Why in the News?
Recently, two reports highlighting India's approach to AI and employment were released by NITI Aayog.
About The NITI Aayog Reports
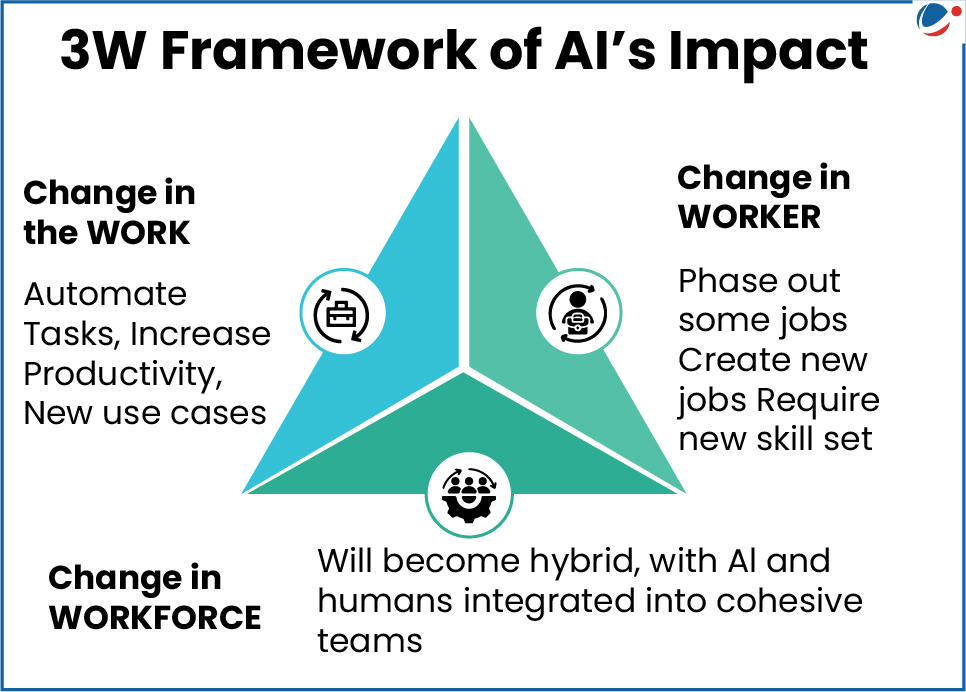
- "Roadmap for Job Creation in the AI Economy": This report outlines India's strategic plan to navigate AI disruption and position itself as the global AI workforce capital. It highlights the 3W framework for AI and the associated impact (refer infographics).
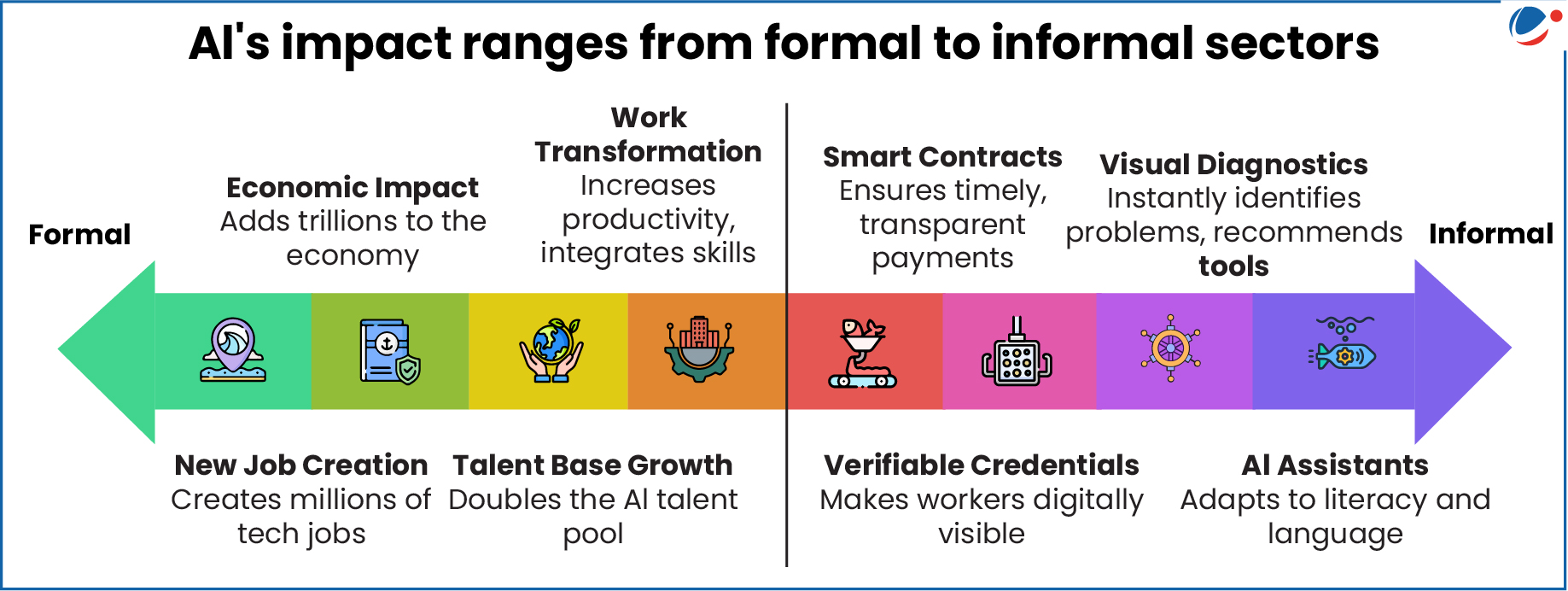
- "Roadmap on AI for Inclusive Societal Development": This report aims to leverage frontier technologies to transform informal workers into a formal, empowered, future-ready labour force.
- AI presents a challenge and opportunity for the Indian economy: It is disrupting established formal jobs while offering an unparalleled pathway to formalize and boost the productivity of the vast informal workforce.
- On similar lines, the Nobel Economic Prize 2025 has been awarded for explaining innovation-driven economic growth, particularly the theory of sustained growth through creative destruction.
- This concept highlights that new technology like AI is creative (innovation) but also destructive (companies/older technologies become outcompeted).
- On similar lines, the Nobel Economic Prize 2025 has been awarded for explaining innovation-driven economic growth, particularly the theory of sustained growth through creative destruction.
AI related risks in India
Operational Risks
- High Job Displacement Risk: Over 60% of formal sector jobs in India are susceptible to automation by 2030, particularly within the IT and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) sectors.
- The report highlights that a "business-as-usual approach" risks irreversible job losses and shrinkage in competitiveness and societal disruption.
- Talent Migration: India has a net negative talent migration for AI professionals (-1.55 per 10,000), risking the loss of highly skilled professionals abroad.
Structural Risks
- Education and Skill Gaps:
- Curriculum: Indian curricula often lag, focusing less on specialized, research-intensive courses compared to global peers.
- Furthermore, computer science education is unevenly offered, unlike in countries like China and Russia where it is mandatory at primary/secondary levels.
- Lagging Research Output: India lags significantly in AI publication citations and its share of granted AI patents fell from 8–10% in 2010 to under 5% in 2023.
- Critical Talent Supply-Demand Gap: The supply of AI talent currently meets only 50% of the existing demand, and this gap is expected to widen, despite growing demand.
- Limited access to informal workers: This is a systemic barrier characterized by the absence of verifiable identities, contracts, and work histories, limiting access to secure jobs and financial services.
- Systemic Access and Usability Gaps: Digital Public Infrastructure remains underutilized due to low digital literacy, linguistic challenges, and complex interfaces that are difficult to navigate.
- Curriculum: Indian curricula often lag, focusing less on specialized, research-intensive courses compared to global peers.
Recommendations
- To establish National AI Talent Mission: As recommended by NITI Aayog, the mission will focus on making AI literacy a foundational skill across schools and universities.
- Key features:
- Building India as a Global AI Talent Magnet to retain domestic talent and attract international experts with AI Talent Visa for fast-track residency.
- Building a national reskilling engine to upskill and reskill millions of professionals for higher-value, AI-augmented roles.
- To establish Mission Digital ShramSetu: To empower informal workers with access and skills in the digital age by harnessing frontier technologies such as AI, blockchain, and immersive learning to enable inclusion at an unprecedented scale.
Conclusion
India stands at a critical juncture where the threat of AI disruption is real, potentially leading to irreversible job losses in the absence of action. By executing a unified, urgent, and mission-driven response through the implementation of the National AI Talent Mission and the Mission Digital ShramSetu, India can proactively capitalize on the tailwinds of new AI roles to emerge as a global AI leader.







