Study scrutinized data from 121 repeating earthquakes recorded between 1991 and 2024 near Antarctica’s South Sandwich Islands to come to this conclusion.
Key findings of Study
- Near surface of earth’s inner core is not as rigid as previously assumed.
- Changes in solid inner core are being caused by interactions with turbulent-molten outer core.
- Possibly affecting its rotation & altering day-length.
- Earth’s inner core’s independent spin appears to be slowing.
- Previously it was believed that it rotated independently due to interactions with mantle.
- Significance of finding: Challenges previous assumptions that structural changes in inner core occur only over geological timescales.
About Earth’s inner core
- About: Innermost solid layer of earth due to pressure caused by Earth’s other top layers.
- Composition: Composed primarily of iron & nickel.
- Radius: Approx. 1,220 kilometers.
- Temperature: ~ 5,200° C.
- Properties: High thermal and electrical conductivity; Help generate Earth’s magnetic field etc.
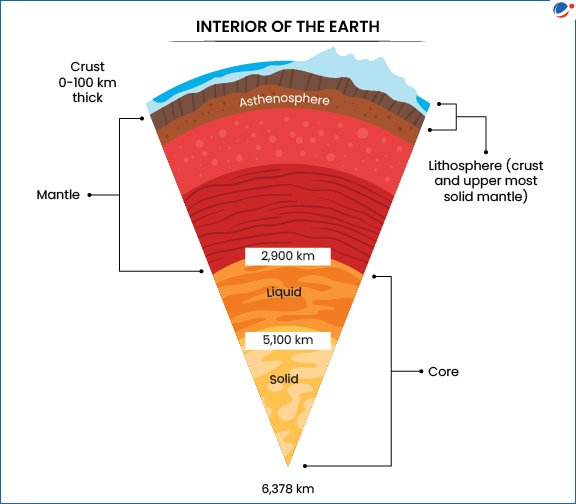
Layers of earth
- Based on Chemical Composition:
- Crust: Outermost layer of earth made of solid rock, mostly basalt & granite.
- Mantle: Lies between crust & core, consisting of hot, dense, iron and magnesium-rich solid rock.
- Core: Inner most layer, comprising of liquid outer core & solid inner core.
- Based on Physical/Mechanical Properties:
- Lithosphere: Outermost physical layer of the Earth
- Asthenosphere: Portion of the Earth's mantle that flows like molten plastic despite being solid.



