Why in the News?
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) completed its 25 years in 2025.
About PMGSY
- Genesis: Phase I launched in 2000.
- Implementation: Centrally Sponsored Scheme by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- Objective: To ensure all-weather connectivity by way of an all-weather road to eligible unconnected rural habitations.
- Phased Evolution of Programme:
- Phase-I: Launched in 2000 to ensure all-weather connectivity to unconnected rural habitations.
- Phase-II: Introduced in 2013, focused on strengthening and consolidating the existing rural road network.
- It prioritized the upgradation of economically important routes linking rural markets, growth centres, and service hubs, to improve transportation efficiency and accelerate rural economic development.
- Road Connectivity Project for Left Wing Extremism Affected Areas (RCPLWEA) for construction/ upgradation of strategically important roads was launched as a separate vertical in 2016.
- Phase-IV: Launched for the period FY 2024–25 to 2028–29.
- To provide all-weather road connectivity to 25,000 unconnected rural habitations, based on Census 2011 population criteria:
- Habitats with a population of 500 and above in plain areas,
- 250 and above in North-Eastern and Himalayan States/UTs, and
- Habitations located in special category areas, including Tribal (Schedule V) regions, Aspirational Districts/Blocks, and Desert areas.
- To provide all-weather road connectivity to 25,000 unconnected rural habitations, based on Census 2011 population criteria:
- Phase-III: Launched in 2019, focused on upgrading of Through Routes and Major Rural Links connecting habitations, inter alia, to Gramin Agricultural Markets, Higher Secondary Schools, and Hospitals.
- Supporting Agency: MoRD has set up the National Rural Infrastructure Development Agency to provide Operational and Management support to the Programme.
- Monitoring: Online Management, Monitoring, and Accounting System (OMMAS) enables real time monitoring of all works.
- The Electronic Maintenance of PMGSY Roads (e-MARG) platform: Uses geo-tagged photos from its mobile app to verify road maintenance work for payments and monitor contractor performance.
Achievements of PMGSY
- Road Infrastructure: Since its inception, PMGSY has sanctioned a total of 8,25,114 km of rural roads, of which 7,87,520 km have been completed, reflecting nearly 95 % physical progress as of December 2025.
- Agriculture: Strengthening of forward and backward linkages, reduction in transportation cost, increased accessibility to market, increasing agricultural productivity, better price realisation of farmers, etc.
- Socioeconomic Transformation: Increased access to health facilities, increase in number of institutional deliveries, reduction in number of school dropouts and increase in access to middle and high schools.
- Tribal and Scheduled Caste Empowerment: PMGSY-IV is being implemented in convergence with two targeted initiatives that aim to ensure the inclusive development of tribal and scheduled caste populations.
- Two targeted initiatives are Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY) and Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN).
- Climate Resilience: Promotion of technologies such as waste plastic, cold mix, and Full Depth Reclamation reduce environmental impact—over 1.24 lakh km of roads have been built using these methods as of July 2025.
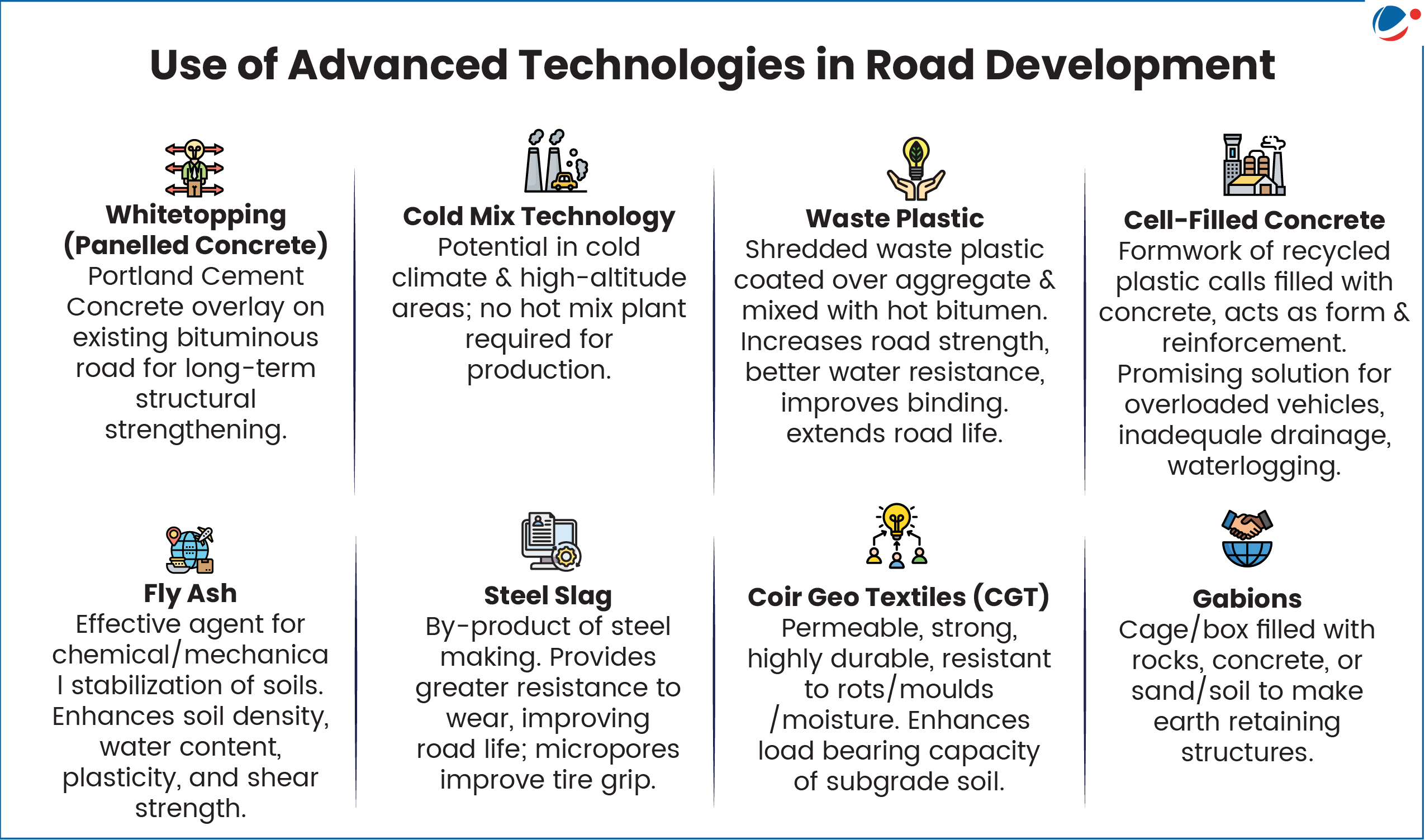
Challenges associated with PMGSY
- Outdated Demographic baseline: Based on the 2011 Census, it does not reflect the present population, settlement expansions, and evolving infrastructure needs.
- Lack of last-mile connectivity: Roads often end at the village periphery, and many small settlements (Desam, Dhanis, Tolas, Majras, Hamlets) remain 2–3 km inside, missing connectivity benefits.
- Slow Progress in LWE Areas: Pending work under the Road Connectivity Project for Left Wing Extremism Areas (RCPLWEA) despite extension.
- Poor Quality of Construction of Roads: Non-compliance with norms, use of poor materials, and failing to withstand weather, traffic, monsoons, etc.
Conclusion
Over the past 25 years, PMGSY has emerged as one of India's most transformative rural infrastructure programmes, redefining connectivity as a foundation for inclusive growth rather than a mere physical asset. Progressively strengthening data updates, ensuring end-to-end connectivity, expediting works in difficult areas, and enforcing quality standards are crucial to achieve inclusive and sustainable rural development.






