Why in the news?
Recently, NITI Aayog's Frontier Tech Hub (NITI-FTH)released a strategic paper on "Quantum Computing: National Security Implications & Strategic Preparedness".
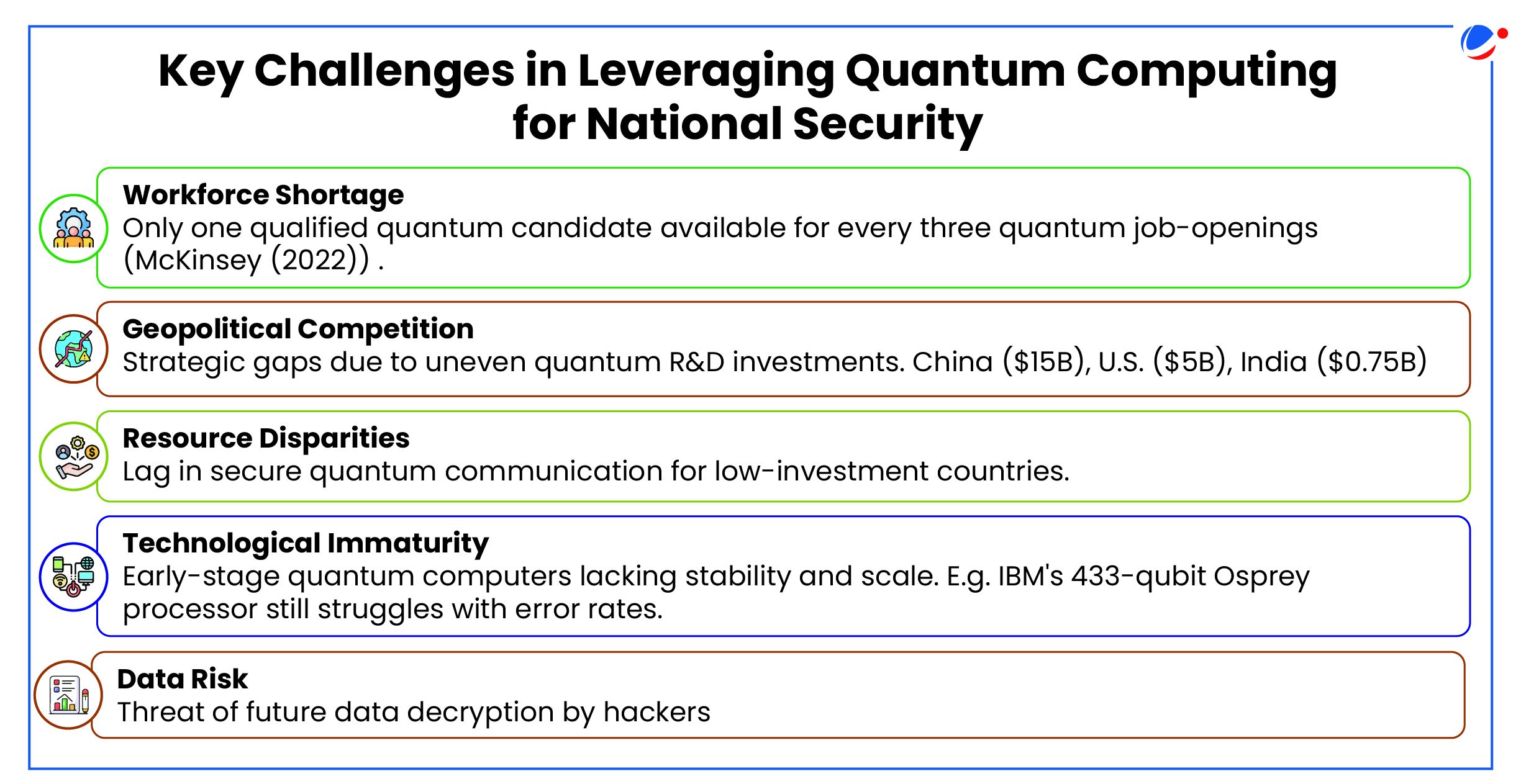
How Quantum computing is reshaping the National Security Paradigm
- Cryptography and Cybersecurity: A powerful quantum computer could break widely used public-key encryption algorithms, forcing nations to adopt Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) (algorithms designed to resist quantum attacks) to safeguard their data.
- E.g. The National Quantum Initiative Act of 2018 of the USA emphasizes national security through PQC to counter future cyber threats.
- Enhanced Intelligence Gathering: Quantum computing could revolutionize intelligence analysis by processing vast, complex datasets beyond classical capabilities, enhancing intelligence to intercept, analyze, and decode communications at an unprecedented scale.
- E.g. NATO's 2024 strategy calls for quantum-ready defense applications, including sensing, imaging, and securing communications through quantum-resistant cryptography.
- Secure Communications: Such as Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) to distribute encryption keys between two parties with provable security.
- E.g. China built the world's longest land-based (2,000 km) QKD network between Beijing and Shanghai that transmits sensitive data securely.
- Military Hardware: Quantum technologies will drive breakthroughs in materials science, leading to next-generation military hardware.
- E.g. Quantum-enabled AI will power autonomous military drones and robotic systems, enhancing both offensive and defensive capabilities.
- Economic Warfare: The ability to break encryption may destabilize financial markets, compromise banking and digital payment systems, creating new threats in economic security.
- E.g. Initiatives like the National Quantum Initiative Act of USA highlights the need of quantum innovation for both economic and strategic security.
- Geopolitical Power: Nations that achieve early breakthroughs in quantum computing will establish a technological and knowledge base that others will struggle to replicate.
- For instance, China's Micius satellite (2016) enabled quantum-secured long-distance communication, showcasing its lead in quantum tech and secure networks.
Key Recommendations
- Continuous Monitoring: Set up a dedicated quantum task force to track global tech progress and adversarial capabilities.
- Cryptographic Intelligence: Conduct regular audits to identify quantum-related vulnerabilities in defense, finance, and critical infrastructure.
- PQC Transition Plan: Implement a risk-prioritized roadmap with accelerated Proofs of Concept (POCs), testing, certification, and cross-sector info sharing for post-quantum cryptography adoption.
- Such as Google Chrome's experiment with post-quantum algorithms like Kyber in real-world browser encryption.
- Strengthening the Quantum Workforce: Initiate Quantum information science (QIS) education at higher education level, workforce training for the existing quantum workforce, and reform immigration for global talent.
- Building a Quantum Ecosystem: Such as the US' Quantum Economic Development Consortium (QED-C); Japan's Quantum Strategic Industry Alliance for Revolution, whose primary focus is to enable and grow the quantum industry.
- International Collaboration on Quantum with like-minded partners to coordinate QIS technology development, such as India and European Commission signed an "Intent of Cooperation on High Performance Computing (HPC), Weather Extremes & Climate Modeling and Quantum Technologies" in 2022.
- Others
- Early Warning System: Leverage scientific intelligence for potential breakthroughs.
- Crypto Agility Framework: Issue clear directives to ensure organizations can swiftly adapt to quantum-era encryption changes or breakthroughs.
- Flexible R&D Funding: Adapt investment priorities based on emerging breakthroughs.
Conclusion: With its transformative potential across defense, intelligence, and secure communications, quantum computing will be a cornerstone in India's journey toward strategic resilience and the vision of Viksit Bharat @2047.
Steps Taken by India in Quantum Technology
|




