The Order prohibits issuance, circulation, & use of US CBDC, also known as ‘Digital Dollar’, within the jurisdiction of USA.
About CBDC
- Definition: CBDC is the electronic version of the nation’s sovereign currency and is issued by respective country's central bank.
- Unlike cryptocurrencies which is decentralised in nature.
- Types of CBDC
- Wholesale CBDCs: Used by financial institutions & market participants for large-scale transactions, such as interbank transfers, securities settlements etc.
- Retail CBDCs: Used by retail consumers, public & business for making daily transactions. These are of 2 types:
- Token-based: Accessed using private & public keys, allowing for anonymous transactions.
- Account-based: Requires digital identification for users to access & use their accounts.
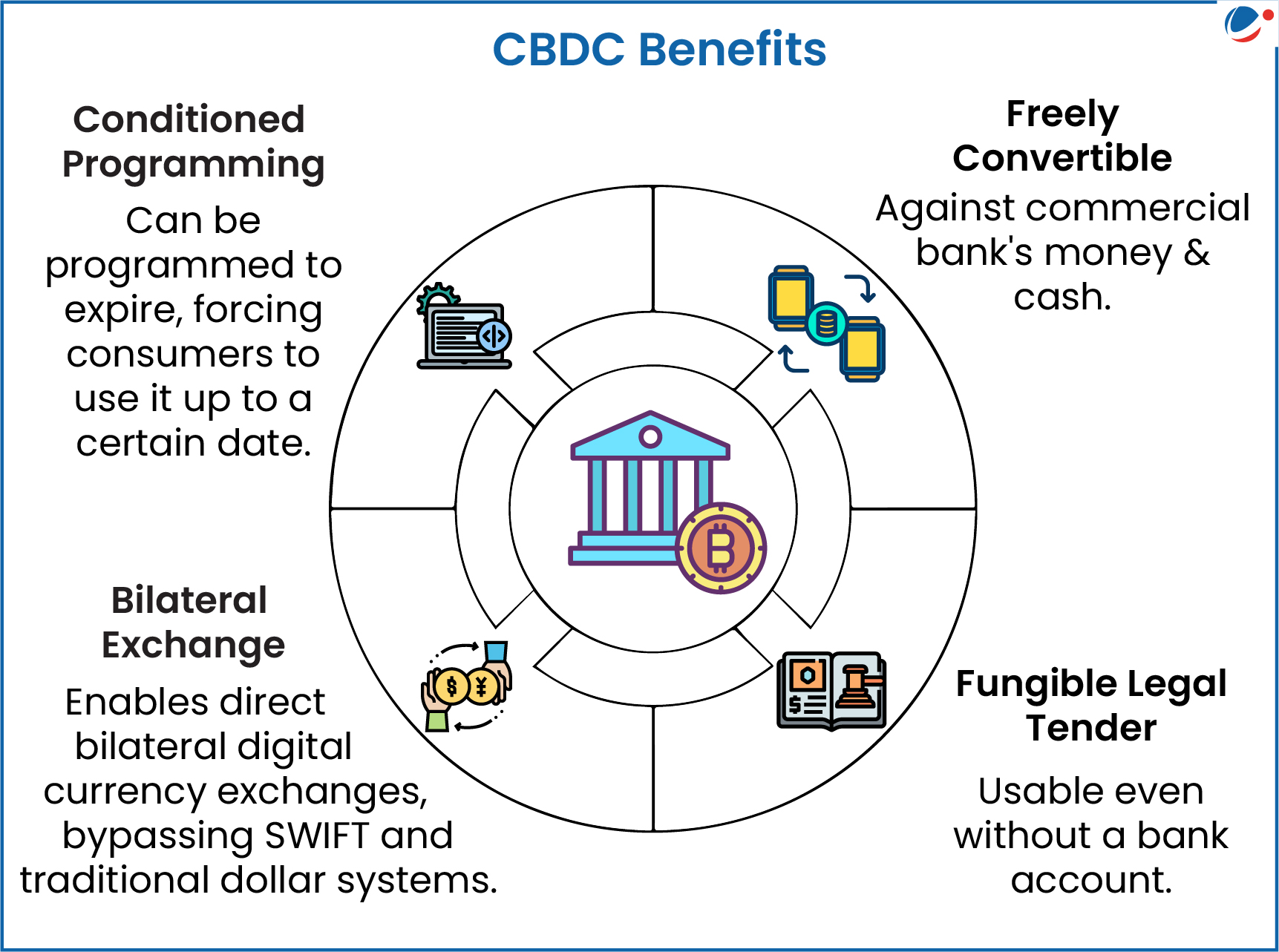
- Features of CBDC
- Must be accepted as a medium of payment, legal tender, and a safe store of value by all citizens, enterprises, and government agencies.
- Convenience of use: Expected to lower the cost of issuance of money and transactions
- Difference with existing money: It is the liability of the central bank (RBI), and not of a commercial bank.
Issues with CBDCs: Threatens financial system stability; compromises individual privacy & protection, cyber security challenges etc.
CBDC initiative in India - RBI’s e-Rupee (e₹)
|





