Introduction
- India needs a growth rate of 8% at constant prices on average for a decade or two in order to realise its economic aspirations of becoming Viksit Bharat by 2047.
- World Economic Outlook of IMF projects India to become a USD 5 trillion economy by FY28 and reach a size of USD 6.307 trillion by FY30.
- Medium-term growth outlook for India must be assessed in context of a new global reality – Geo-economic fragmentation, China's manufacturing prowess and dependency of efforts for energy transition on China.
Geo-Economic Fragmentation (GEF)
- GEF is defined as a policy-driven reversal of global economic integration often guided by strategic considerations.
- This process encompasses different channels including trade, capital, and migration flows through which fragmentation is reshaping the global economy.
- GEF is replacing globalization leading to imminent economic realignments and readjustments.
- UNIDO projected that China will account for 45% of all global manufacturing, outmatching the US and its allies by 2030.
- China dominates energy transition technologies with nearly 80% share of solar panels (polysilicon, ingots, wafers, cells, and modules), and world's battery manufacturing capacity.
- Implications of GEF
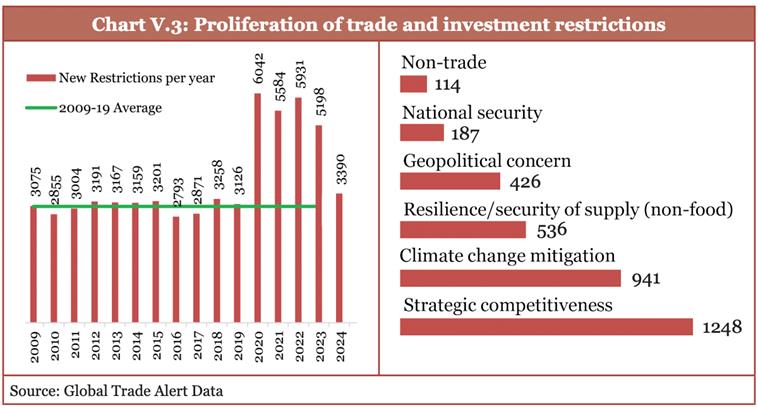
- Increased trade and investment restrictions: Between 2020 and 2024, over 24000 new restrictions related to trade and investments have gone into place globally.
- Concentrated FDI flows: Global FDI flows are increasingly concentrated among geopolitically aligned countries, increasing vulnerability of emerging markets and developing economies.
Deregulation and Economic Freedom: A catalyst for growth
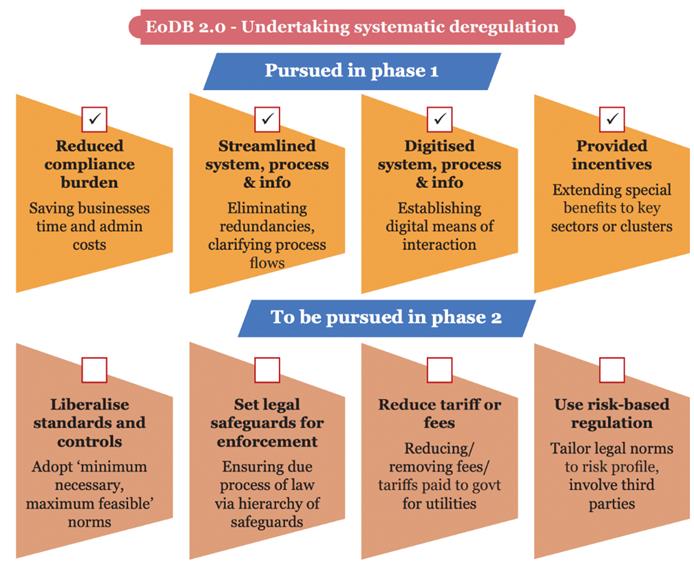
- States can undertake systematic deregulation by reviewing regulations for their cost-effectiveness by following a three-step process:
- Identifying areas for deregulation under Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) 2.0 and creation of a viable Mittelstand, i.e. India's SME sector.
- Comparing regulations with other states and countries.
- Estimating cost of each of these regulations on individual enterprises.
One Line SummaryIndia's medium-term growth outlook remains strong, driven by deregulation, investment-led growth, and skill development, but global economic risks and domestic challenges in employment and infrastructure need continuous policy attention. |
Relevance for UPSC
|




