived low resale value of older vehicles and high cost of buying new, fuel-efficient vehicle become prohibitive without sufficient financial support.
- Weak enforcement: Inadequate checks and corruption at local levels often lead to fake certification for old vehicles, allowing them to bypass regulations and remain on the road.
Way Forward
- Build scrapping infrastructure: Encourage PPP in setting up scrapping facilities, build an integrated supply chain for recycled materials from scrapped vehicles, etc.
- Simplified vehicle scrapping process: Enable scrapping centers to offer a one-stop service for vehicle owners, handling processes from deregistration of the vehicle to recycling the materials to reduce bureaucratic hurdles and makes the process more efficient.
- Strengthened enforcement: Implement regular and strict emission testing for older vehicles, centralized system for tracking vehicles that have exceeded their permissible age, etc.
- Integrate management of Electric End-of-Life Vehicles (ELVs) and batteries from the outset to ensure sustainability, safety, and environmental responsibility.
- Public awareness: Collaborate with local communities, NGOs, and vehicle associations to spread awareness and facilitate the scrapping process.







