Introduction
- India's external sector continued to display resilience amidst global headwinds of economic and trade policy uncertainties.
Global trade dynamics
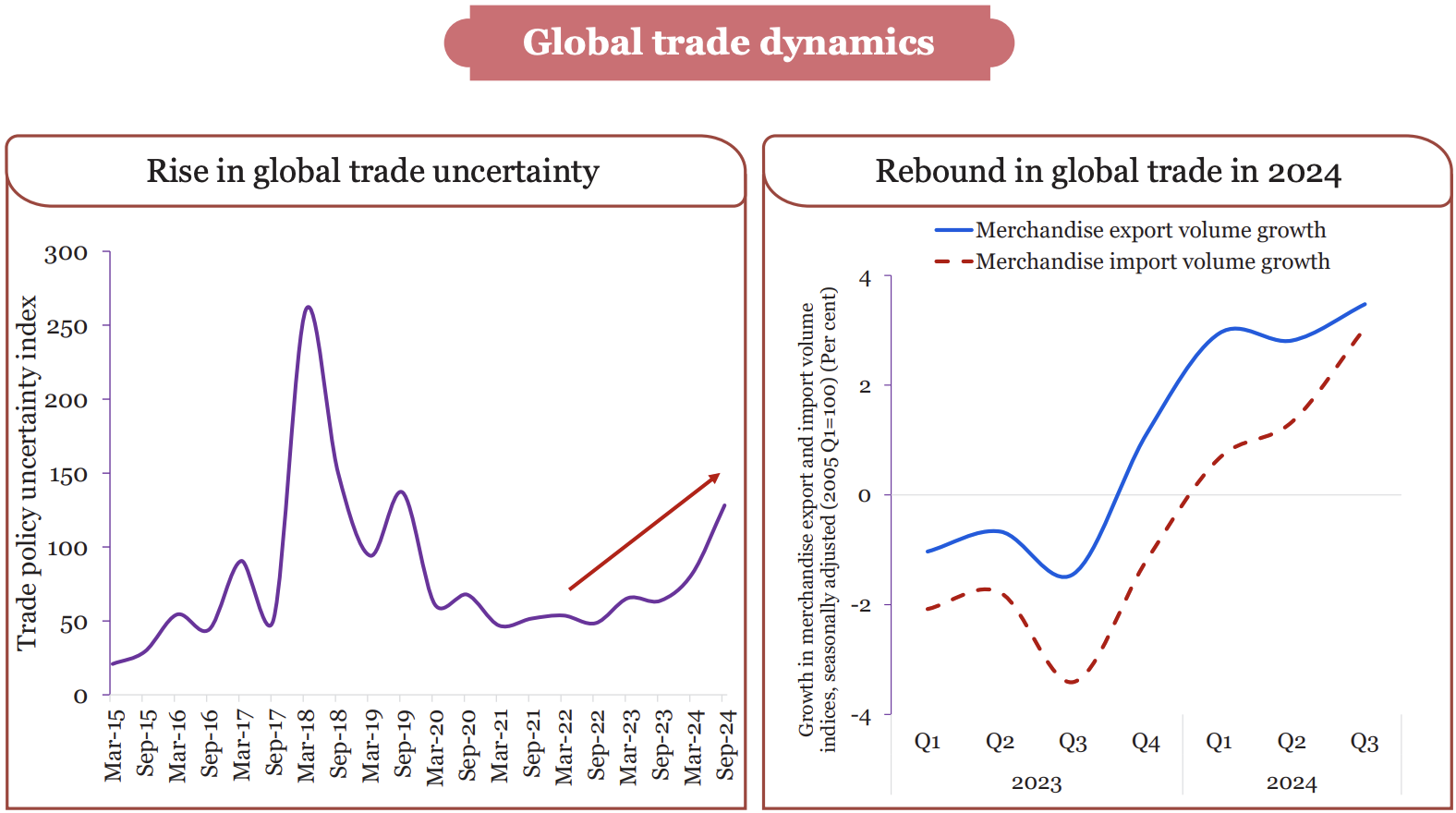
- Disruptions in the Red Sea that began in November 2023 have forced changes in trade routes, causing higher shipping costs and longer delivery times.
- Conflicts in the Hormuz Strait (which channels 21 % of global petroleum liquid consumption) have disrupted energy trade and increased prices.
- Climate change enhanced uncertainties: For instance, drought in the Panama Canal, affecting approximately 5% of global maritime trade volumes that transit through it.
- Rise in the political proximity of trade since late 2022. This indicates a preference for bilateral trade between countries.
Global trade performance in 2024
- As per World Trade Organization (WTO), a year-on-year (YoY) growth of 3.5 % (merchandise export) and 3 % (merchandise import) in Q3 of 2024 (seasonally adjusted, 2005 Q1=100).
- Global services exports and imports grew by 7.9% and 6.7 %(YoY) respectively, during the same period.
Tariff policies
- Increased emphasis on free trade and enhanced collaboration in international trade policies under the WTO has reduced border tariffs among nations.
- For instance, between 2000 and 2024, the average tariff rates on dutiable items in India decreased from 48.9% to 17.3%, while in China, they fell from 16.4 %to 8.3 %.
Non-tariff measures (NTMs)
- Global Trade Alert database shows that between 2020 and 2024, over 26,000 new restrictions related to trade and investments have been globally imposed.
- Sectors most affected by NTMs include agriculture, manufacturing, and natural resources.
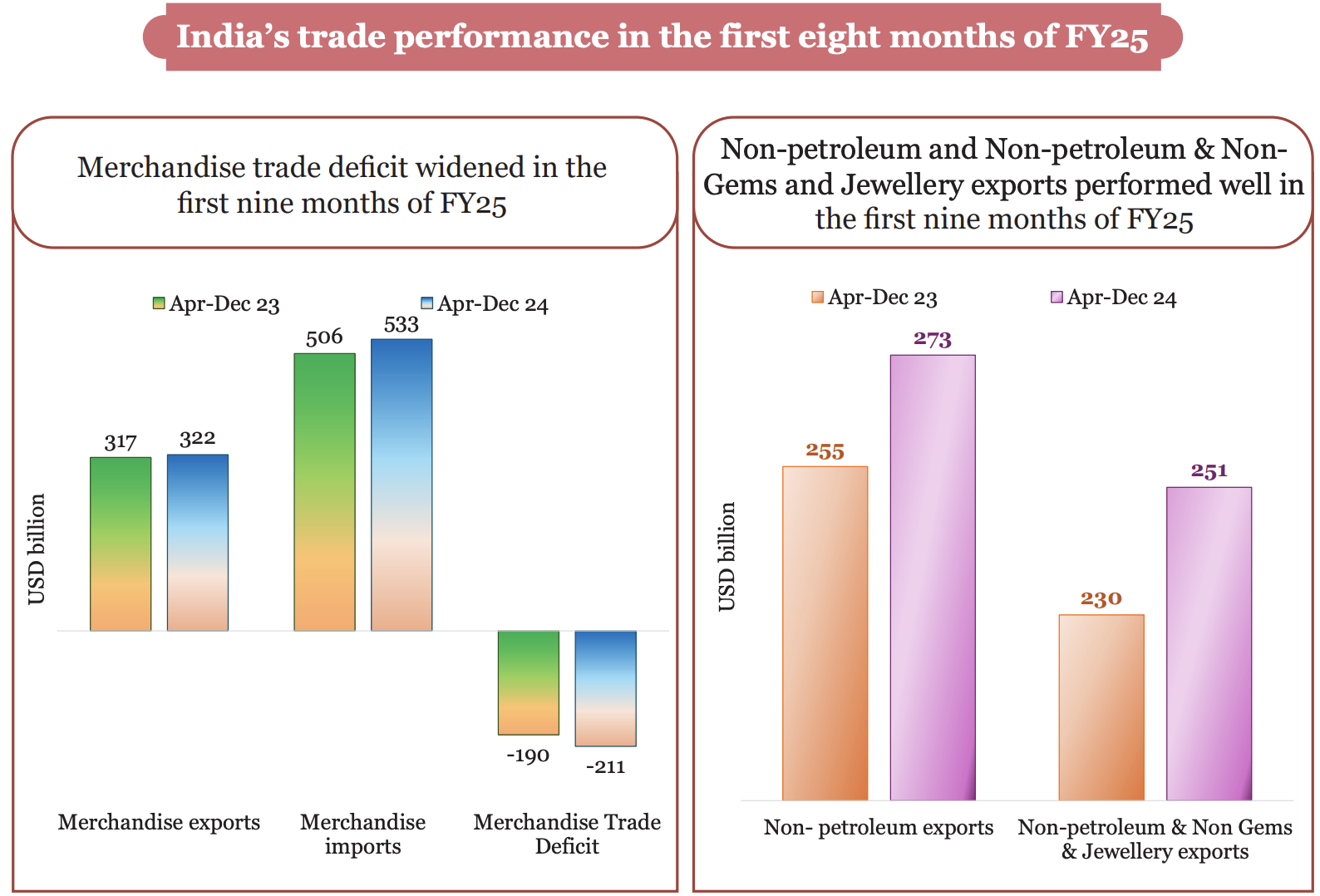
Trend in India's trade performance
- Overall exports (merchandise + services) grew by 6 % (YOY) in the first nine months of FY25.
- Services sector grew by 11.6 % during the same time.
- Total imports during the same period reached USD 682.2 billion, registering a growth of 6.9 % on the back of steady domestic demand.
- India commands 10.2 % of the global export market in 'Telecommunications, Computer, & Information Services', ranking 2nd largest exporter in the world (UNCTAD).
India Balance of payments: Resilience amid challenges
- Current account: Current account deficit (CAD) stood at 1.2 % of GDP in Q2 of FY25, supported by rising net services receipts and an increase in private transfer receipts.
- Capital and Financial Account: Over the period from Q1 of FY23 to Q2 of FY25, India has generally recorded surpluses in the capital account, largely driven by robust inflows from FDI, FPI, and external loans.
Performance of FDI flows of India
- Gross Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows increased by 17.9 % in FY25 in comparison to FY24.
- Over the long term, FDI inflows into India have surpassed the USD 1 trillion mark from April 2000 to September 2024.
Foreign Exchange Reserves of India
- India's foreign exchange reserves comprise foreign currency assets (FCA), gold, special drawing rights (SDRs) and reserve tranche position (RTP) in the IMF
- It stood at USD 640.3 billion as of the end of December 2024, sufficient to cover 10.9 months of imports and approximately 90 % of the country's external debt.
External debt position of India
- India's external debt remained stable over the past few years, with the external debt to GDP ratio standing at 19.4 % at the end of September 2024.
Outlook
- Global trade dynamics have changed significantly in recent years, shifting from globalization to rising trade protectionism, accompanied by increased uncertainty.
- To remain competitive and enhance its participation in global supply chains, India must continue reducing trade costs and improving facilitation to boost export competitiveness.
One-Line SummaryIndia's external sector remains resilient, with strong FDI inflows, growing service exports, and a balanced trade strategy, but challenges like trade restrictions, supply chain vulnerabilities, and global slowdown require strategic policy responses. |
Relevance for UPSC
|







