This initiative aims to revolutionize the coal industry by using in-situ coal gasification.
About Coal Gasification
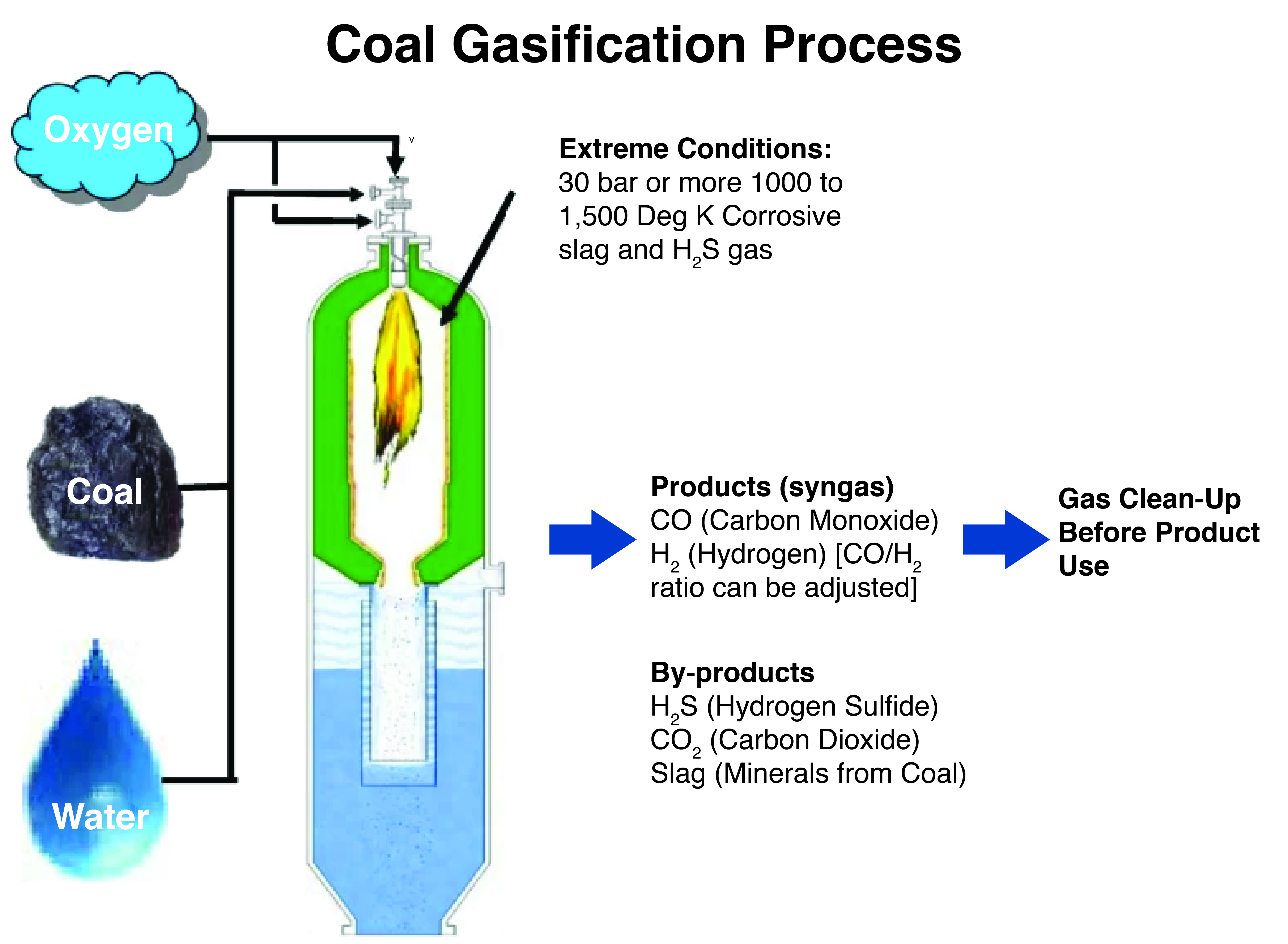
- It is a process to convert underground coal into valuable gasses like methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide (CO), and carbon dioxide (CO2).
- In gasification process, coal is partially oxidised by air, oxygen, steam, or CO2 under controlled conditions to produce a liquid fuel known as syngas.
- Syngas (synthesis gas) can be used for power generation, making methanol etc.
- Syngas is a mixture of CO and hydrogen and produce gaseous fuels like Methane etc.
Advantages of Coal Gasification
- Provide access to coal resources that are economically unviable through traditional mining methods.
- Sustainable and efficient use of India’s huge coal reserves (third largest in world).
- India is highly dependent on imported fuel – crude oil and natural gas, 82% and 45% of total requirement.
Associated concerns
- Lack of technology for conversion of India's coal (low grade and high ash content) to syngas.
- Huge quantity of waste, black water generation, costly systems for CO2 removal etc.
- Produces more CO2 than conventional coal-powered thermal power plant.
Initiatives taken
- Under National Coal Gasification Mission, India aims for 100 million tons coal gasification by 2030.
- 100% FDI in coal mining.
- Viability Gap Funding scheme for promotion of Coal/Lignite Gasification Projects.





