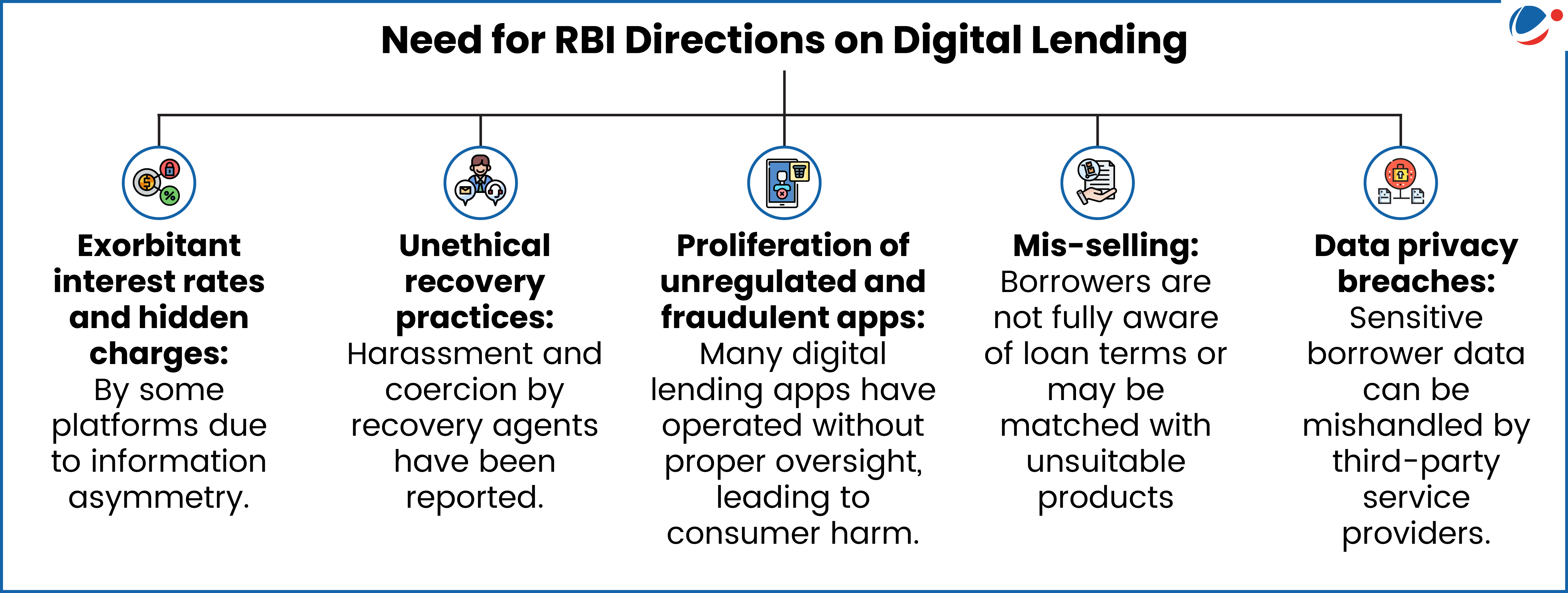
Key objectives of directions include enhancing borrower protection, ensuring data transparency, and promoting responsible Digital lending practices.
Key Highlights of the RBI Directions
- Defines digital lending as a remote and automated lending process by use of digital technologies for customer acquisition, credit assessment, loan approval, disbursement, recovery etc.
- Applies to: Commercial Banks, Primary (Urban)/State/Central Co-operative Banks, NBFCs (including Housing Finance Companies) and All-India Financial Institutions.
- Mandatory reporting of Digital Lending Apps (DLAs): via the RBI’s Centralized Information Management System (CIMS) portal to create a transparent public directory of legitimate DLAs.
- Enhanced due diligence: BY the financial entities on Lending Service Providers’ (LSPs) technical capabilities, data privacy, borrower conduct, and regulatory compliance.
- LSP is an agent of a financial entity who carries out digital lending functions on their behalf.
- Disclosures to borrowers: Financial entities and LSPs must disclose key details such as terms and conditions, privacy policies etc. allowing borrowers to make informed choices.
- Grievance redressal Officer: To be appointed by LSPs to deal with digital lending-related complaints and issues.