The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) on Earth Day (22nd April) launched Accelerating Innovative Monitoring for Nature Restoration (AIM4NatuRe).
About AIM4NatuRe Initiative
- AIM4NatuRe is an acronym of Accelerating Innovative Monitoring for Nature Restoration.
- Aim: To improve monitoring and reporting of global ecosystem restoration efforts.
- Initiative leverage cutting-edge technology, standardized data frameworks, and capacity development to restore at least 30% of degraded ecosystems by 2030, as outlined in Target 2 of the Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
- It is part of FAO’s AIM4Forests Programme, expanding the scope beyond forests to provide a holistic approach to nature restoration monitoring.
Article Sources
1 source34 critically endangered vultures were transferred from the Vulture Conservation Breeding Centre (VCBC) in Pinjore (Haryana), to Maharashtra.
About VCBC, Pinjore
- Genesis: Established in 2001 with the UK Government’s ‘Darwin Initiative for the Survival of Species’ fund.
- Partners: Haryana Forest Department and the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS).
- Aim: To save three species of vultures, the White-backed, Long-billed and Slender-billed.
- Location: Edge of the Bir Shikargaha Wildlife Sanctuary, Haryana.
- Achievement: Confirmed that diclofenac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, was the main cause of vulture mortality.
Alien or non-native beetle, Small Hive Beetle (Aethinatumida), was recorded for the first time in India in West Bengal.

About SHB
- Native: Sub-Saharan Africa.
- It seldom causes harm to Africa but creates havoc across other regions.
- Characteristics: Oval-shaped, reddish-brown, and 5-7 mm long, its life cycle goes through different stages: eggs, larva, pupa and adult.
- Damage: Females of SHB enter the beehives through cracks and crevices to lay eggs, which on hatching feed voraciously on the stored pollen, honey, and honeybee eggs and defecate in the honeycombs making it unfit for human consumption.
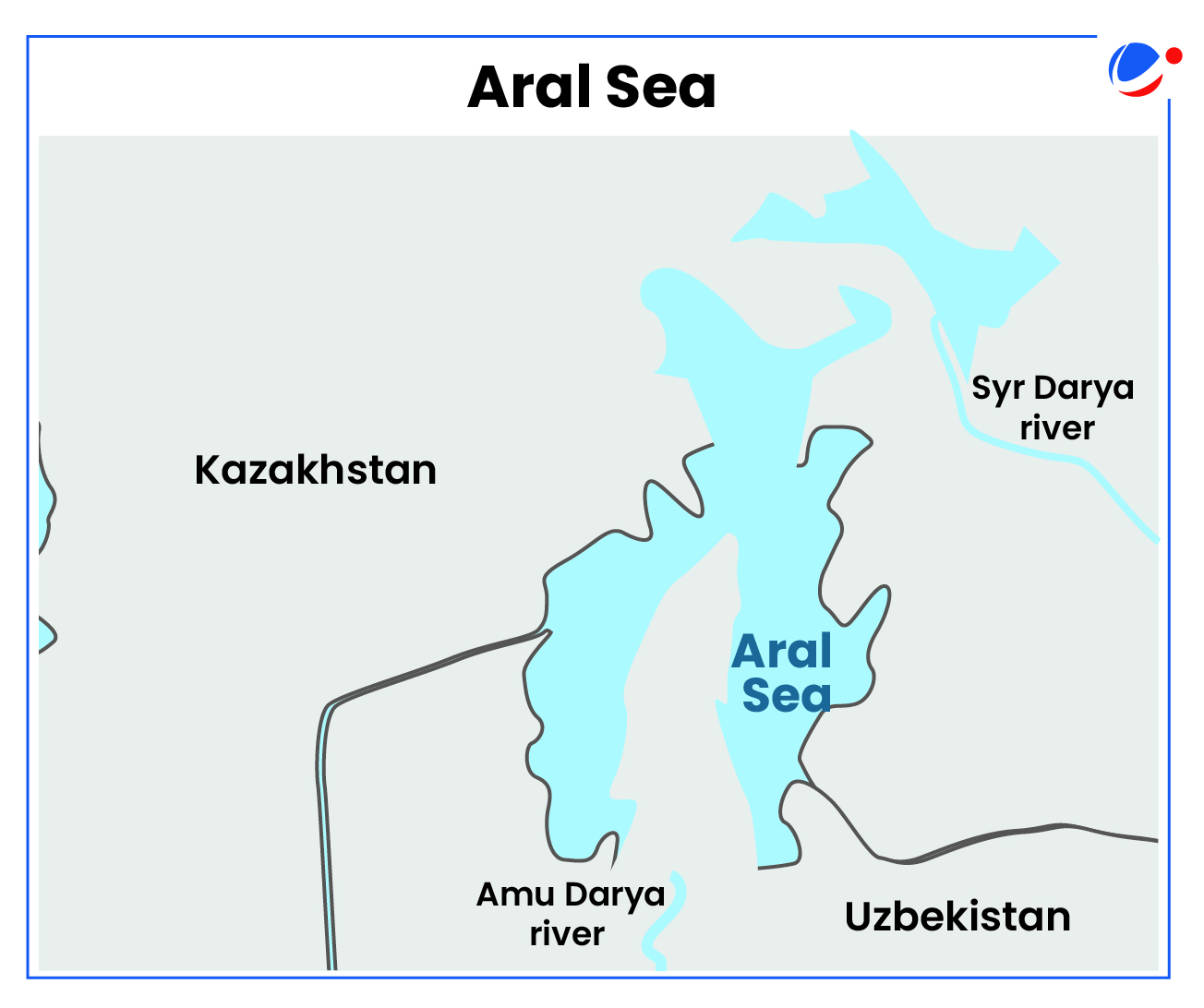
Research indicates signs of geological changes (elevation of the dried land of the basin) since the water disappeared on Aral Sea.
About Aral Sea
- About: Was once a large saltwater lake of Central Asia.
- Location: Boundary between Kazakhstan (North) and Uzbekistan (South).
- It was fed by Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers.
- Cause of Disappearance: Diversion of the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers during the Soviet era.
- The dried-up Aral Sea became the hazardous Aralkum Desert, which ranks as a major global dust source.
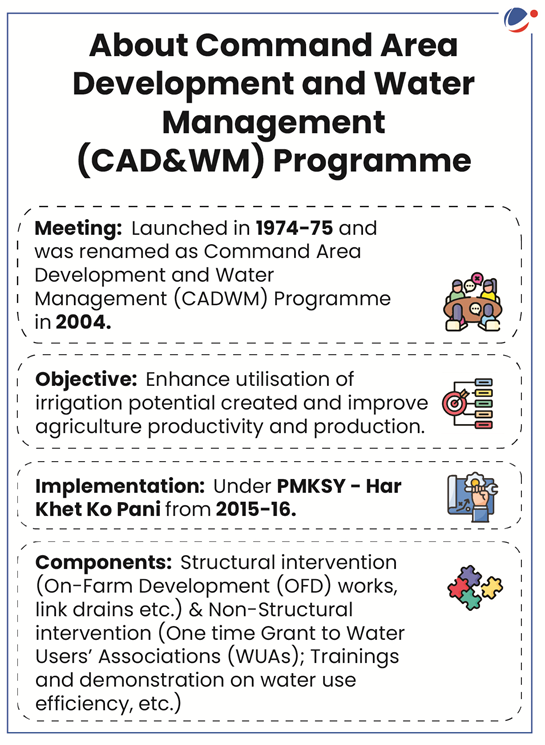
Union Cabinet approved modernization of Command Area Development And Water Management (M-CADWM).
- M-CADWM as a sub-scheme of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) is set to run for the period 2025-2026.
- PMKSY was launched in 2015-16 to enhance physical access of water on farm and expand cultivable area under assured irrigation, improve on-farm water use efficiency, etc.
Key Features of M-CADWM
- Objective: Modernization of the irrigation water supply network to supply of irrigation water from existing canals or other sources in a designated cluster.
- It will make robust backend infrastructure for micro-irrigation by farmers from established source to the Farm gate up to 1 hectare with underground pressurized piped irrigation.
- Technology: Use of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA), Internet of things technology will be used for water accounting and water management.
- Potential benefits:
- Increase the Water Use Efficiency (WUE) at the farm level, increase agriculture production & productivity.
- Sustainable farming by Irrigation Management Transfer (IMT) to Water User Society (WUS) for management of irrigation assets.
- WUS will receive handholding support for the next five years, helping them connect with economic entities like Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Attracting youth into farming by adopting the modern method of irrigation
Ghaziabad Nagar Nigam pioneered India's first certified Green Municipal Bonds.
- It was issued under the Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban, raising ₹150 crore for the development of a cutting-edge Tertiary Sewage Treatment Plant (TSTP).
- TSTP ensures that treated water meets the highest standards, making it suitable for reuse in industrial processes.
- The TSTP was developed under the Public-Private Hybrid Annuity Model (PPP-HAM), with 40% municipal funding.
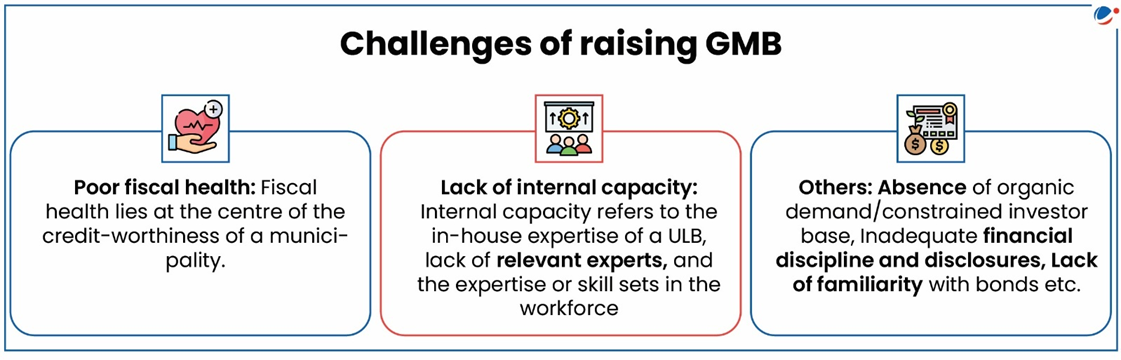
Green Municipal Bond (GMB)
- Municipal bonds refer to non-convertible debt securities issued by a municipal body or another entity that is established for such purposes and entrusted with functions under Article 243W of the Indian Constitution.
- Green bonds are used to raise funds specifically for the climate mitigation, adaptation and other environment friendly and low carbon projects (World Bank).
Significance of GMB
- Sustainable development: Investors are increasingly focused on integrating Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) factors into their investment processes.
- Low cost, long term capital: They are cost-competitive with other bonds and can provide capital at a lower cost than commercial bank loans.
- Broaden investor base: As existing traditional financing sources such as domestic bank loans are not sufficient to support capacity addition.
Odisha notified Similipal tiger reserve as national park.
- Out of the 2,750 sq km of the Reserve, 845.70 sq km has been notified as National Park, making it largest in Odisha, leaving behind Bhitarkanika.
- It is the 107th National Park and the second in the eastern state, after the Bhitarkanika.
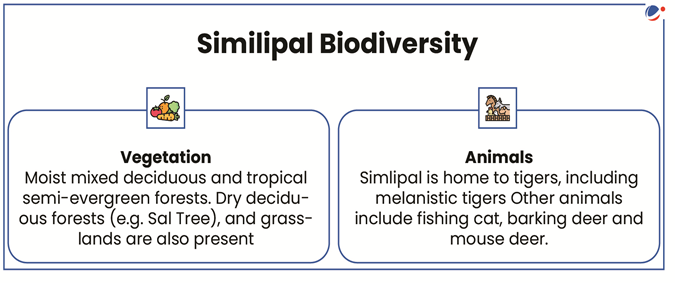
About Simlipal Forest
- Location: Mayurbhanj District of Odisha in Chottanagpur region.
- Major Rivers: Burhabalanga, Palpala Bandan, Salandi, Kahairi, and Deo.
- Simlipal is also protected as a Wildlife Sanctuary, a Tiger Reserve (under Project Tiger), a Biosphere Reserve (under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme, since 2009), and forms part of Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve.
What is a National Park?
- About: It is an area, whether within a sanctuary or not, given the highest protection to conserve its wildlife and environment by reason of its ecological, faunal, floral, geomorphological, or zoological importance.
- No human activity is permitted inside the national park, except for the ones permitted by the Chief Wildlife Warden of the state.
- Also, under the Forest Right Act of 2006, certain tribal groups are permitted to live inside the National Parks.
- Notification: By the State Governments under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- However, once notified, no alteration of the boundaries can be done by the State Government, except on a recommendation of the National Board for Wildlife.
Article Sources
1 sourceCheetah Project Steering Committee cleared the relocation of some of the cheetahs from Kuno National Park to Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
About Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
- Geographical: Gandhi Sagar is a wildlife sanctuary located at eastern Madhya Pradesh. It is spread over two districts of Madhya Pradesh i.e. Mandsaur and Nimach.
- This region is known as Nimar region.
- Type: The forest of this sanctuary is part of Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forest.
- River: River Chambal Passes through it.
- Dam: This sanctuary is spread over the area surrounding to Gandhi Sagar dam backwater.
- Trees: Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, Palash etc.
- Wildlife: Wild Dogs (Dholes), Chinkara, Leopard, Otter, Mugger crocodile.
- Historical: It is part of the world famous Chaturbhuj Nala rock shelters.
India And IBCA Signed the Headquarters Agreement.
- The Agreement provides India to host the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) Headquarters and Secretariat helping IBCA efficiently discharge its official functions.
More on the Agreement
- It pertains to visas, privileges and immunities being extended to the IBCA Secretariat and personnel, premises, etc.
- Further, India to provide a budgetary support of 150 crore rupees to IBCA for creating a corpus, building infrastructure, meeting recurring expenditure for 5 years from 2023-24 to 2028-29.

Other Efforts for Conservation of Big Cats
|
During the 10th Anniversary of UNESCO Global Geoparks (UGGPs), 16 new sites across 11 countries were added to the GGN.
- GGN is a non-profit International Association founded under UNESCO.
- It establishes ethical standards that must be adopted by Global Geoparks.
Major Geoparks added to GGN
- Kanbula (China): Located on the edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, it features the ancient Maixiu volcanoes, which are exceptionally well-preserved, and the Yellow River.
- Mt Paektu (North Korea): It was the location of one of the largest eruptions in recorded history (Millennium Eruption around 1000 CE).
- North Riyadh (Saudi Arabia): Obaitharan Valley (Wadi Obaitharan), located at the base of Tuwaiq Mountain, is a lush reserve that supports the region’s water supply.
- Valley is also home to ancient coral reef systems.
UNESCO Global Geoparks (UGGP)
- Genesis: Introduced in 2015 as a key component of the International Geosciences and Geoparks Programme (IGGP).
- Geoparks: UGGPS are single, unified geographical areas where landscapes of internationalgeological significance are managed with a holistic concept of
- protection,
- education and
- sustainable development.
- Management: Managed by a body having a legal existence recognised under national legislation.
- Reassessment Period: UGGP status is not permanent; it is reassessed every four years.
- Mandatory Networking: Membership of the GGN is obligatory for UGGPs.
- Current Status: There are 229 UNESCO Global Geoparks in 50 countries (none in India).
Article Sources
1 source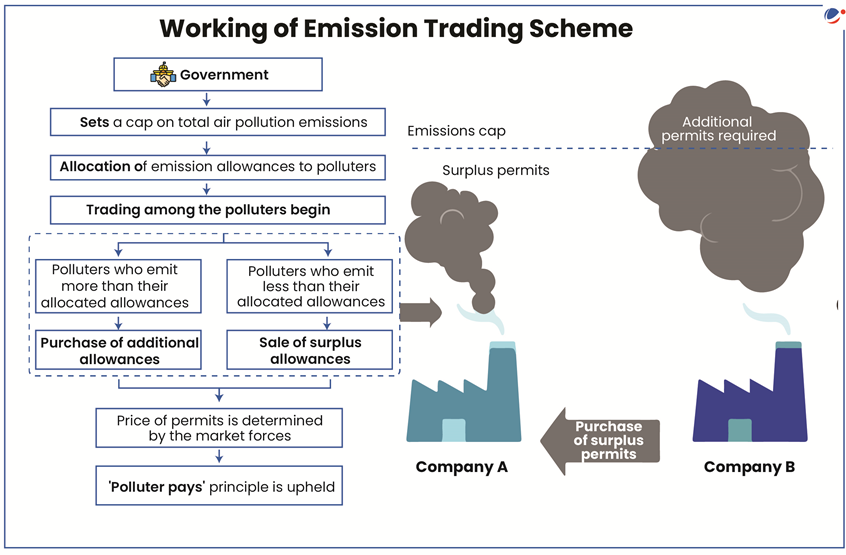
A new study has revealed that the Surat Emission Trading Scheme (ETS) launched in 2019 has been successful in controlling particulate matter emissions cutting Pollutants By 20-30%.
- Pollution abatement costs also dropped by over 10 %, and compliance with environmental laws rose among participating plants.
About Surat ETS
- Overview: It is the world’s first-ever market for trading in particulate matter emissions.
- It is also India’s first pollution trading scheme of any kind.
- The concept of ETS first originated in US, targeting sulfur dioxide (SO2) pollution.
- Objective: To curb air pollution in accordance with the polluters pay principle.
- Working Mechanism: It is based on market-linked ‘cap and trade’ mechanism (Refer Image).
- This approach has been used in Europe for greenhouse gases and in China for carbon emissions.
- ETS uses Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS) devices for monitoring.
- Trading: Industries trade permits on a platform developed by NeML (National Commodities and Derivatives Exchange e-Markets).
- Participating units are also required to submit an 'Environmental Damage Compensation' amount (rate varies according to size of industry).
International Maritime Organization (IMO) approved Net-Zero Framework for Global Shipping.
- The IMO Net-zero Framework is the first in the world to combine mandatory emissions limits and GHG pricing across an entire industry sector.
- Shipping accounts for almost 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Key Features
- It will be included in Annex VI (Prevention of air pollution from ships) to the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL).
- Aim: Net-zero emissions by or around, i.e. close to 2050.
- Implementation: Set to be formally adopted in October 2025 before entry into force in 2027.
- Once into force, it will become mandatory for large ocean-going ships over 5,000 gross tonnage, which emit 85% of the total CO2 emissions from international shipping.
- Ships will be required to comply with:
- Global Fuel Standard: Ships must reduce, over time, their annual greenhouse gas fuel intensity (GFI) – that is, how much GHG is emitted for each unit of energy used.
- Global Economic Measure: Ships emitting above GFI thresholds will have to acquire remedial units to balance its deficit emissions, while those using zero or near-zero GHG technologies will be eligible for financial rewards.
- IMO Net-Zero Fund: It will be established to collect pricing contributions from emissions.

Article Sources
1 sourceSecond WHO Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health was held in Catragen, Columbia.
About the Conference
- It was co-organized by WHO and Columbia and other UN Agencies like UNEP, WMO etc.
- Objectives: Accelerating action for clean air, clean energy access and climate change mitigation.
Key Highlights
- Over 50 countries, have committed to the shared goal of reducing the health impacts of air pollution by 50% by 2040.
- India reaffirmed its commitment to reducing air pollution's health impacts by 2040 through actions aligned with the National Clean Air Programme.
India urges BRICS nations to unite on ‘Baku to Belem Roadmap’ to mobilise USD 1.3 trillion in climate finance annually by 2035 to support Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Baku to Belem Roadmap
- UNFCCC COP29, held in Baku (Azerbaijan), agreed on a new global finance goal and a framework for raising ambition for climate finance in run-up to COP30 in Belém (Brazil).
- It aims at scaling up climate finance to developing country parties to support low greenhouse gas emissions and climate-resilient development pathways and implement NDCs.






