Introduction
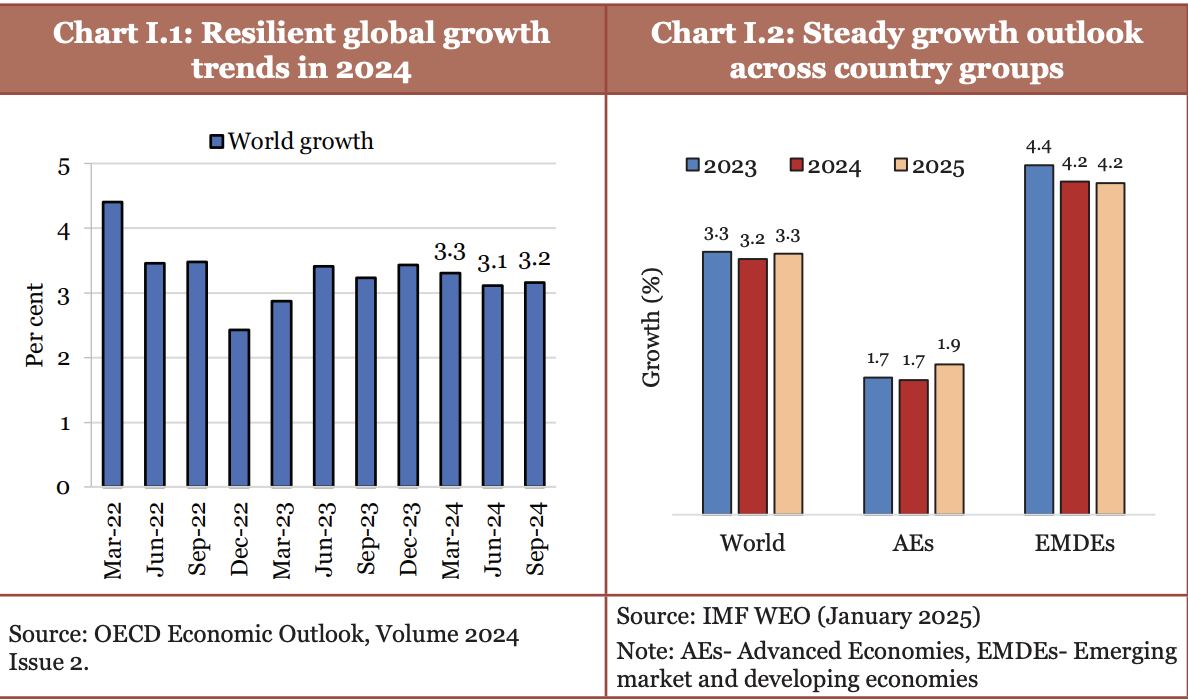
- The global economy on an average grew by 3.3 % in 2023 against the IMF projection of 3.2 % growth in the next 5 years.
- Slowdown in global manufacturing, especially in Europe and parts of Asia, due to supply chain disruptions and weak external demand.
- Services sector performed better, supporting growth in many economies.
Global economic scenario
- Inflationary pressures: Inflation rates across economies have trended downward steadily, approaching central bank target levels.
- Disinflation seems to have slowed due to the persistence of services inflation, while core goods inflation has fallen to negligible levels.
- Global uncertainty:
- Tensions in the Middle East have disrupted trade through one of the critical shipping routes – Suez Canal (a key route for 15% of global maritime trade).
- Geopolitical Economic Policy Uncertainty index increased from 121.7(2023) to 133.6 (2024) due to global concerns about economic policies.
- World Trade Uncertainty Index increased from 8.5(2023) to 13 (2024) driven by trade tensions and policy shifts in major economies.
Indian Economy
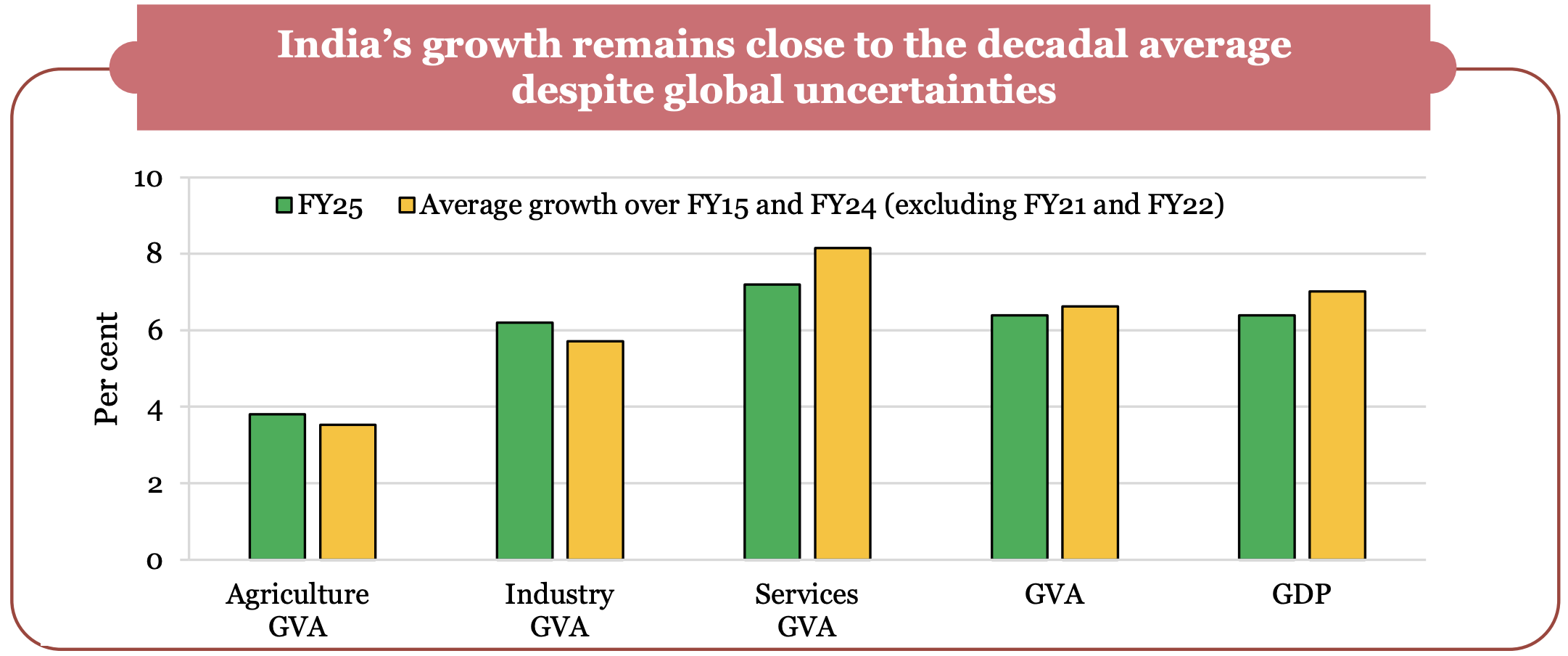
- Growth: India's real GDP growth is estimated at 6.4% in FY25 (as per first advance estimates of national income), which equates nearly to its decadal average.
- Demand side: Private final consumption expenditure at constant prices is estimated to grow by 7.3 %, driven by a rebound in rural demand.
- Supply side: Real gross value added (GVA) is estimated to grow by 6.4%.
- Sector Performance:
- Agriculture sector is expected to rebound to a growth of 3.8 % in FY25.
- Industrial sector is estimated to grow by 6.2 % in FY25.
- Strong growth rates in construction activities and electricity, gas, water supply and other utility services are expected to support industrial expansion.
- Growth in the services sector is expected to remain robust at 7.2%, driven by healthy activity in financial, real estate, professional services, public administration, defence, and other services.
- Despite various challenges, India continues to register the fastest growth in manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI).
- PMI services have been in an expansionary zone during first half of FY25, supported by growth in new orders, rise in output, improvement in sales and enhanced employment generation.
- Inflation: Retail headline inflation, as measured by the change in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), has softened from 5.4% in FY24 to 4.9% in April – December 2024.
- Capital expenditure (CAPEX) improved continuously from FY21 to FY24.
- Post general elections, CAPEX grew YOY by 8.2% during July –November 2024.
- External Sector
- India accounts for seventh-largest share in global services exports, underscoring India's global competitiveness in the sector.
- During April to December 2024, non-Petroleum and non-Gems & Jewellery exports went up by 9.1 % reflecting resilience of India's merchandise exports amid volatile global conditions.
- Employment trends:
- As per the 2023-24 annual Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) report, the unemployment rate (for individuals aged 15 years and above) has steadily declined from 6% (2017-18) to 3.2 % (2023-24).
- India's formal sector has expanded significantly, with net Employees' Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) subscriptions rising from 61 lakh in FY19 to 131 lakhs in FY24.
Outlook and Way forward
- Keeping in mind the upsides and downsides to growth, the Survey expects the real GDP growth in FY26 to be between 6.3 and 6.8%.
- Overall, India will need to improve its global competitiveness through grassroots-level structural reforms and deregulation to reinforce its medium-term growth potential.
One-Line SummaryIndia's economic growth remains robust, driven by strong domestic demand, infrastructure investments, and macroeconomic stability, but external risks like inflation and global slowdown require cautious policy management. |
Relevance for UPSC
|







