Introduction
- The 'Agriculture and Allied Activities 'sector contributes ~16% of the country's GDP for FY24 (PE) at current prices and supports ~46.1% of the population.
- High-value sectors like horticulture, livestock, and fisheries have become key drivers of overall agricultural growth.
- India produces 11.6% of the world's cereals, but its crop yields are much lower than other top producers.
- For the fiscal year 2024-25, the MSP for Arhar and Bajra has been increased by 59% and 77% over the weighted average cost of production, respectively.
Seeds-quality and use of fertilisers: the critical differentiator
- In the 2023-24 season, ICAR produced 1.06 lakh quintals of breeder seeds across 1,798 varieties for 81 crops.
- Key Interventions includes Seed banks, 'Urea Gold' (combines urea with sulphur to enhance nutrient uptake), PM PRANAM initiative.
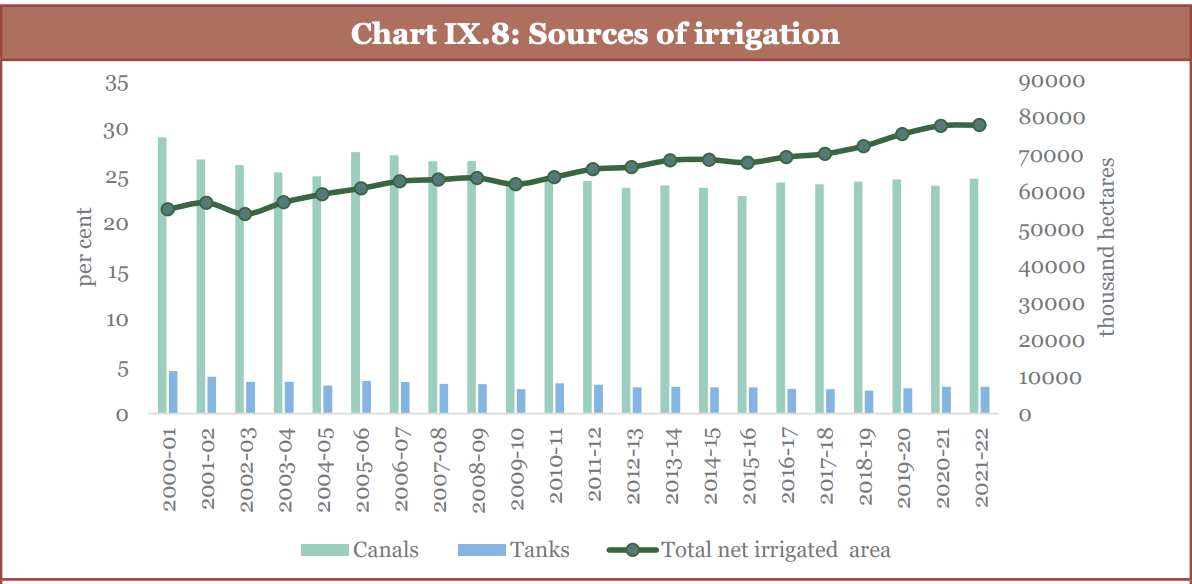
Rainfall and irrigation system: Building efficiency and extending coverage
- The agriculture sector is highly vulnerable to weather changes, with only 55% of the net sown area irrigated.
- Moreover >2/3rd of India's agricultural land faces the threat of drought.
- Key Interventions in this aspect includes Per Drop More Crop (PDMC) under Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY), Micro irrigation Fund (MIF), Rain-fed Area Development (RAD).

Agriculture credit: A critical input
- India has 7.75 crore operational KCC accounts.
- KCC was expanded in 2018-19 to support the working capital needs of fisheries and animal husbandry.
- Key Interventions in this field includes Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS), Prompt Repayment Incentive (PRI), Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY), PM-KISAN.
Agriculture mechanisation: Facilitating access
- The high machinery cost presents a significant barrier to promoting farm mechanisation among small and marginal farmers.
- Key Interventions includes The Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanisation (SMAM) which helps in establishing Custom Hiring Centres (CHCs), Farm machinery banks enable the renting of machinery at affordable rates, drones to Women SHGs.
Agriculture extension: The Enabler
- Agricultural extension is vital in disseminating knowledge, enhancing productivity, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Key Interventions: Sub-Mission on Agricultural Extension (SMAE) to bolster agricultural extension services, enhance entrepreneurship and improve productivity.
Improvement in agriculture marketing infrastructure
- Key interventions includes Agriculture Marketing Infrastructure (AMI) sub-scheme, Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), e-NAM Scheme.
Climate action in agriculture
- Studies have indicated that a potential 2°C rise in annual temperature and a 7 % increase in annual rainfall by 2099 could lead to an 8-12 % decline in Indian agricultural productivity.
- Key Interventions: National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture , Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY), Mission Organic Value Chain Development for North Eastern Region (MOVCDNER).
Allied sectors: Potential to Build Resilience
- The fisheries sector has shown the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% followed by livestock with a CAGR of 8%
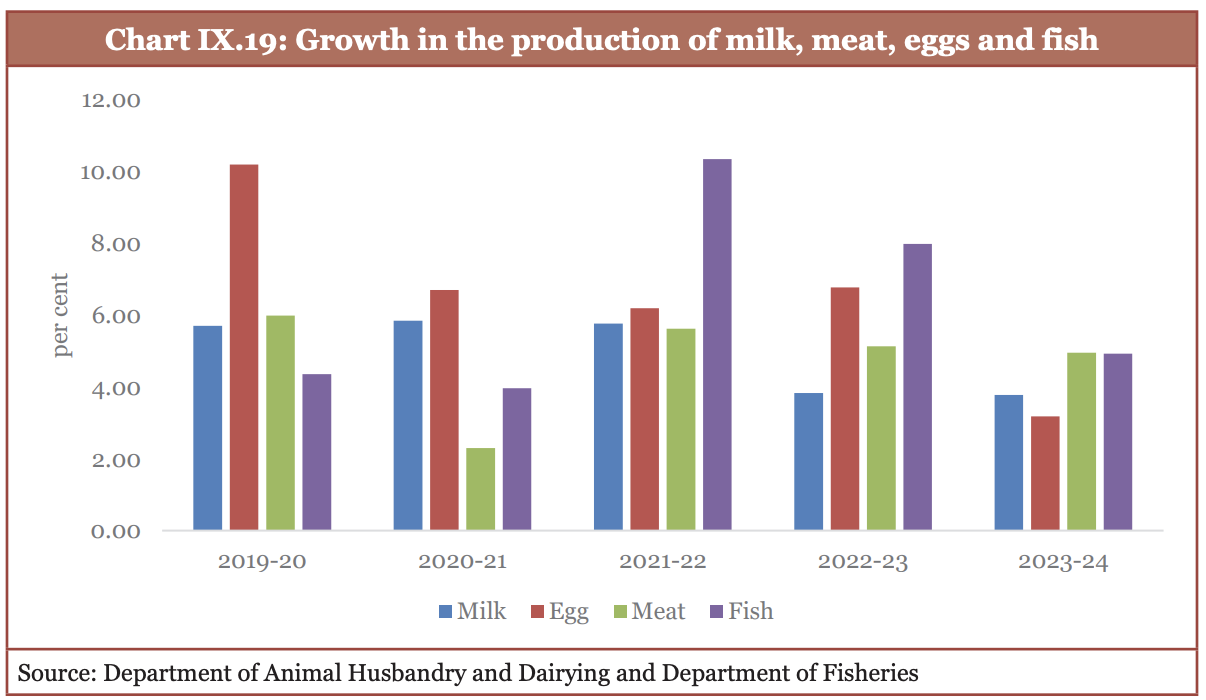
- Key Interventions: Rashtriya Gokul Mission, Livestock Health and Disease Control Program, Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF).
Cooperative societies: Strengthening the Institution to serve better
- They serve a vital function across many sectors, including agriculture, credit and banking, housing, and women's welfare
- Key Interventions: Introduction of Model Bye-Laws specifically for Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), transformation of PACS into Common Service Centres (CSCs), establishment of retail petrol and diesel outlets and the setting up of micro-ATMs within cooperative societies.
Food processing industries: Critical for the Economy
- It makes upto 12.41% of total employment in the organised sector.
- In FY24, agri-food exports constituted ~11.7% of India's total exports.
- Share of processed food exports within agri-food exports has risen from 14.9% in FY18 to 23.4% in FY24
- Key Interventions: Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY), Production Linked Incentive Scheme for Food Processing (PLISFPI), Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) scheme.
Food management: Enabling Food Security
- Key Interventions: National Food Security Act (NFSA), Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana,Credit Guarantee Scheme for electronic-negotiable warehouse receipt (e-NWR)-based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF) to facilitate post-harvest lending for farmers.
Conclusion
India's agricultural sector is vital for economic growth and food security. Despite challenges, it has shown resilience with stable growth, supported by government initiatives to boost productivity, diversify crops, and provide social security for farmers.
One-Line SummaryIndia's agriculture sector is transforming through productivity reforms, digital innovations, and climate resilience, but market access, financial support, and sustainability challenges remain. |
Relevance for UPSC:
|





