Why in the News?
ECOWAS marked its 50th anniversary this year.
About ECOWAS
- Established: Established on 28 May 1975 by 15 West African countries through the Treaty of Lagos.
- Headquarter: Abuja, Nigeria.
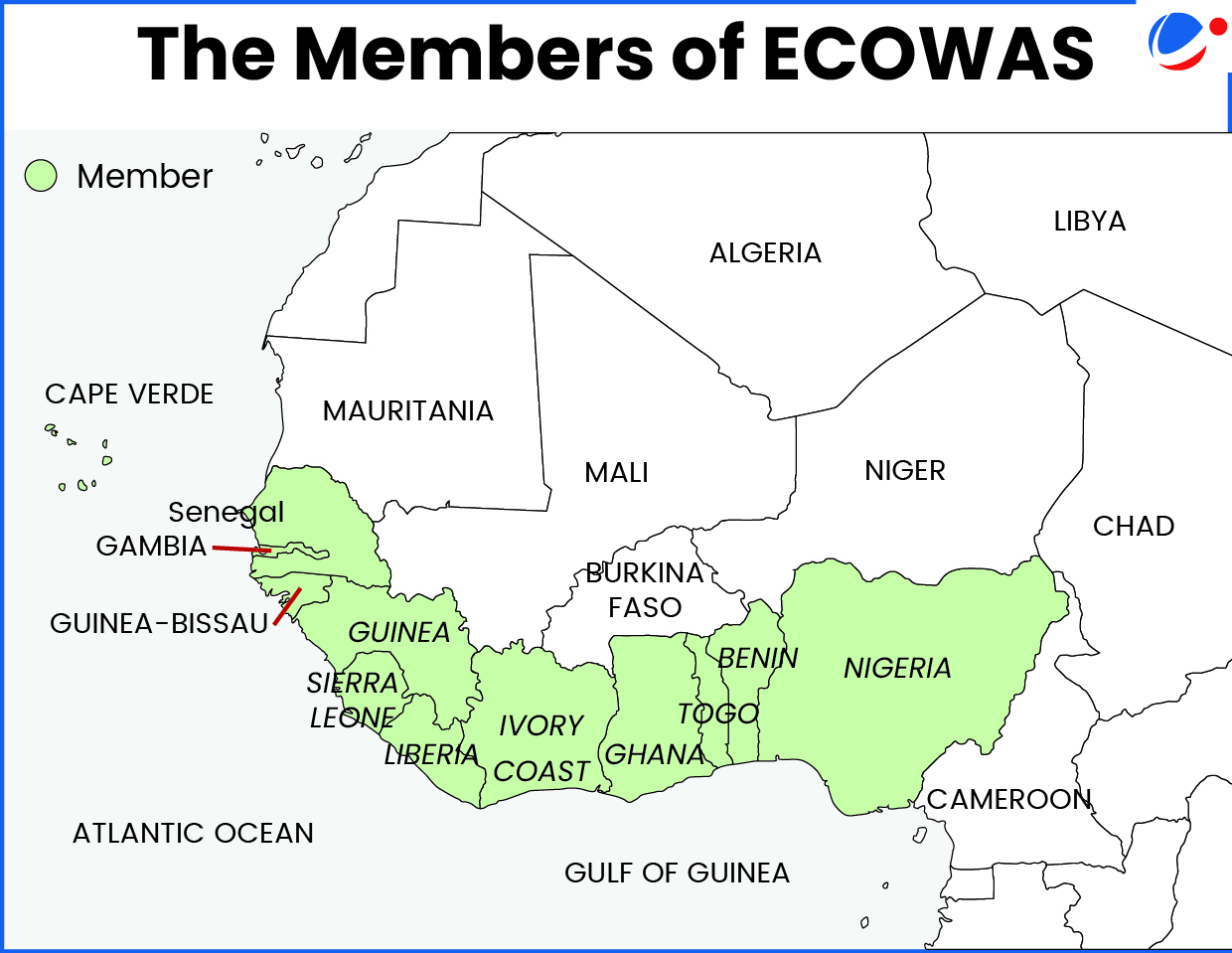
- Regional Bloc: ECOWAS comprises 12 West African countries (June 2025).
- Its member countries include Benin, Cabo Verde, Côte d'Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
- Aim: To promote cooperation and integration for an economic union in West Africa, improving living standards, ensuring economic stability, strengthening member relations, and contributing to Africa's development.
- ECOWAS established its free trade area in 1990 and adopted a common external tariff in January 2015.
India–ECOWAS Relations
- Diplomatic Relations: India became an Observer to ECOWAS in 2004.
- ECOWAS supports India's bid for permanent UN Security Council membership.
- South–South Cooperation: India supports regional development of western Africa. E.g. MoU between ECOWAS Centre for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency and India's International Solar Alliance (ISA) for renewable energy cooperation.
- Economic Cooperation: In 2006, India gave the grouping a line of credit (LoC) worth USD 250 million to supplement Focus Africa Programme.
- India launched an integrated programme 'Focus Africa' from the year 2002-03 to increase interactions between India and Africa by identifying the areas of bilateral trade and investment.
Conclusion
As ECOWAS enters its sixth decade, it stands at a historic crossroads. While its legacy of integration, peacekeeping, and human development is commendable, internal fragmentation, political instability, and citizen disconnect threaten its future relevance.




