Vaccine, developed by scientists at University of Florida, in its first-ever human clinical trial quickly reprogrammed the immune system to glioblastoma, most aggressive and lethal brain tumor.
- Treatment of brain cancers are challenging due to poor chemotherapy response, debilitating side effects from radiotherapy and surgery.
About mRNA Vaccines
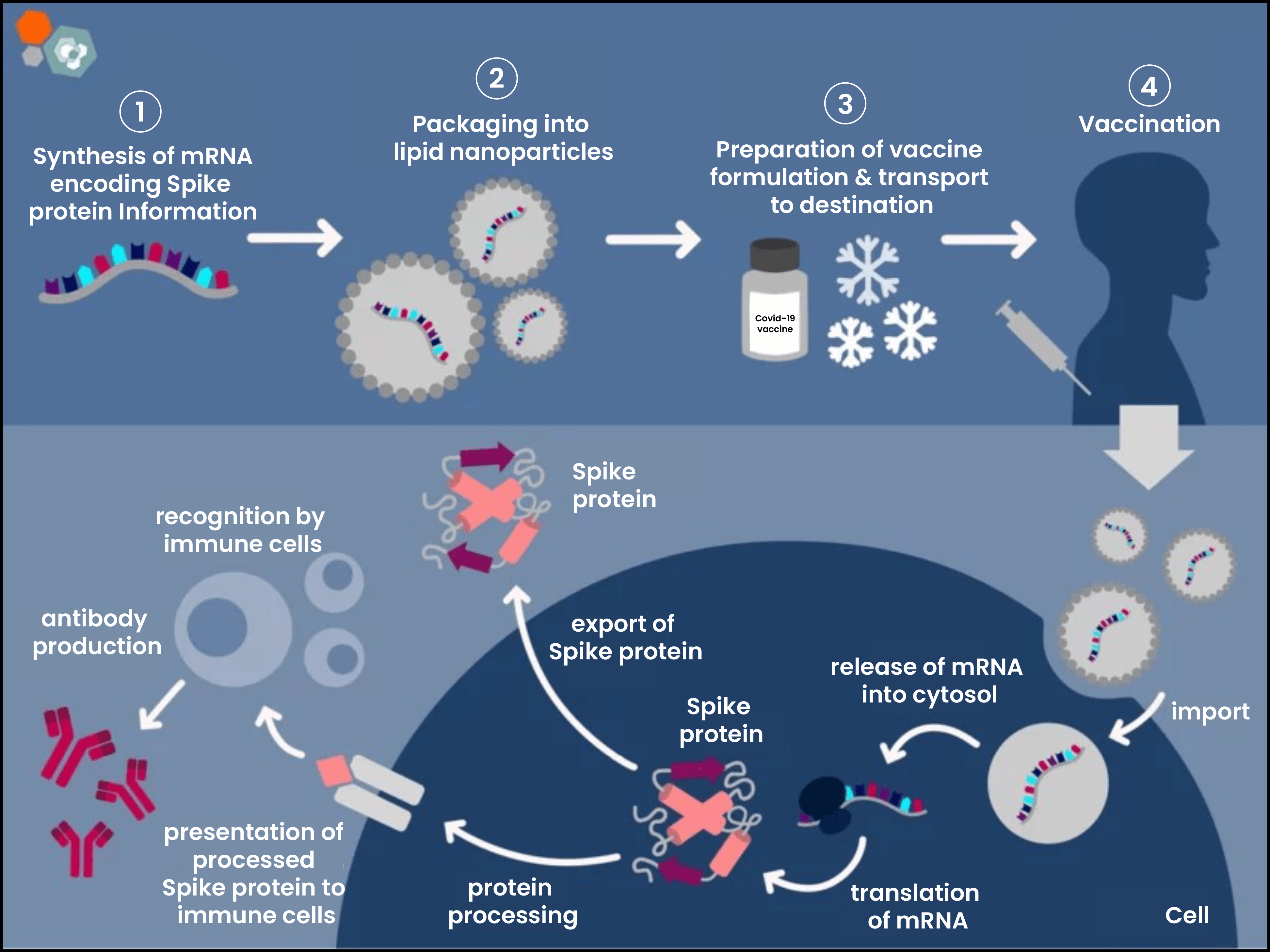
- mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) is a genetic molecule that contains instructions or recipe that directs cells to make a protein using its natural machinery.
- It delivers genetic material, encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles, into body to prompt protein production that match up with parts of pathogen called antigens.
- Immune system sees these foreign antigens as invaders—dispatching defenders called antibodies and T-cells—and training immune system for potential future attacks.
Other Vaccine Technologies
- Live-attenuated vaccines: Contain weakened live pathogens from bacteria or viruses. e.g., the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) Vaccine.
- Inactivated vaccines: Uses deactivate live pathogens, creating immunity without causing disease. e.g., Polio vaccines.
- Viral vector vaccines: Uses a harmless virus to deliver genetic code to host cells. e.g., Ebola vaccine.
- Subunit vaccines: Made from a pathogen piece, excluding live pathogens, and can be produced from the original pathogen or recombinantly. e.g., Pneumococcal vaccines.




