Previously known as the Rural Health Statistics, the report provides comprehensive annual data on health infrastructure and human resources.
Key finding
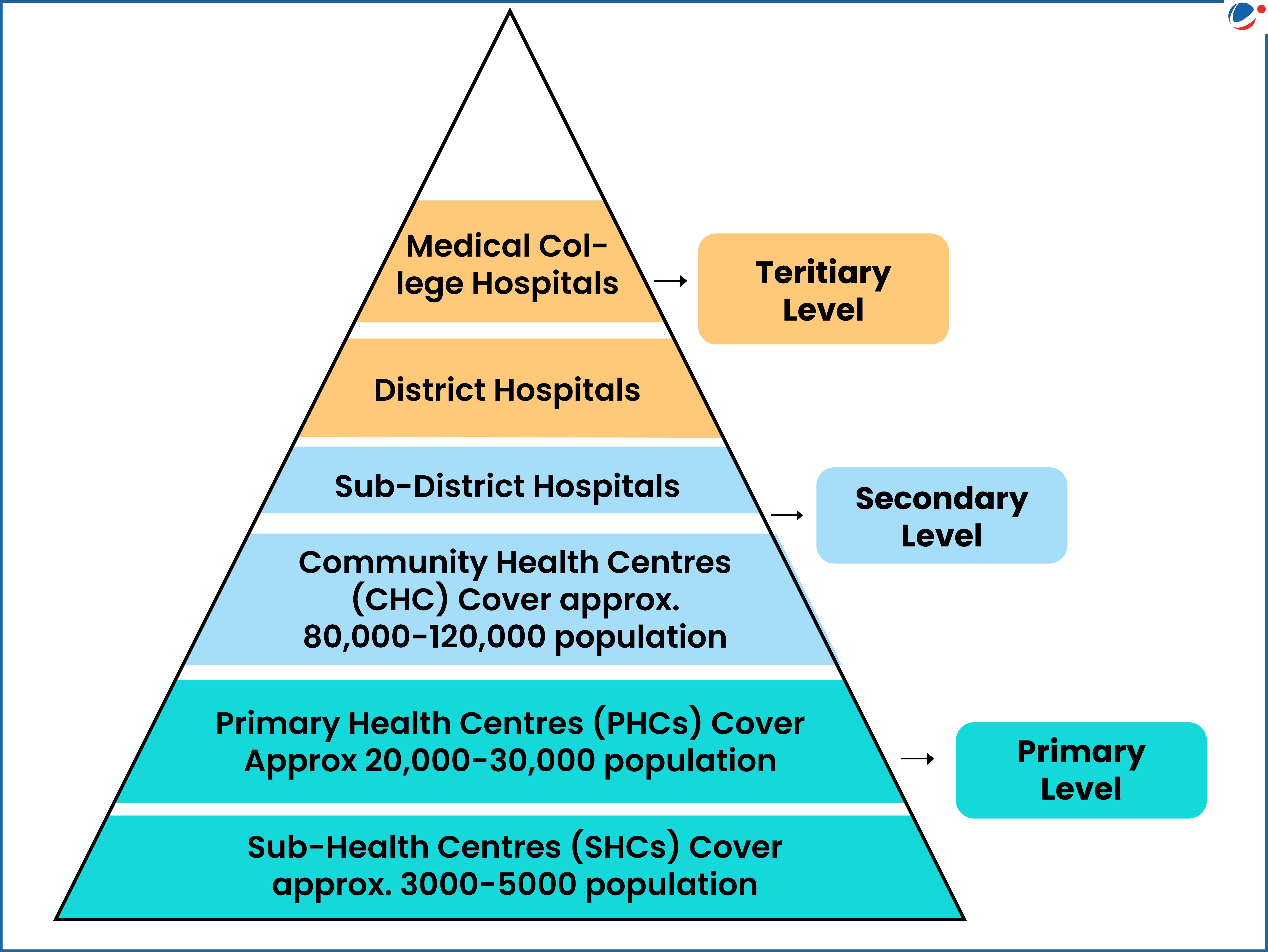
- There are 714 district hospitals, and 362 medical colleges in India.
- Rural
- Rise in health facilities: Between 2005 to 2023, number of SCs, PHCs, and CHCs, has increased.
- More PHCs in rural areas: Around 32,000 PHCs are functioning around the country of which around 25000 PHCs are in rural areas.
- Shortage of doctors: Between 2005 to 2023, availability of doctors and medical officers in PHCs has increased from around 20,000 (2005) to around 32,000 (2023).
- However, vacancy has also more than doubled in the same period.
- Infrastructure gap: Most of the SCs in Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh among others are running in rented buildings.
- Urban
- Inter-State disparity in availability of services: There is a shortfall of around 36% of U-PHCs (Urban PHCs) as per the urban population norms.
- However, U-PHCs exist above the required normas in Andhra Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Andaman & Nicobar Island, Chandigarh and Delhi.
- Infrastructure gap: Most of the U-PHCs in Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Karnatak, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Praadesh, among others are functioning in rented buildings.
- Inter-State disparity in availability of services: There is a shortfall of around 36% of U-PHCs (Urban PHCs) as per the urban population norms.
 About India’s Public healthcare system
|





