
Parliamentary Committee on Public Accounts sought comprehensive review of GST Framework.
Key Issues Highlighting the Need for Review of GST Framework
- Issues of MSMEs: Struggle with compliance due to complexity of Inverted Duty Structure and administrative burden.
- Issues of Exporters: Face delays in input tax credit (ITC) refunds, causing cash flow issues and reducing global competitiveness.
- Issues of steel rolling mills: Pay dual taxes as scrap dealers evade GST (thus, hindering ITC claims by mills); some businesses relocate to states with GST relaxations.
- Tax evasion by Online Gaming Sector: Despite recent amendments to the GST law targeting this sector, tax evasion persists due to varied business models.
- From October 1, 2023, online gaming is taxed at 28% GST.
- Suppliers of online money gaming must register under the Simplified Registration Scheme of the IGST Act.
- The Directorate General of GST Intelligence (DGGI) can direct intermediaries to block unregistered offshore gaming platforms violating the IGST Act.
Way ahead
- Simplified GST compliance framework specifically designed for MSMEs,
- Dedicated fast-track refund processing system for exporters, ensuring that ITC claims related to exports,
- A detailed independent study to understand the revenue streaming models adopted by various gaming platforms and accordingly develop a comprehensive guidelines specifically tailored to the online gaming sector.
10th report on ‘Demands for Grants (2025-26)’ of Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) highlights various issues and gives recommendations thereof for making Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) & Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Regulations effective:
Areas | Issues | Recommendations |
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) |
|
|
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) |
|
|
Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Regulations |
|
|
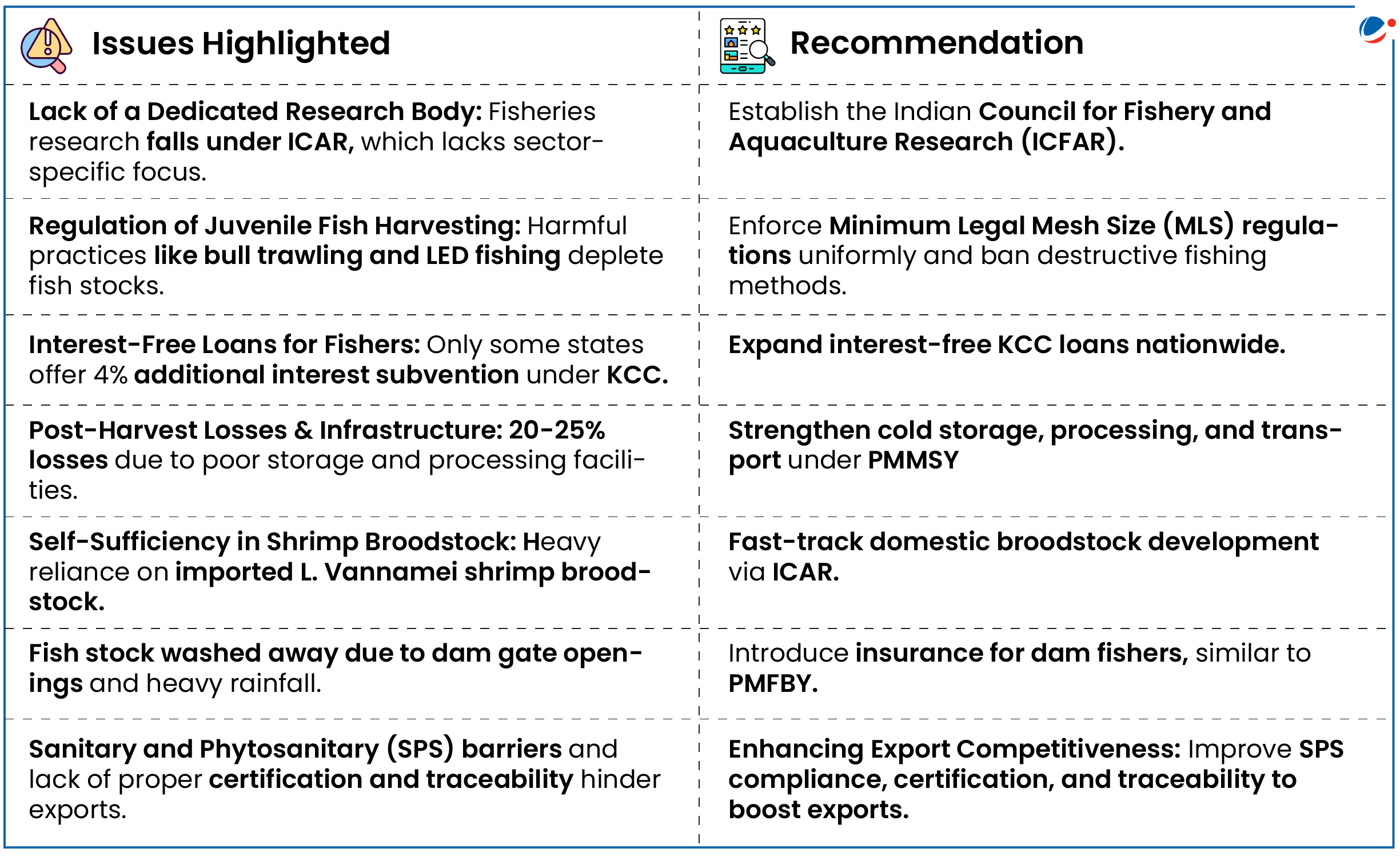
The report evaluates the government's response to recommendations aimed at improving the fisheries sector, enhancing employment opportunities, and increasing revenue generation.
- India is 3rd largest fish-producing country, accounting for approximately 8% of global fish production.
- Over the years, the sector’s contribution to agricultural GVA has risen from around 4% to over 6.72%.
Key Highlights
Recently, Union Government has notified a scheme for Cooperative Sugar Mills under modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme.
About Scheme for Cooperative Sugar Mills
- Ministry: Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Department of Food & Public Distribution
- Aim: Conversion of existing sugarcane-based feedstock ethanol plants into multi-feedstock based plants to use grains like Maize and Damaged Food Grains (DFG).
- Under modified Ethanol Interest Subvention Scheme, Government is providing Interest subvention @ 6% per annum or 50% of rate of interest charged by banks/financial institutions, whichever is lower.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia’s tobacco exports have doubled over the last 4 years.
Tobacco
- India’s Status: Second largest producer (after China) as well as second largest exporter (after Brazil).
- Major Producing States: Gujarat (45% of total cultivated area, 30% production), Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, UP and Bihar.
- Favourable Conditions:
- Temperature: Between 20° to 27°C is required.
- Rainfall: When grown as a rainfed crop then requires at least about 500 mm of well-distributed rainfall during the crop growing season. (Usually not grown in the area if rainfall exceeds 1200 mm).
- Soil: sandy or sandy loam soil. Cigarette-tobacco growing areas of Andhra Pradesh are an exception in that the crop is grown on heavy black soil.
The report recognizes that India needs to grow by 7.8% on average over the next 22 years to become High-Income Country (HIC) by 2047.
- India became a Low Middle-Income Country (LMIC) in 2007-08 and is currently on track to become an Upper Middle-Income Country (UMIC) by 2032.

Key Challenges In Becoming HIC By 2047
- Slow Structural Transformation: Agriculture still employs 45% of the workforce (2023-24) while traditional market services and construction (low productivity) together constitute nearly 30%.
- In contrast, the share of manufacturing in total employment was around 11% and modern market services accounted for only 7%.
- Declining Private Investment: Private investment surged post-1990s reforms but it has fallen as a share of GDP, particularly since the global financial crisis in 2008.
- Underutilisation of Demographic Dividend: Over 2000-19, the working-age population increased by 37.4%, but employment increased by only 15.7%.
- During this period, the labor force participation rate fell from 58% to 49% remaining low by middle-income countries standards.
Key Strategies for Growth
- Boost Investment: Increase investment from 33.5% to 40% of GDP by 2035 through better financial regulations, easier MSME credit, and simplified FDI policies.
- Create Jobs: Encourage private investment in job-rich sectors like agro-processing, manufacturing, transport, and care economy.
- Balanced Regional Growth: Less developed states focus on basics (health, education, infrastructure), while developed states advance next-gen reforms.
Public debt can drive development by funding critical expenditures, but excessive debt growth poses challenges, especially for developing nations.
- United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) ’s 2024 report warns of rising debt risks, urging immediate global action to ensure stability.
Key Findings of the Report

- Global Debt Surge: Public debt reached $97 trillion in 2023, with developing countries' debt rising twiceas fast as developed nations.
- India's public debt was recorded at 2.9 trillion US dollars.
- Debt Servicing Strains: 54 developing nations spend more on interest payments than on social sector.
- Unequal Financial System: Developing nations pay 2 to 12 times more in interest than developed countries.
Challenges Posed by the Rising Global Public Debt
- Debt Overhang: High debt levels can stifle economic growth by discouraging investment and consumption.
- Liquidity Challenge: The withdrawal of nearly $50 billion by private creditors from developing countries has worsened liquidity constraints.
- The creditor base with West-dominated institutions (private, multilateral, and bilateral creditors) makes debt restructuring expensive.
Recommendations
- Debt restructuring mechanisms to address coordination challenges.
- Expand contingency financing to prevent debt crises.
- Enhance participation of developing countries in global financial governance.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia and Japan have renewed the $75 billion bilateral currencies swap agreement.
About BSA:
- It is an agreement between two central banks to exchange a cash flow in one currency against a cash flow in another currency according to predetermined terms and conditions.
- Purpose of India - Japan BSA: It is a two-way currency swap mechanism, allowing both countries to exchange local currencies for US dollars when needed.
- Significance: Help manage exchange rate volatility and provide liquidity during financial crises
National Highways Infra Trust (NHIT) completed largest INVIT monetization in roads sector.
- NHIT is the Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) set up by National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) in 2020 to support India's Monetization programme.
Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT)
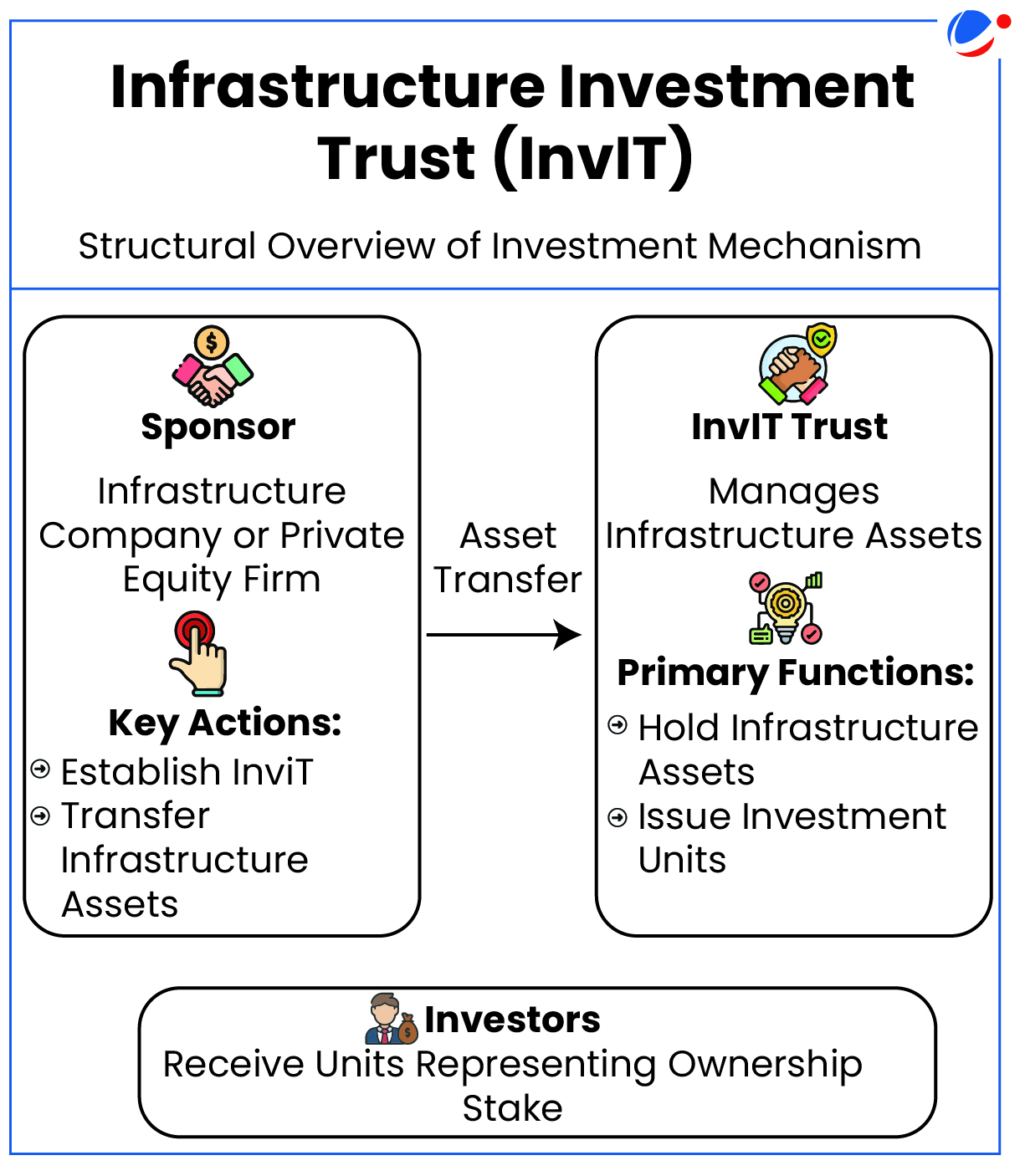
- Definition: It is an investment vehicle, like a mutual fund or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs).
- InvITs enable direct investment of money from individual and institutional investors in infrastructure projects.
- Investments can be made directly or through SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle)/Holding Company by the InvIT.
- InvITs earn income through tolls, rents, interest or dividends from their investments.
- The interest, dividend, and rental income are taxable in the hand of the unitholder.
- Regulation: InvIT are regulated by the SEBI (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014.
- SEBI requires InvITs to distribute at least 90% of their income to investors.
- InvITs are recognized as borrowers under the ‘Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002’.
- Types of InvITs: Public InvITs, Private listed InvITs and Private unlisted InvITs.
- Advantages of InvITs: Access to retail investors to invest in large infrastructure projects, low ticket size, liquidity (as units are listed on stock exchanges), etc.
- AM is the process of creating new sources of revenue for the government and its entities by unlocking the economic value of unutilised or underutilised public assets.
Asset Monetization (AM)
|
Article Sources
1 sourceMinistry of Finance launched a new credit assessment model using MSMEs' digital footprints to streamline credit appraisal and disbursement.
About New Credit Assessment Model
- It will leverage the digitally fetched and verifiable data available in the ecosystem and devise automated journeys for MSME loan appraisal.
- It aims to improve financial inclusion, reduce reliance on traditional credit scores, and support MSMEs with easier access to formal credit.
- It was announced in Union Budget 2024-25 that public sector banks (PSBs) will build their in-house capability to assess MSMEs for credit, instead of relying on external assessment.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia’s Venture Capital (VC) funding surges 43% to $13.7 billion in 2024.
About VC
- It is a form of private equity and a type of financing for startup companies and small businesses with long-term growth potential.
- Venture capital usually takes the form of equity shares or a future claim on equity, such as convertible debt, which in return allows the venture capital firm to receive a share of ownership in the business.
- Venture capitalists provide backing through financing, technological expertise, or managerial experience
Valueattics Re has become the first private firm to receive IRDAI’s nod to commence reinsurance business in India.
- Currently, public sector General Insurance Corporation (GIC Re) is the only reinsurance company operating in India.
About Reinsurance
- Reinsurance is a risk management practice where insurance companies transfer a portion of their risk to another insurance company (reinsurer) to protect themselves from large financial losses.
- Regulator: Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI).
- Laws: Governed under the Insurance Act, 1938 and IRDAI (Re-Insurance) Regulations, 2018.
Article Sources
1 sourceCentre for Development of Telematics launches ‘Samarth’ a cutting edge Incubation Program for telecommunications and IT sectors.
About Samarth
- Aim: Encourage the development of sustainable and scalable business models, offer access to cutting-edge resources, and help Startups Bridge the gap from ideation to commercialization.
- Implementation Partner: Software Technology Parks of India (STPI), premier S&T organization under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
UpLink initiative under World Economic Forum’s (WEF) cut carbon emissions by 142,400 tonnes in 2023-2024.
About UpLink Initiative
- It is an initiative focused on impactful early-stage innovation.
- It was founded in 2020 by WEF in collaboration with Deloitte and Salesforce.
- It builds ecosystems that enable purpose-driven, early-stage entrepreneurs to scale their businesses for the markets that are essential to a net-zero, nature-positive and equitable future.
- Objectives: Accelerate impact of early-stage innovators, Enable Innovation Ecosystems and Influence perception.






