PM laid the foundation of the Mahi Banswara Rajasthan Atomic Power Project (MBRAPP).
- Location: Banswara, Rajasthan near the Mahi Dam on River Mahi.
- Capacity: 4 x 700 MWe PHWR (4 nuclear power units of Indigenous PHWRs (Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors)).
- It will be developed by Anushakti Vidhyut Nigam (ASHVINI), a joint venture between Nuclear Power Corporation India Limited (NPCIL) and National Thermal Power Corporation Limited (NTPC).
- The project is part of India’s “fleet mode” initiative.
- Under this Initiative, ten identical 700 MW reactors are being built across India under uniform design and procurement plans.
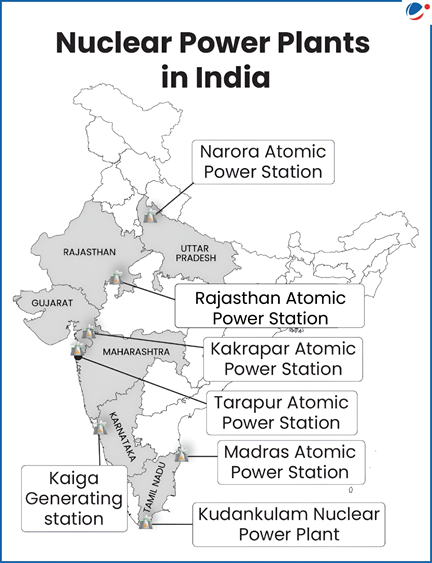
Nuclear Power Capacity in India
- India currently has 24 reactors across 7 power plants with installed nuclear energy capacity of 8180 MW (January 30, 2025).
- The government plans to increase this to 22,480 MW by 2031-32.
- Nuclear power accounts for 3.61% of India’s total electricity generation in 2022-23, making it fifth-largest Non-fossil fuel source of electricity.
- India is currently in the 1st stage of its three-stage Nuclear Power Programme (NPP).
- The 1st Stage is based on uranium fuelled PHWRs.
- The 2nd Stage and 3rd stage are based on Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs) utilising plutonium-based fuel and Thorium, respectively.
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia’s first fully indigenous 4G (5G-ready) network has been deployed by BSNL and developed through collaboration between C-DOT, Tejas and TCS.
- This provides India the capability to quickly develop technologies for fast tracking adoption of 5G and laying foundation for 6G.
Significance of indigenous 4G Stack
- Strategic Autonomy: Empowers India to control its telecom infrastructure, therefore reducing dependency on foreign technologies and foreign vendors, and enhancing national security.
- Cloud native: Enables rapid upgrades, scalability and easier future migration path to 5G.
- Improving Accessibility: Expected to benefit tribal regions, remote villages, and hilly areas by providing access to quality digital services.
- Supply Chain Development: Localised manufacturing and deployment are creating employment, strengthening supplier ecosystems, and nurturing a skilled domestic workforce.
- Technological Capability: With this, India is now among the select five nations globally with the capability to launch fully indigenous 4G services.
Article Sources
1 sourceIt was approved by the Executive Council of the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) ensuring seamless scheme execution, effective private sector participation and long term innovation.
- ANRF was established with Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) Act, 2023.
- It acts as an apex body to provide high-level strategic direction of scientific research.
- Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) established by 2008 Act has been subsumed into ANRF.
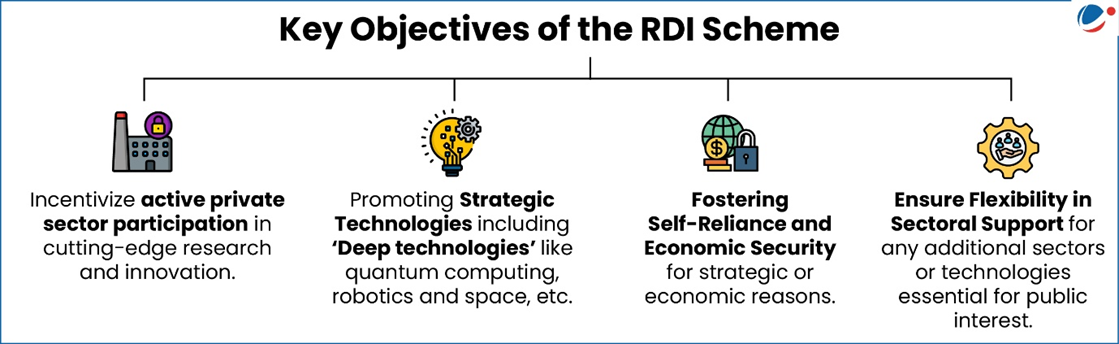
RDI Scheme
- About: Establishes ₹1 Lakh crore RDI Fund approved by the Union Cabinet on July 1, 2025.
- Nodal Department: Department of Science & Technology (DST)
- Funding Structure: Two Tiered
- Special Purpose Fund (SPF): Being set up under the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) to serve as the first-level custodian.
- Second-Level Fund Managers (SLFMs): Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs), Development Finance Institutions (DFIs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), or Focused Research Organizations (FROs) like Technology Development Board (TDB), Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), IIT Research Parks, etc.
- Exclusions: Grants and short-term loans are not supported.
- Coverage: Financing can cover up to 50% of assessed project cost for transformative RDI projects at Technology Readiness Levels (TRLs) 4 and above.