5 countries were elected to serve as non-permanent members of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- These countries are Bahrain, Colombia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Latvia, and Liberia.

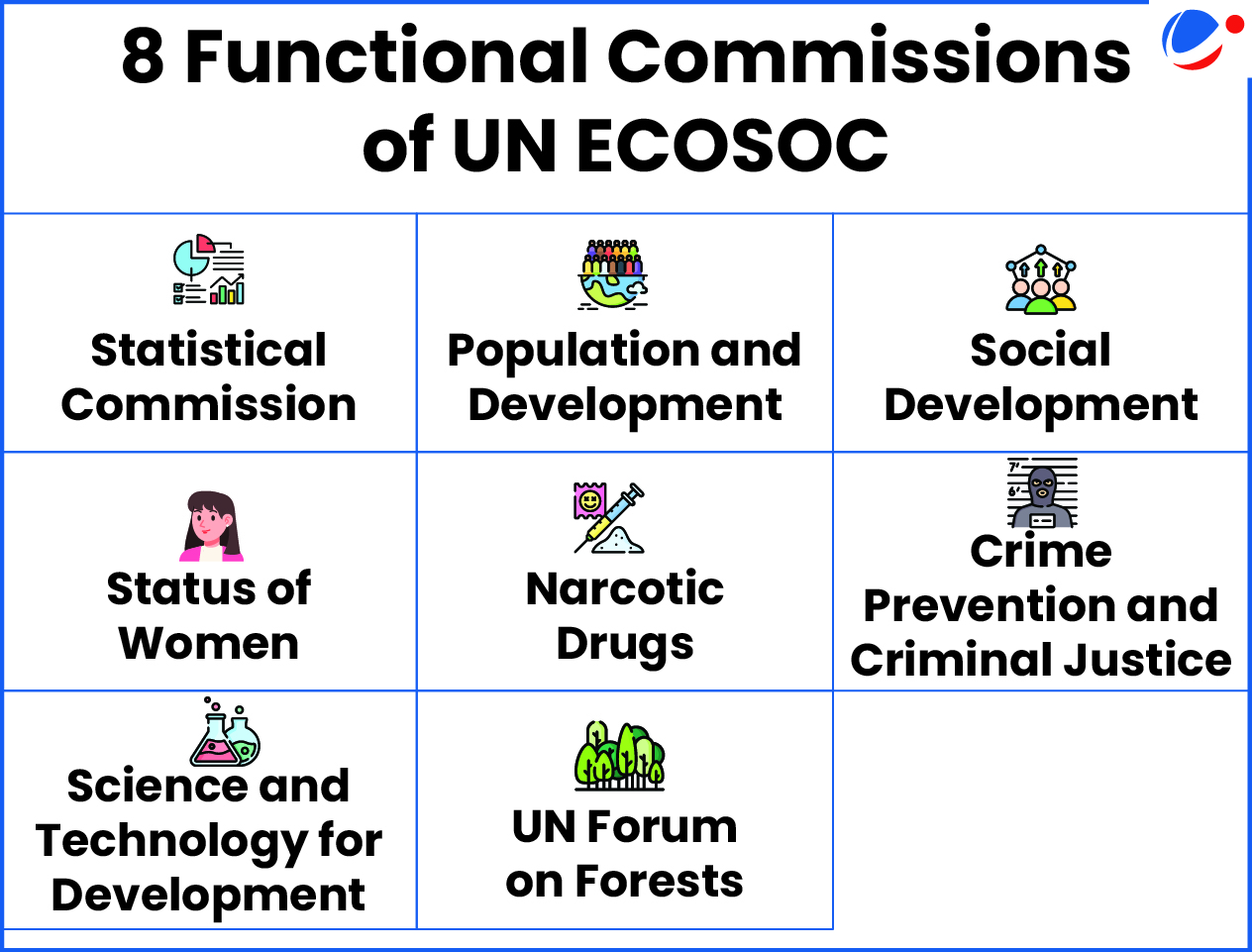
About UNSC
- Genesis: Established in 1945 through the UN Charter as one of the 6 principal organs of the UN.
- Purpose: Maintaining international peace and security.
- Members: 5 permanent members (P5) and 10 non-permanent members (refer to the infographic).
UNSC Reform Proposal (2024)
- Proposed by: G4 Nations (India, Brazil, Germany, Japan)
- Need:
- Misuse of veto power by permanent members
- Poor regional representation
- Does not reflect current global realities
- Key provisions of proposed reforms
- Expanded Membership:11 permanent and 14–15 non-permanent members
- Equitable Regional Representation: 6 new permanent seats to be distributed among Africa, Asia-Pacific, Latin America & Caribbean, and Western Europe/Other States.
- No veto for new permanent members initially: This provision to be reviewed 15 years after reforms are implemented.
Related newsPakistan has been elected as the Chair of the UNSC's Taliban Sanctions Committee and Vice-Chair of the Counter-Terrorism Committee for 2025. Taliban Sanctions Committee (TSC)
Counter-Terrorism Committee (CTC)
|
Article Sources
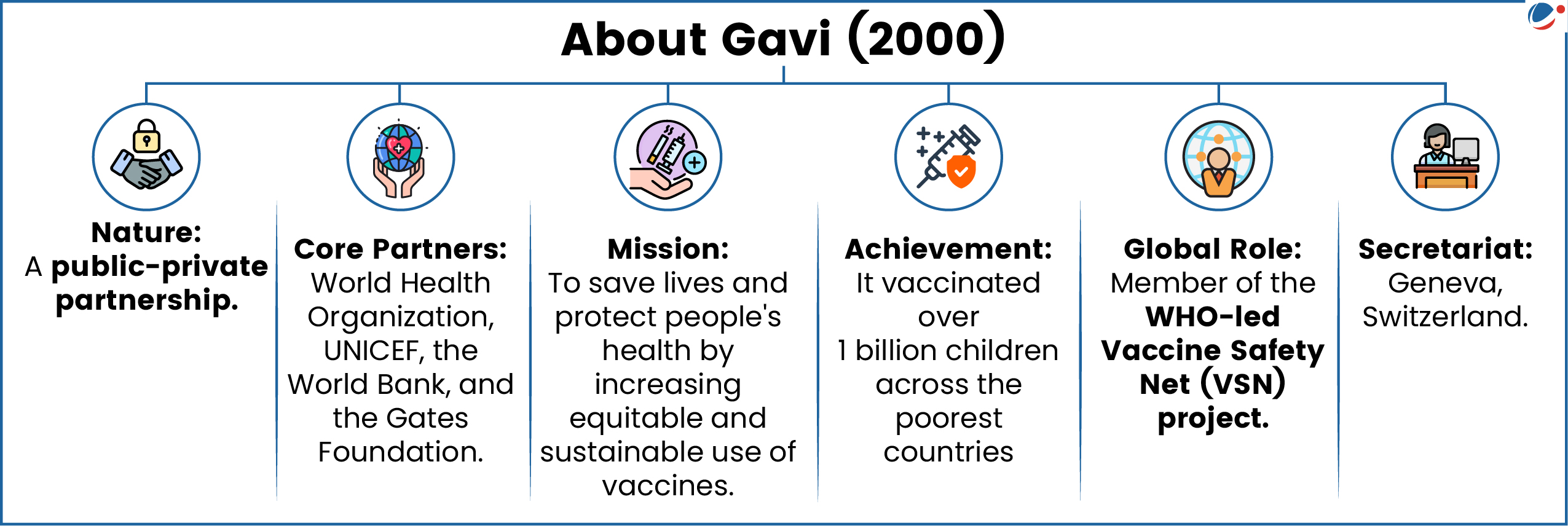
1 sourceThe US has accused Gavi, along with the World Health Organisation (WHO), of silencing dissenting views and legitimate questions about vaccine safety.
- The US has long been one of biggest supporters of Gavi.
Rising trend of US withdrawal from Global Alliance
- In recent years, the United States has exhibited a rising trend of withdrawing from key global alliances and institutions such as the WHO, the Paris Climate Agreement, UN Human Rights Council, UN Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA), etc.
- As a global superpower, the U.S.'s withdrawal carries far greater implications for international governance.
Impact of US Withdrawing from Global Alliances
- Weakening of Multilateralism/Rule-Based Order: E.g. Israel withdraws participation from UN Human Rights Council.
- Undermine Climate Actions: 2024 was recorded as the hottest year and the USA stands as the world's second-largest greenhouse gas emitter behind China.
- Shortage of Funds for Health: US exit could leave institutions with fund crunch. E.g., In 2024, US-funded about 15% of WHO's total funding.
- Other: It creates a leadership vacuum that can be filled up by China (it may reduce India's influence in global organisations' decision-making), etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceChina formally established the IOMed as a global alternative to traditional institutions such as the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the Permanent Court of Arbitration.
About IOMed
- Purpose: dedicated to resolving international disputes through mediation.
- Members: Over 30 countries joined as founding members including Indonesia, Pakistan, and Belarus.
- Most founding members are from Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean, highlighting its non-Western orientation.
- Scope:
- Disputes between states,
- Disputes Between a state and nationals of another country,
- International commercial disagreements
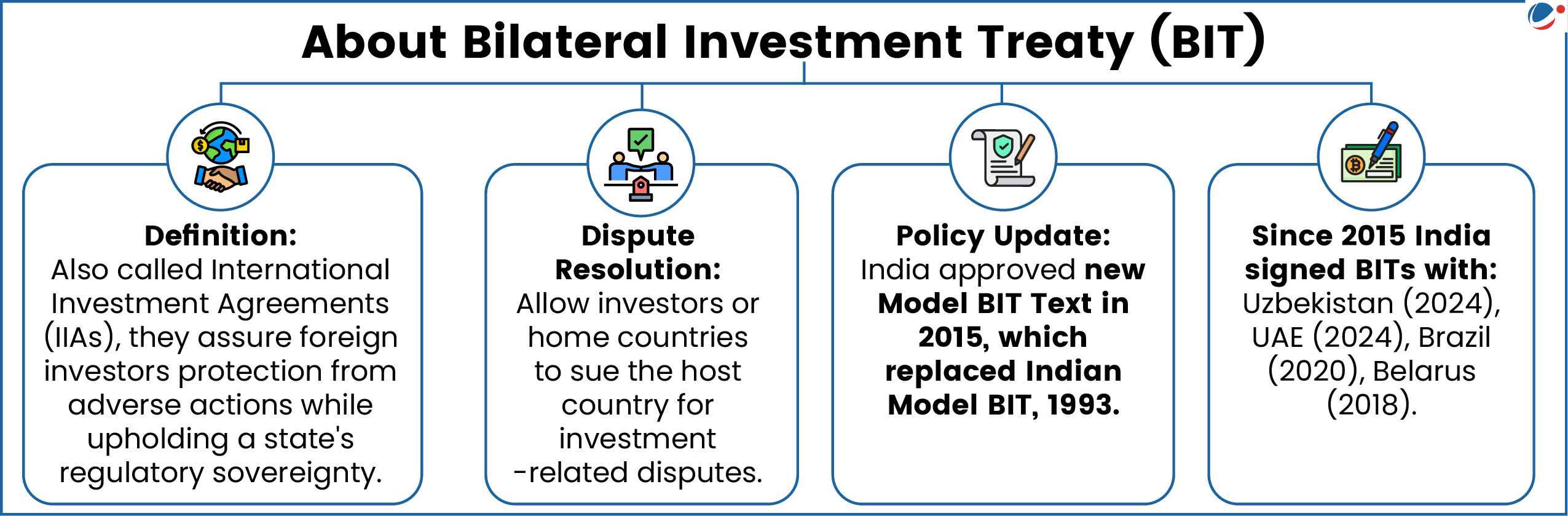
The Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) signed in June 2019, entered into force with effect from 5th June 2025.
- This new BIT replaces the earlier agreement enforced in 2000, ensuring continuity in the protection of investments between the two nations.
India-Kyrgyzstan Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT)
- The BIT balances the investor rights with the sovereign regulatory powers of both countries and reflects a shared commitment to create a resilient and transparent investment climate.
- Key Features of the BIT
- This removal will ensure more consistent treatment.
- General exceptions E.g., Protection of environment, ensuring public health and safety, etc.
- Definition of Assets: Enterprise-based definition with an inclusion and exclusion list & clarifies investment characteristics: capital commitment, profit expectation, risk assumption, etc.
- Exclusions for Policy Space: Excludes local government, government procurement, taxation, compulsory licenses, etc.
- Removes the Most Favored Nation (MFN) clause: Which previously allowed investors to selectively import favorable provisions from other treaties signed by the Host State.
- The BIT contains General and security exceptions: The attempt is to carve out a policy space for the State.
- Revised dispute resolution mechanism: Requires investors to first use local remedies before international arbitration, promoting alternative dispute resolution.
Article Sources
1 source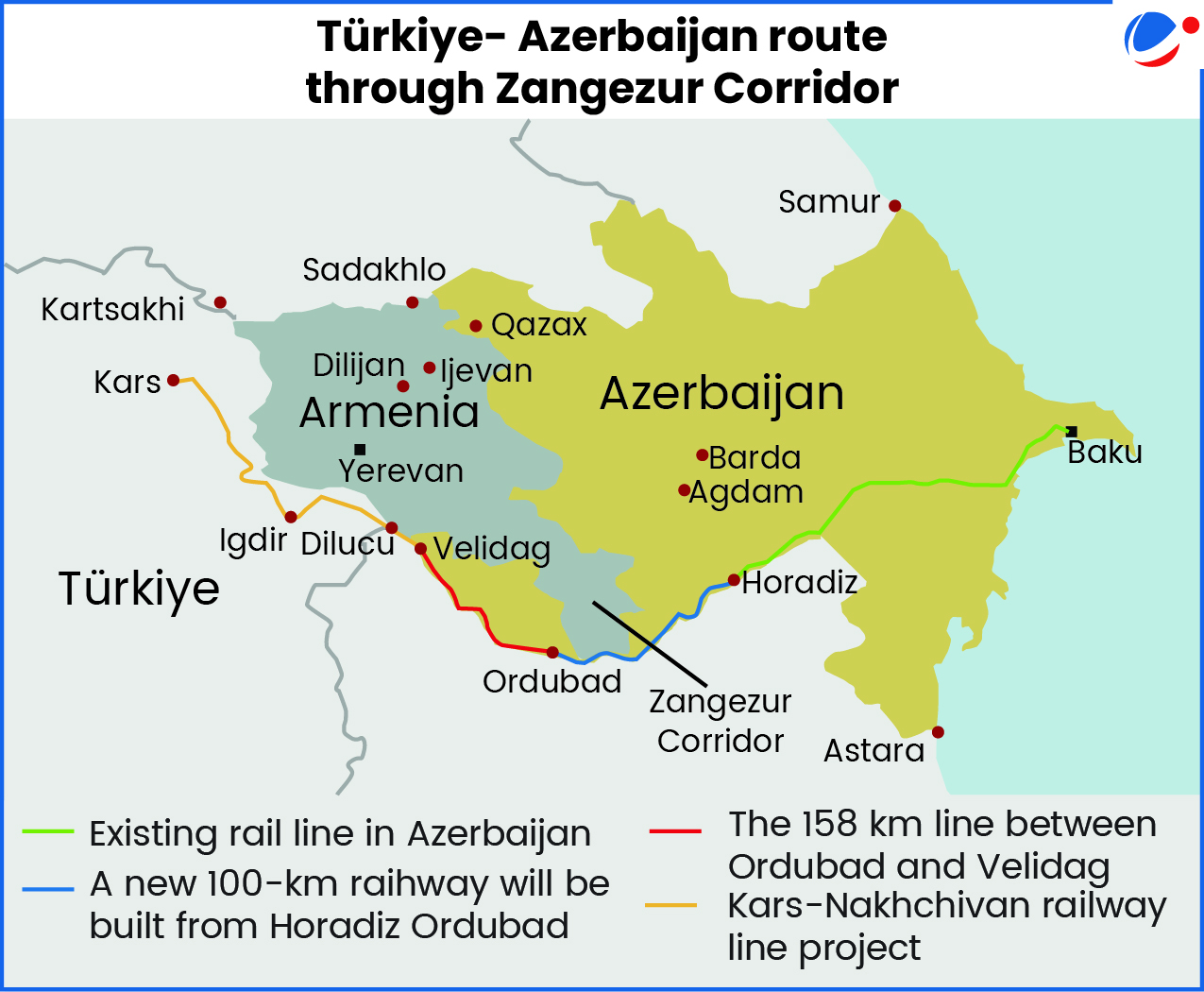
Türkiye urged Armenia and Azerbaijan take steps to open the Zangezur Corridor.
- The two countries have been in conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh (Artsakh) since 1917. The region is internationally part of Azerbaijan, but mainly ethnic Armenians live there.
About Zangezur Corridor
- Location: It is a proposed 43-kilometer transport route through Armenia’s Syunik Province.
- Objective: Connecting Azerbaijan’s Baku Port in Caspian Sea to the Nakhchivan Autonomous Region, a western exclave of Azerbaijan separated by Armenian territory, and further to Turkey.
- India’s concerns: It can undermine India’s investments in Chabahar Port and International North South Corridor (INSTC) by offering a competing pathway, reducing India’s regional leverage.
Ministry of External Affairs rolled out e-Passport and Passport Seva Programme 2.0.
About e‑Passport
- An ePassport is a combined paper and electronic passport with a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Chip and an antenna embedded as an inlay of passport that contains the personal particulars and biometric information of the passport holder.
- The underlying technology supporting the security of the ePassport is the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) solution.
- ePassport safeguards the passport from forgery and potential fraudulent activities like fake passports while confirming the genuineness at border controls.