Cabinet approves Vibrant Villages Programme-II (VVP-II).
- VVP-II builds upon the foundation laid by the first phase, VVP-I, which targeted border villages along the northern frontier.
- This initiative highlights India’s commitment to Viksit Bharat@2047, ensuring safe, secure, and self-sufficient land borders.
About Vibrant Villages Programme-II (VVP-II)
- Type: Central Sector Scheme with 100% Centre funding (unlike VVP-I, which was Centrally Sponsored).
- Coverage: Strategic villages along international land borders (ILBs) across 17 states/UTs (excluding northern border blocks covered under VVP-I (2023-24)).
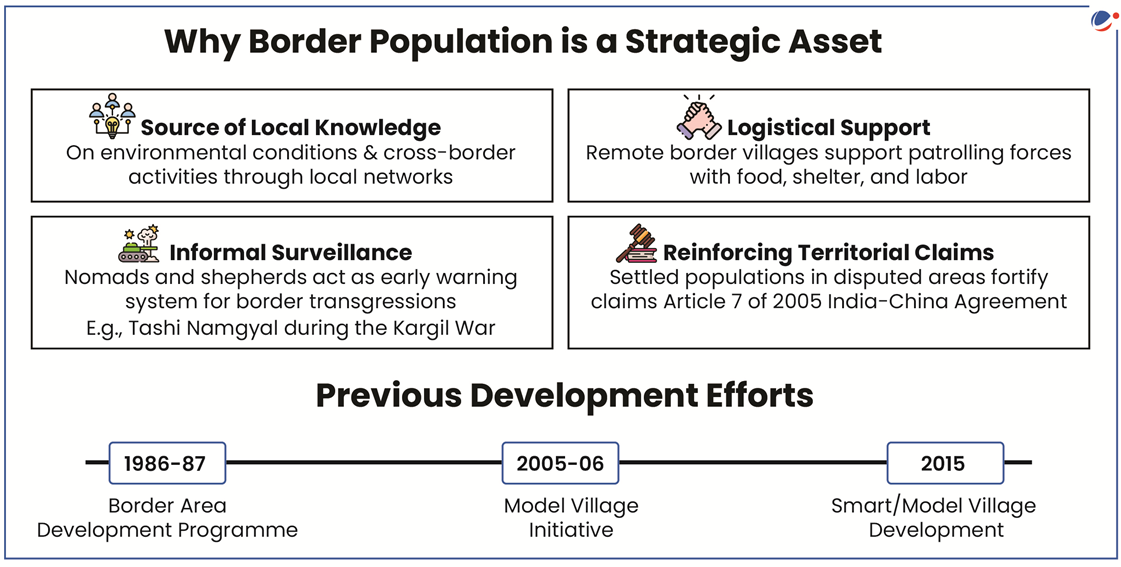
- Objective: Improve living conditions, provide livelihood opportunities, control trans-border crime, and integrate populations as ‘eyes and ears’ for internal security.
- Tenure: Financial Years 2024-25 to 2028-29
Key Features of VVP-II
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in roads, housing, sanitation, drinking water, and SMART classrooms, with all-weather road connectivity under the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (MGSY-IV).
- Value Chain & Livelihood Development: Support for cooperatives, SHGs, and border-specific outreach activities to create sustainable livelihoods.
- Welfare Scheme Convergence: Implement existing welfare schemes in the identified villages, ensuring full coverage under the convergence model.
- Cultural & Tourism Promotion: Organizing fairs, festivals, awareness camps, and national day celebrations to boost tourism and promote local heritage.
- PM Gati Shakti: Shall be used for effective implementation of the project.
Recently, Department of Revenue under the Union Ministry of Finance issued notification to include Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) under the Section 66 of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002.
- This would help I4C to share and receive information from the Enforcement Directorate and other law enforcement agencies, so as to strengthen the country’s fight against cyber-enabled financial crimes.
Section 66(Disclosure of information) of PMLA Act, 2002
- Enables the Director (Directorate of Enforcement) or any other authority specified by him to share the information with the concerned agency for necessary action.
- Sharing of information shall be on the basis of information or material in his possession, that the provisions of any other law for the time being in force are contravened.
About Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Officially inaugurated in 2020, it is an initiative of the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, envisaged to act as the nodal point to curb Cybercrime in the country.
- In July 2024, it was made an attached office on the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Objective: To provide a framework and eco-system for Law Enforcement Agencies for dealing with Cybercrime in a coordinated and comprehensive manner.
Verticals of I4C: National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), National Cybercrime Threat Analytics Unit (NCTAU), National Cybercrime Ecosystem Management Unit (NCEMU), Joint Cyber Crime Coordination Team (JCCT), etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceCentre approved 26 Rafale Marine (M) Fighter Jets From France.
- These fighter jets will be for the Indian Navy and will be deployed on the country’s first indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant.
- The Indian Air Force operates 36 Rafale jets, acquired earlier.
About Rafael aircraft
- Manufacturer: Dassault Aviation, a French aerospace company.
- “Omnirole” capabilities: Which means able to carry out all combat aviation missions such as air defense, strikes, reconnaissance, nuclear deterrence, etc.
- Generation: 4.5 generation with maximum speed 1.8 Mach (1 Mach=1235km/hr).
Various Latest Generation Aircrafts | Specifications | Examples |
Fourth generation jet fighters (1970- 1980s) | Ability to both switch and swing roles between air-to-air and air-to-ground. | MiG-29, F-16, Mirage-2000 etc. |
Four and half generation jet fighters | Added ‘stealth’, radar absorbent materials, thrust vector controlled engines, to extend the range of fourth generation fighters. | Eurofighter Typhoon, Rafale etc. |
Fifth generation jet fighters | Advanced stealth technologies and advanced weapons, | F-22 Raptor,Chengdu J-20 etc. |
U.S.-China 6th-Gen Aircraft Battle
- USA: The US President announced plans to move forward with a next-generation fighter jet dubbed F-47.
- China: In December 2024, China flew two sixth-generation fighter prototypes, the J-36 and J-50.
- Sixth-generation fighter jets are characterized by attributes such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration, Hypersonic capabilities, Unmanned capabilities, etc.
DRDO successfully conducts release trials of Long-Range Glide Bomb ‘Gaurav’.
Weapon Specifications
- Type: Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB).
- Weight: 1,000 kg class
- Range: ‘Gaurav’ achieved 100 km range with pinpoint accuracy.
- Development: Designed and developed indigenously
Article Sources
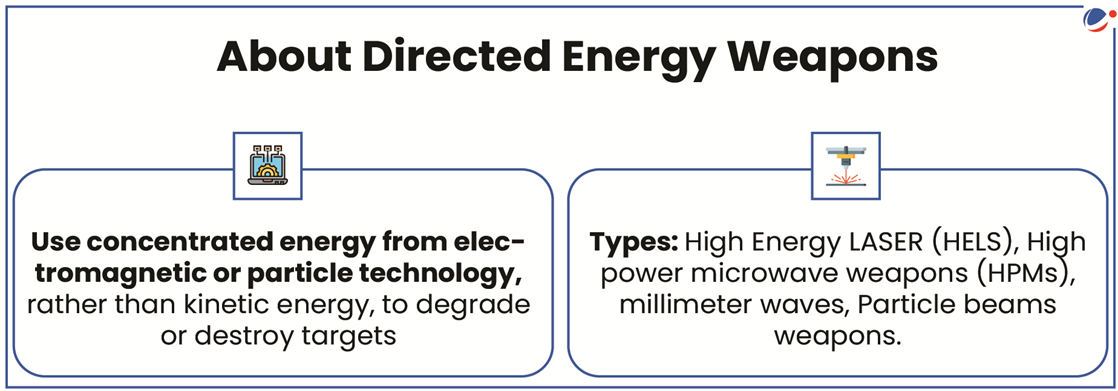
1 sourceDRDO successfully conducted a trial of a Mk-II(A) LASER- Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system at the National Open Air Range (NOAR) in Kurnool (Andhra Pradesh).
- India became the fourth country in the world, after the US, China, and Russia who possess advanced LASER weapon capabilities.
About Mk-II(A) DEW system
- Developed by: Indigenously by DRDO’s Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS), Hyderabad.
- Potential targets: It can disable drones, missiles, and aircrafts.
- Mechanism: Once detected by a radar or inbuilt Electro Optic (EO) system, it engages targets and uses an intense high-energy 30 kilowatt LASER Beam to cut through the target, leading to structural failure.
- Characteristics: Lightning speed of engagement, precision, and can have lethality delivered to the target within a few seconds.
Significance of DEW System
- Potential to revolutionize the battle space economics: It can reduce the reliance on expensive ammunition while also lowering the risk of collateral damage.
- Counter-electronic capabilities: High-power microwave (HPM) weapons can disable electronic systems, radars, and communications without physical destruction.
- For offensive and defensive warfare: Such as for tactical air defence, anti-ballistic missile defence, and anti-satellite (A-SAT) applications, Low-power lasers for crowd control and deterring pirates.
INS Varsha, under Project Varsha to be operational by 2026.
About Project Varsha
- It is a classified naval project aimed at strengthening India’s underwater nuclear capabilities.
- Objective: To develop a secure underground base to house a fleet of over 12 nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs).
- Location: Coastal village Rambilli in Andhra Pradesh.
- Similar to Project Varsha from the east, Karwar base in Karnataka under Project Seabird safeguards the west coast.
Exercise | Details |
Exercise Desert Flag-10 | Indian Air Force is participating in Exercise Desert Flag-10.
|
Operation ATALANTA | European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR) Operation ATALANTA has proposed a joint exercise with the Indian Navy. About Operation Atalanta
|
Exercise ‘Dustlik’ | 6th edition of Exercise Dustlik started in Pune, Maharashtra.
|
Exercise Tiger Triumph | The Fourth edition of Exercise Tiger Triumph has commenced at Vishakhapatnam coast.
|
INIOCHOS-25 | Indian Air Force to Participate in Multinational Air Exercise in Greece. About INIOCHOS-25
|





