IBAT Alliance doubled its investment in biodiversity data from 2023 to 2024
- Increased investment will support three key global biodiversity datasets i.e., World Database on Protected Areas, IUCN Red List and World Database of Key Biodiversity Areas.
About IBAT Alliance
- Headquarter: The UK
- Genesis: Founded in 2008
- It is a coalition of four of the world’s largest and most influential conservation organisations.
- These four organizations are: Birdlife International, Conservation International, The International Union of Conservation for Nature (IUCN), The United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC)
- Mission: To provide data, tools and guidance that help organisations act on biodiversity-related risks etc.
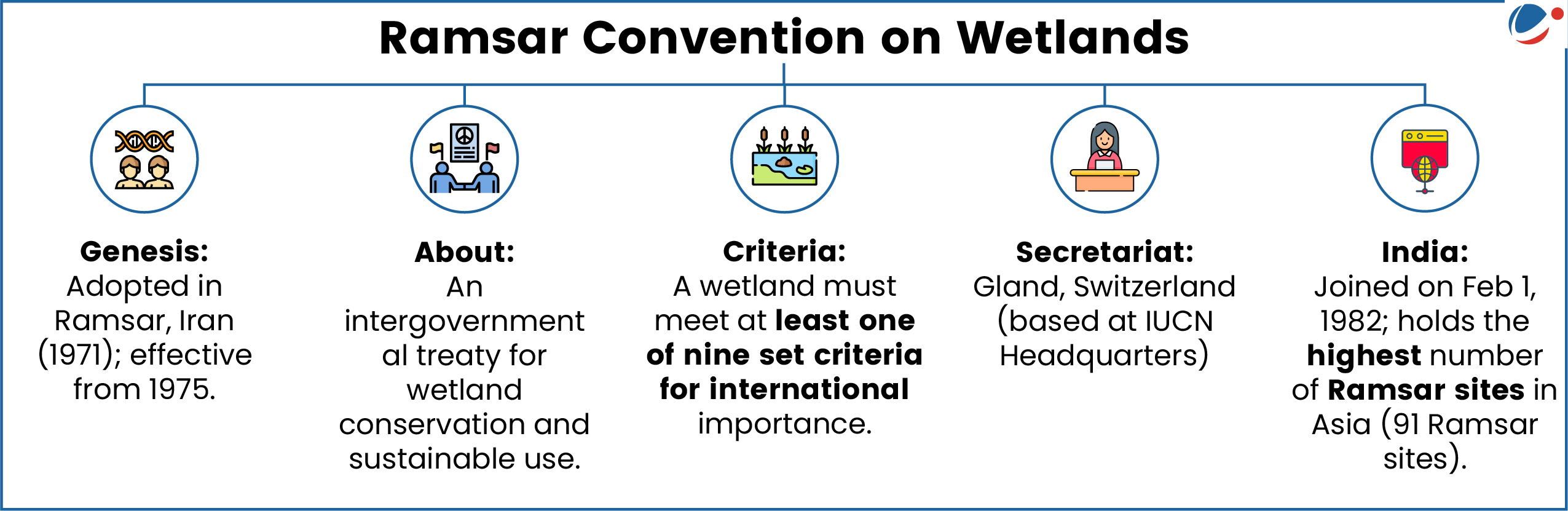
India added two more wetland into Ramsar list of Wetlands of International Importance.
- Khichan and Menar wetlands in Rajasthan were declared Ramsar Sites on world environment day 2025, raising India's total count to 91.
- World Environment Day is celebrated annually on 5th June (Since 1973) led by the UN Environment Programme. The theme for 2025 is Beat Plastic Pollution.
- With the addition of these wetlands, Rajasthan now has four Ramsar sites, including Sambhar Salt Lake and Keoladeo Ghana National Park in Bharatpur.
About New Ramsar Sites | |
|
|
|
|
Article Sources
1 sourceTamil Nadu notified Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi to preserve a critical stopover point along the Central Asian Flyway for thousands of migratory wetland birds.
About Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus):
- IUCN Status: Least Concern
- Distribution: Africa, western Asia (India), and southern Europe.
- Habitat: Breeds in shallow wetlands that are either saline or alkaline.
- Features: This species has a great dispersal capacity outside of the breeding season, but it is highly philopatric (to return to or remain near a particular site or area).
- The Kachchh Desert Wildlife Sanctuary in the Great Rann of Kachchh (GRK) in Gujarat State, is a unique Protected Area, that supports South Asia’s only breeding ground of Greater Flamingos, internationally renowned as the “Flamingo City”.
The 1st assembly of the IBCA convened in New Delhi, endorsed the India's Union Minister of Environment, Forest & Climate Change, Shri Bhupender Yadav, as the President of IBCA.
- The Assembly of the IBCA serves as its apex decision-making body and is convened annually/biannually.
About IBCA
- It is a multi-country, multi-agency coalition of 95 big cat range countries, non-range countries with an interest in big cat conservation.
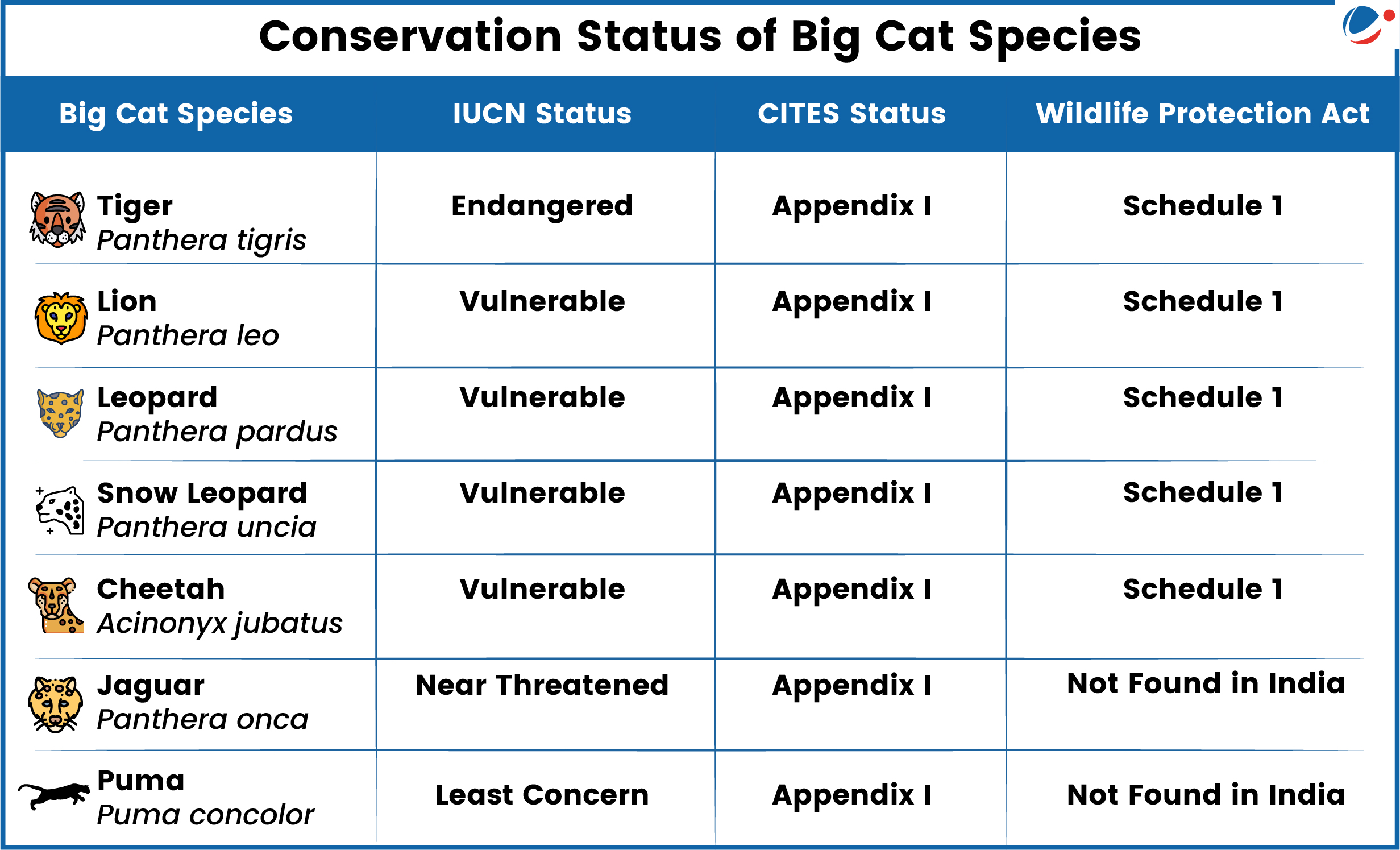
- These Big Cats include Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar & Puma. (refer to table)
- Genesis: Launched in April 2023 (occasion of 50 years of India's Project Tiger)
- Main Goal: To foster collaboration and synergy by establishing a platform dedicated to sharing best practices in big cat conservation.
- Founding Members (16): Armenia, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ecuador, India, Kenya, Malaysia, Mongolia, Nepal, Nigeria, Peru, Suriname, & Uganda.
- India is the host country & Secretariat for the IBCA.
Article Sources
1 sourceResearchers have coined a new term to describe extended periods of atmospheric thirst called Thirstwaves.
About Thirstwave
- A thirst wave has at least three consecutive days when daily evaporative demand is greater than its historical 90th percentile value for that period.
- Evaporative demand is a measure of how thirsty the atmosphere is.
- A combination of factors drives evaporative demand, including temperature, wind speed, humidity, and sunshine.
- Studying these ‘thirstwaves’ can help farmers better manage their water resources and improve crop yields.
Article Sources
1 sourceVolcano | Features |
Mount Etna |
|
Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki |
|
Kilauea volcano |
|
Its creation follows a United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) resolution in 2022 that called for the establishment of such an intergovernmental body.
- The negotiations were convened by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP), which will now also host the panel.
- The New panel will provide nations with Independent, policy-relevant scientific advice on issues related to chemicals, waste and pollution prevention.
- It completes a global scientific trifecta, alongside the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES).
Need for the Panel
- To reduce the impact of the triple planetary crisis: The crisis of climate change, the crisis of nature and biodiversity loss, and the crisis of pollution and waste.
- To reduce the impact of Chemicals, Waste and Pollution as
- Chemicals used daily in modern life have increased and there can be unintended negative impacts.
- Municipal solid waste generation is predicted to grow from 2.1 billion tonnes in 2023 to 3.8 billion tonnes by 2050.
- Death from modern forms of pollution have risen by 66% over the past two decades.
International Labour Organization’s (ILO) member states have adopted the first ever international convention on biological hazards at work.
About the Convention (ILO Convention 192)
- It calls on Member States to formulate national policies and adopt measures on occupational safety and health that include–
- the prevention and protection against biological hazards, and
- the development of preparedness and response measures to deal with accidents and emergencies.
- India’s Concerns:
- The blanket application across all sectors and enterprise sizes, regardless of exposure level, may place greater burden on MSMEs and informal enterprises in developing countries.
- Concerns about the definitions used in the instrument as they are too broad, possibly leading to their application outside the actual workplace, leading to over-regulation.
About Biological Hazards (Biohazards)
|
Other Key Highlights of the Conference
- First standard-setting discussion on decent work in the platform economy:
- Related to fundamental principles and rights at work, fair remuneration, social security, occupational safety and health etc.
- The platform economy refers to economic activities that occur on digital platforms, which are online marketplaces connecting suppliers and consumers eg. Uber, Amazon etc.
- Adopted a Resolution to reduce informality and support the transition to formal work.
- It calls for urgent action to improve working conditions, extend social protection, and create decent jobs.
- Amendments to the Code of the Maritime Labour Convention, 2006 (MLC, 2006).
- To address violence and harassment on board, reinforce the right to shore leave and repatriation, and call for recognizing seafarers as key workers.
- The Code establishes minimum working and living standards for all seafarers on those ships.
- It is also an essential step toward ensuring fair competition and a level-playing field for quality ship owners.
- India ratified it in 2015.
State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2025 Report is released by the World Bank Group.
- As per the report, number of operational Carbon Pricing (CP) instruments has grown, from 5 (2005) to 80 presently, with India, Brazil, and Türkiye actively developing them.
Key Highlights of the Report
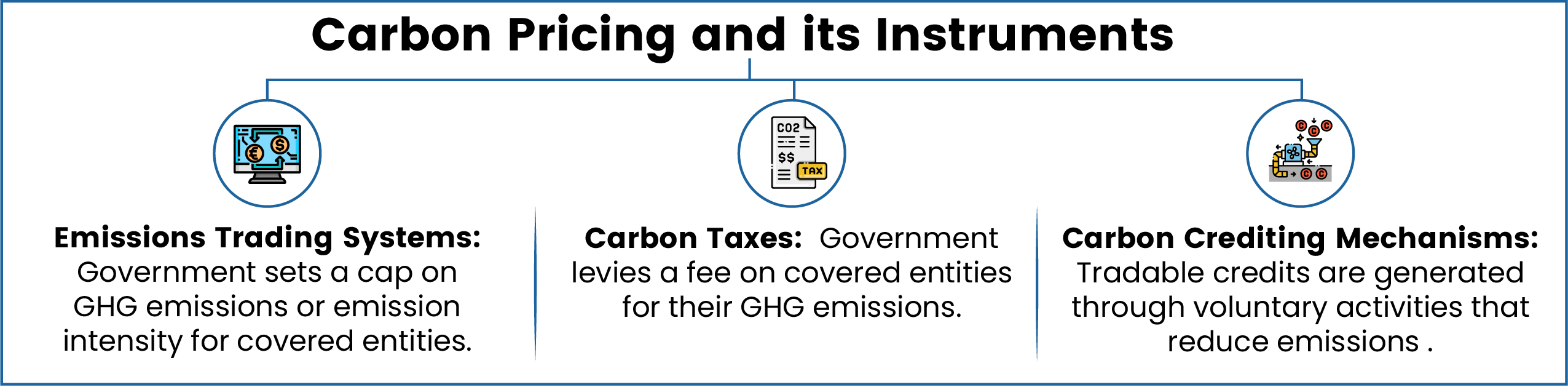
- Coverage: CP covers around 28% of global Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, with 43 carbon taxes and 37 Emission Trading Systems (ETSs).
- Revenue Generation: Globally, ETSs and carbon taxes continued to generate over USD 100 billion (2024) for public budgets.
- Sector Wise Coverage: Power followed by industry sector have the highest coverage.
- Agriculture and Waste remains largely uncovered.
- Carbon Credit Supply Vs Demand: Supply continued to outstrip demand, with almost 1 billion tons of unretired credits in 2024, globally.
Key Provisions on CP
Global
- Article 6 of Paris Agreement (CoP 21, UNFCCC): Provides basis for facilitating international recognition of cooperative carbon pricing approaches.
- COP29 (Baku, Azerbaijan), UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) adopted the final rules for Article 6.2 (cooperative approaches) and Article 6.4 (the Paris Agreement Crediting Mechanism).
- Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanisms (CBAMs): Imposes Carbon price at the border on emissions from imported goods. E.g., EU’s CBAM.
India
- Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (2023): Provides two mechanisms,
- Compliance Mechanism: Obligated entities complies with prescribed GHG emission reduction norms.
- Offset mechanism: Non-obligated entities registers projects for GHG emission reduction/ removal/ avoidance for Carbon Credit Certificates.
Article Sources
1 sourceWorld Meteorological Organization releases State of the Climate in Asia 2024 Report
- WMO is a specialized agency of the United Nations.
Key Findings
- Hottest Year: 2024 was Asia’s warmest or second warmest year on record, with temperatures 1.04°C above the 1991–2020 average.
- Rapid Warming: Asia is warming twice as fast as the global average.
- Glacial Loss: Reduced snowfall and extreme heat drove glacier melt in the Central Himalayas and Tian Shan.
- Record Sea Temperatures: Highest sea-surface temperatures recorded. Decadal warming rate is almost double the global average.
Article Sources
1 sourceRevised mission document of the National Mission for a Green India (or Green India Mission (GIM) was unveiled.
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) unveiled the document on the occasion of World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought (June 17).
About Green India Mission
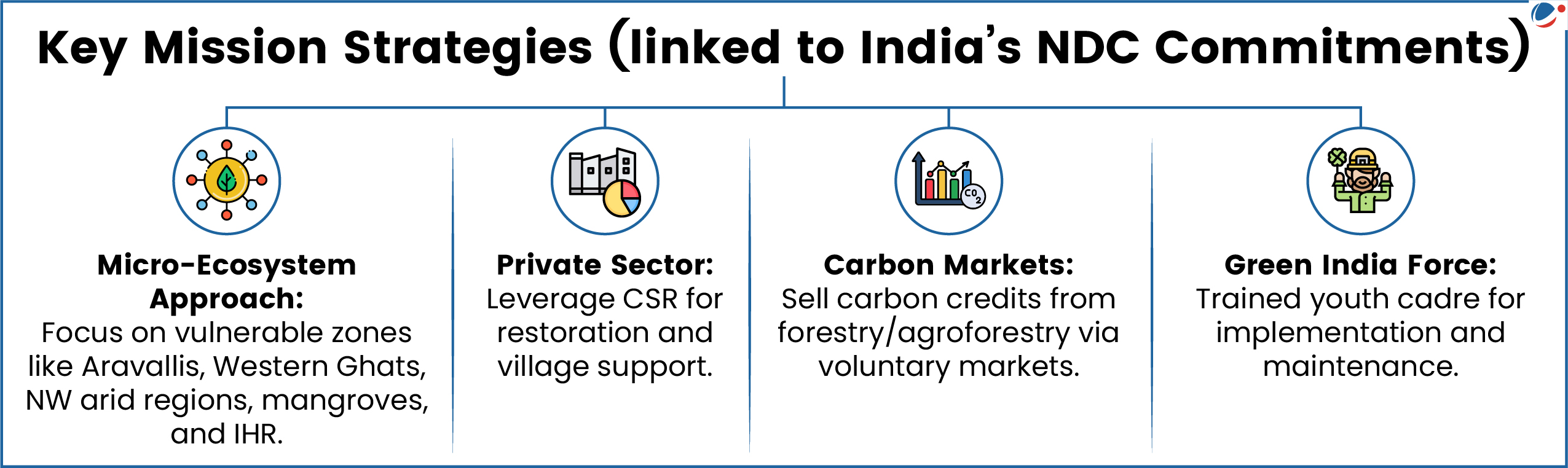
- Genesis: Launched in 2011. It is one of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
- Objectives:
- Increase forest and tree cover on forest/non- forest lands (Afforestation over 24 million hectares will be taken up)
- Improve ecosystem services including carbon sequestration
- Creation of an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3.0 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent by 2030, etc.
- Three Sub-Missions
- Improve forest quality and ecosystem services
- Increase forest/tree cover and restore ecosystems
- Enhance and diversify incomes of forest-dependent communities.
- Funding: Part of the funding will come from Mission’s allocation and the rest from the National CAMPA (Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority) Fund.
- Timeline: 10 years (2021-2030)
- Implementation: Follows a bottom-up model with Joint Forest Management Committees (JFMCs) as key implementers.
The report has been released by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Key findings
- Increase in severity: 40% of the world’s land area faces increasingly frequent and severe droughts.
- Some of the recent examples of major droughts include Europe (2022), California (2021), Horn of Africa & Somalia, etc.
- Economic impact: 3% - 7.5% annual increase in the economic cost of an average drought episode.
- Countries like India, Australia, etc. may face water-related disruptions in the operations of hydroelectric power stations.
- Inland water transport is impacted (E.g. recent drought in panama canal).
- Crop yields can decline by up to 22%.
- Ecological:
- Reduction in soil moisture: Since 1980, 37% of global land has experienced significant soil moisture decline.
- Groundwater decline: Groundwater levels are falling globally, with 62% of monitored aquifers in decline.
- Other:
- Droughtsare responsible for 34% of disaster-related deaths (World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 2021) and exacerbate poverty, inequality and displacement.
Article Sources
1 sourceA study done by researchers from a UK University found that 21% of the global ocean had become darker between 2003 and 2022, especially in the Arctic, Antarctic, and Gulf Stream region.
What is the Darkening of the Ocean?
- It refers to a reduction in light penetration into the global oceans, shrinking the photic zone.
- The photic zone is the sunlit layer (about 200 meters in depth) where most marine life (nearly 90%) thrives.
- As per the study, the current darkening of the oceans could be due to ecological shifts, potentially driven by phytoplankton and zooplankton blooms.
Reasons behind darkening of the Ocean
- In Coastal Oceans: Combination of nutrient, organic material and sediment loading near the coasts, caused by factors such as agricultural runoff and increased rainfall.
- In Open Oceans: Driven by warming of the surface oceans (leading to algal bloom) and climate-driven changes in the ocean circulation patterns.
Impact of the Ocean Darkening
- Marine ecology and productivity: Ocean darkening limits light-dependent processes such as growth, communication, reproduction, photosynthesis, etc., thus, limiting ocean productivity.
- Fisheries industry: Fish stocks decline due to habitat compression and disrupted reproductive cycles.
- Regulation of climate: hampers carbon absorption and oxygen production, affecting climate regulation.
Brazil and France Launch launched the Blue NDC Challenge.
- An inaugural group of eight countries – Australia, Fiji, Kenya, Mexico, Palau, and Seychelles – has already joined the initiative.
About Blue NDC Challenge
- It calls on all countries to place the ocean at the heart of their NDCs ahead of COP30.
- Supported by: Ocean Conservancy, the Ocean & Climate Platform, and the World Resources Institute through the Ocean Resilience and Climate Alliance (ORCA).
Role played by Ocean in addressing the climate crisis
- Carbon Dioxide Absorption: The ocean absorbs approximately 30% of global carbon dioxide emissions, acting as a significant carbon sink.
- Coastal habitats like mangroves and seagrasses sequester carbon at rates up to four times higher than terrestrial forests
- Heat Regulation: It captures about 90% of the excess heat generated by greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Energy: Offshore wind energy has the potential to meet over one-third of global electricity needs.

The third United Nations Ocean Conference (UNOC3) concluded with the adoption of the Nice Ocean Action Plan.
- UNOC3 was held in Nice, France.
- It was co-hosted by France and Costa Rica.
Key Highlights of Action Plan
- A global roadmap adopted to support the achievement of SDG 14, focused on conserving and sustainably using oceans, seas, and marine resources.
- Declaration recognized that SDG 14 is the least funded of all SDGs.
- Reaffirms commitment to develop an international legally binding instrument on plastic pollution.
- Called for coordinated global action to reduce climate and acidification impacts on oceans and coastal communities reliant on them.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has updated the guidelines on ‘Waste to Energy’ and ‘Biomass’ components of the National Bioenergy Programme.
- Bioenergy: It is a form of renewable energy generated when we burn biomass fuel which comes from organic material such as harvest residues, crops and organic waste from our homes, etc.
What is the National Bioenergy Programme?
- Launched: In 2022
- Implementation: Two phases with a total budget of Rs. 1715 Crore; Phase-1 (2021-22 to 2025-26).
- Objective: Utilize surplus biomass (primarily from rural areas) for power generation, while providing additional income for rural households.
- Central Financial Assistance (CFA): To be provided to project developers based on various aspects of projects.
- For special categories like the North East Region, hilly states, SC/ST beneficiaries, etc., 20% more CFA will be provided.
- There are 3 components of the programme
- Waste to Energy Programme: Support projects for generating Biogas, BioCNG, Power, or Syngas from urban, industrial, and agricultural waste/residues.
- Biomass Programme: Support Biomass Briquette/Pellet manufacturing plants and Biomass (non-bagasse) based cogeneration projects.
- Biogas Programme: Support biogas plants for clean cooking fuel, small power needs, improved sanitation, women empowerment, etc.
- Biogas is 95% methane (CH₄) and CO₂, with traces of N₂, H₂, H₂S, and O₂
Key Features of Revised Guidelines | |
Waste to Energy Programme
| Biomass Programme
|
Article Sources
1 sourceWorld Economic Forum (WEF) recently released Energy Transition Index (ETI), 2025.
Key Findings
- Sweden ranked first followed by Finland, Denmark and Norway
- India’s rank dropped from rank 63 in 2024 to rank 71 in 2025.
About ETI
- It ranks countries on their progress towards energy transition from fossil fuels to clean energy.
- It takes into account two main aspects to put together the Index:
- System Performance (energy security, equity & sustainability)
- Transition Readiness (regulation, infrastructure, investment etc.)
- The Index uses 43 indicators under these broad categories using data from multiple sources and scores countries on a scale of 0 to 100.





