Scientists have warned that ACC might slow down by around 20 per cent by 2050 in the high carbon emissions scenario.
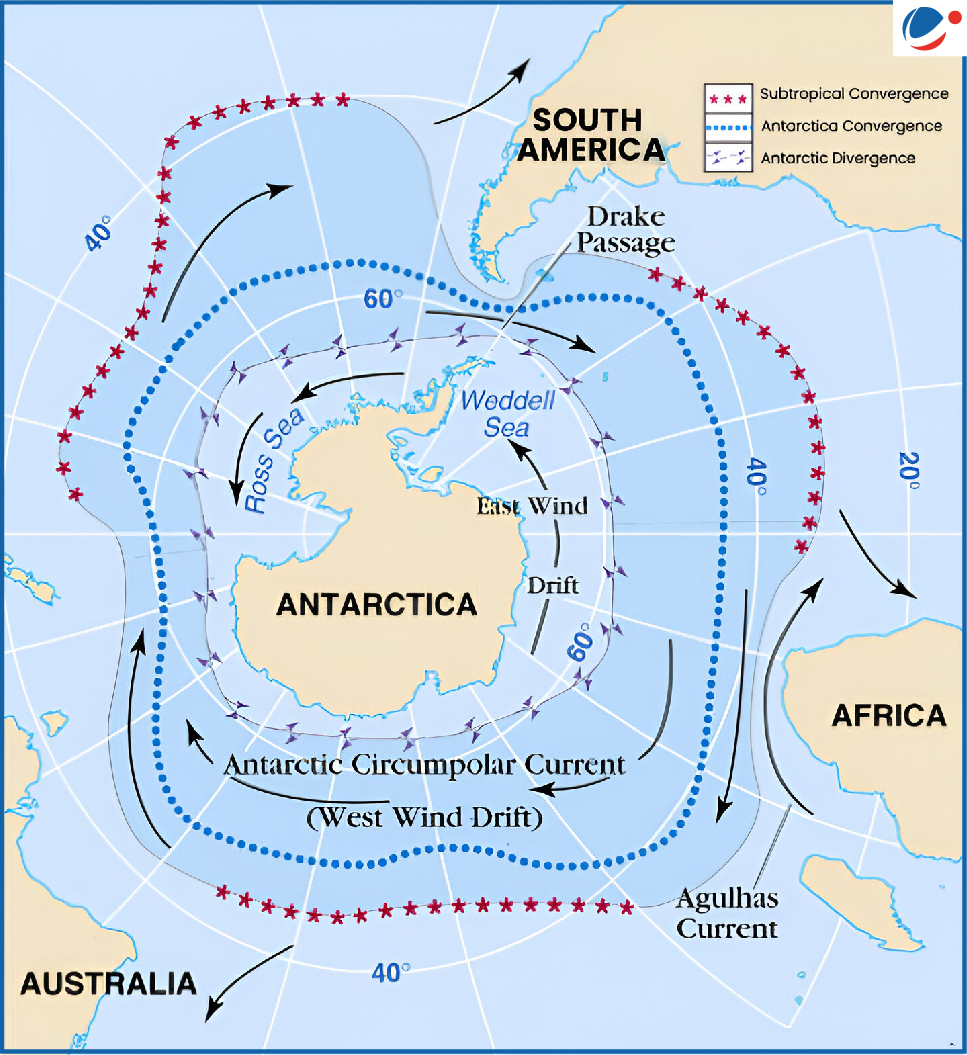
What is ACC?
- ACC is the strongest and the largest wind-driven current on Earth and moves clockwise around Antarctica, driven by strong westerly winds.
- It is the only current that goes all the way around the planet and connects the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
- Significance:
- It’s a type of cold current that acts as a barrier and prevents warmer waters from reaching Antarctica.
- Significantly influences uptake of heat and carbon dioxide in the ocean.
- Blocks invasive species (e.g., bull kelp, shrimp, mollusks) from other continents reaching Antarctica.
Reasons for weakening of ACC
- Changes in Ocean Salinity: Due to accelerated melting of ice shelves (from global warming) around Antarctica has resulted in weakening of Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW).
- AABW is a sinking process and a critical component of global ocean circulation tied to circulation of ACC.
- Changes in Wind Patterns: Climate change can alter pattern of westerly winds in Southern Hemisphere.
- Positive Feedback Loop: Reduced sea ice can exacerbate warming & freshwater input, creating a feedback loop that further weakens ACC.
Potential Impact of weakening of ACC
|



