WTO was established in 1995 after the Marrakesh Agreement following the Uruguay round negotiation (1986-94) of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
- It succeeded the GATT which had regulated world trade since 1948.
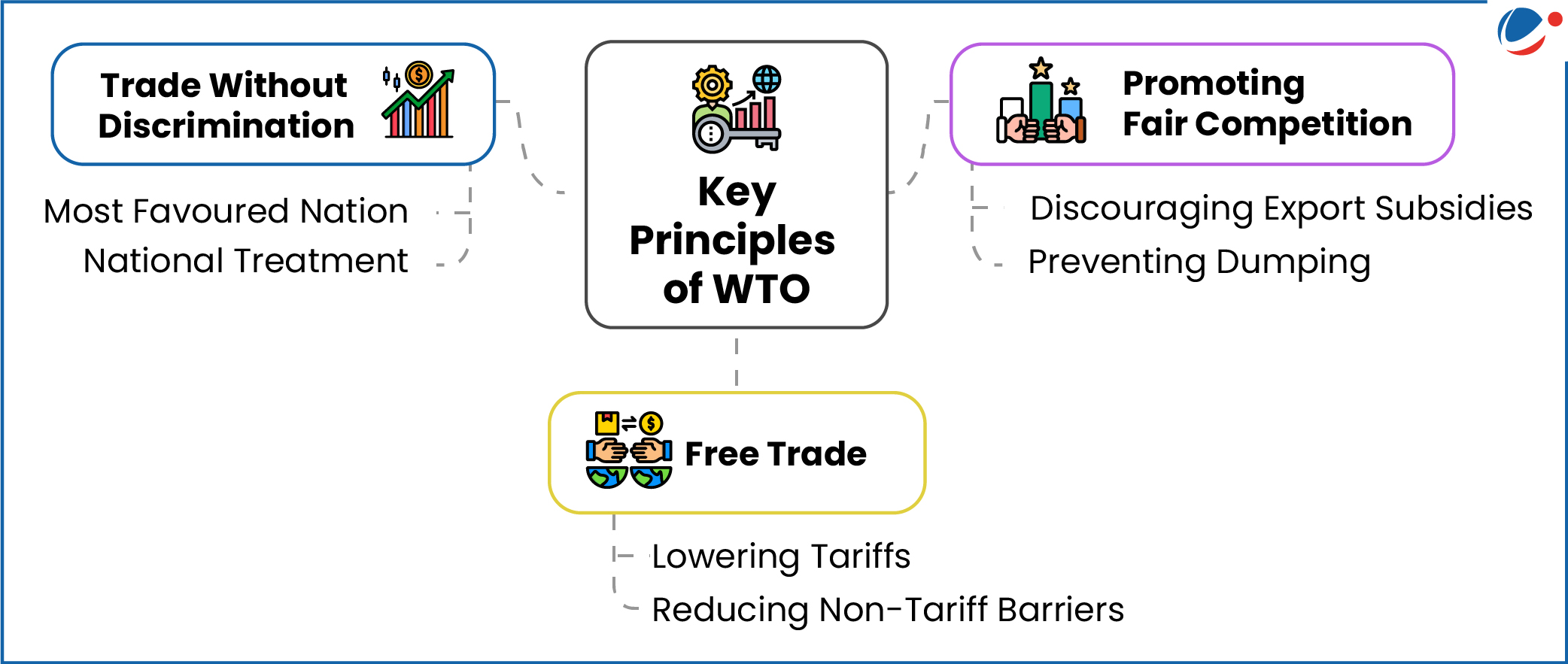
About WTO
- It is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations.
- The goal of WTO is to ensure that trade flows as smoothly, predictably and freely as possible.
- Key Institutional Mechanism
- Ministerial Conference (MC) is highest decision-making body
- Dispute Settlement Body (DSB)
- Members: 166 members representing 98 per cent of world trade
- HQ: Geneva, Switzerland
Key Agreements of WTO
- The Agreement on Trade-Related Investment Measures (TRIMS): Members may not apply any measure that discriminates against foreign products or that leads to quantitative restrictions under WTO principles. E.g., local content requirements.
- Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS): Plays a critical role in resolving trade disputes over intellectual property.
- Agreement on Agriculture (AoA): Focuses on agricultural trade liberalization, Addresses market access and domestic support for agricultural producers.
- Other:
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS)
- General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)