Introduction
- Bank credit has grown at a steady rate in the current financial year, with credit growth converging towards deposit growth.
- There has been a consistent improvement in the profitability of scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) as reflected in a fall in gross non-performing assets (GNPAs).
- This is accompanied by a rise in the capital-to-risk weighted asset ratio (CRAR).
Performance of the banking sector and credit availability
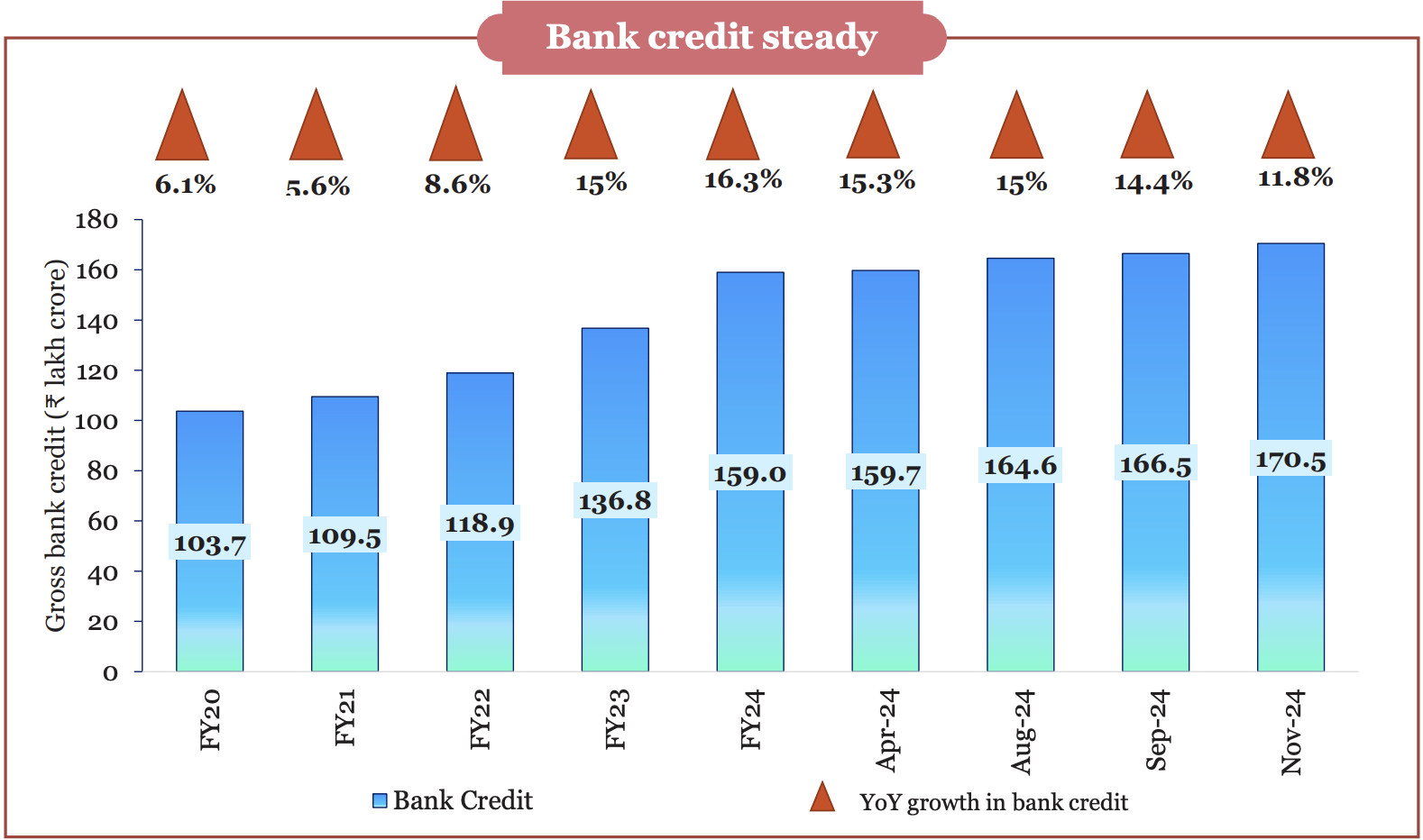
- Credit growth: Credit growth outpaced nominal GDP growth for two successive years.
- The credit-GDP gap narrowed to (-) 0.3 % in Q1 of FY25 from (-) 10.3 % in Q1 of FY23.
- Improved asset quality: The gross non-performing assets (GNPAs) ratio of Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) has declined consistently from its peak in FY18 to 2.6 % at the end of September 2024.
- At the end of September 2024, the Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) of SCBs stood at 16.7%, and all banks met the Common Equity Tier-1 (CET-1) requirement of 8%.
- Global comparison: India's bank credit to private non-financial sector to GDP ratio is lower than that of Advanced Economies (AEs) such as US, UK, and Japan.
- Compared to emerging market economies (EMEs), the ratio is also lower. Still, it is higher than that of Indonesia and Mexico.
- Rural Financial Institutions: Regional Rural Bank's number of branches grew substantially from 14,494 in 2006 to 21,856 in 2023.
- Financial Inclusion: Improvement in RBI's Financial Inclusion Index from 53.9 in March 2021 to 64.2 by March 2024.
Developments in capital markets
- ₹11.1 lakh crore mobilised from primary markets primary markets (equity and debt) during Apr-Dec 2024(5% more than the amount mobilised in FY24).
- Number of Demat accounts rose by 33% to 18.5 crore at the end of December 2024 on a YoY basis.
- Number of initial public offerings (IPOs) increased to 259 in Apr-Dec 2024 from 196 in Apr-Dec 2023 (up 32.1% YoY).
- BSE stock market capitalisation to GDP ratio stood at 136 % at the end of December 2024.
- Far higher than other Emerging Market Economies like China (65%) and Brazil (37 %).
Developments in the Insurance sector
- Total insurance premium grew by 7.7% in FY24, reaching ₹11.2 lakh crore.
- Decline in insurance penetration from 4% in FY23 to 3.7% in FY24.
- Life insurance penetration dropped marginally from 3 % in FY23 to 2.8 %in FY24.
- Non-life insurance penetration remained stable at 1%.
Developments in the pension sector
- As of September 2024, the total number of subscribers reached 783.4 lakh, showing a YoY growth of 16% from 675.2 lakh in September 2023.
- According to the Mercer CFA Institute Global Pension Index, 2024, India's overall index value has moderated from 45.9 in 2023 to 44 in 2024.
Cybersecurity aspects of India's financial sector
- Reports indicate that almost one-fifth of all reported cyber incidents involve financial institutions, with banks being the most affected.
- According to IMF's Global Financial Stability Report, cyberattacks have resulted in extreme financial losses, which have increased fourfold since 2017, amounting to USD 2.5 billion.
Efficacy of Insolvency Law
- Under Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, ₹3.6 lakh crore realized in resolution of 1,068 plans till September 2024.
- It amounts to 161 % against the liquidation value and 86.1 % of the fair value of the assets involved.
Outlook
- Challenge: Dominance of financial markets in shaping policy and macroeconomic outcomes, a phenomenon known as 'financialization.'
- It led to unprecedented levels of public and private sector debt (some visible to regulators and some not) in advanced economies.
- Way forward: India should strive to maintain the fine balance between financial sector development and growth on the one hand and financialization on the other.
One-Line SummaryIndia's monetary policy remains stable, ensuring inflation control and economic growth, while strong banking reforms, NBFC oversight, and digital financial expansion drive financial sector resilience. |
Relevance for UPSC
|





