Why in the news?
Global Financial Stability Report 2024 released by International Monetary Fund (IMF) warns cyber risks as a growing threat to macro financial stability.
Key Findings of the report
- Nearly one-fifth of all cyber risks affect financial firms.
- Number of cyber-attacks has doubled since COVID-19 pandemic.
- Only 47% of the surveyed countries had formulated a national and financial sector-focused cyber-security strategy.
Reasons Behind rise in cyber attacks
- Rapid Digital Transformation and Technological Innovations:
- Covid-19 Pandemic has led to surge in remote work, delivery applications, and contactless payments.
- Evolution of fin-tech companies exposes financial systems to cyber threats due to digitalized operations and interconnectedness leading to platform frauds.
- Heightened global geopolitical tensions: E.g. surge in cyber-attacks after Russia's invasion of Ukraine
- Lack of strong internal controls: As per PwC's Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey 2022 four out of every ten platform frauds in India were conducted by internal perpetrators.
- Lack of Swift Action and Detection discourages individuals to report these crimes.
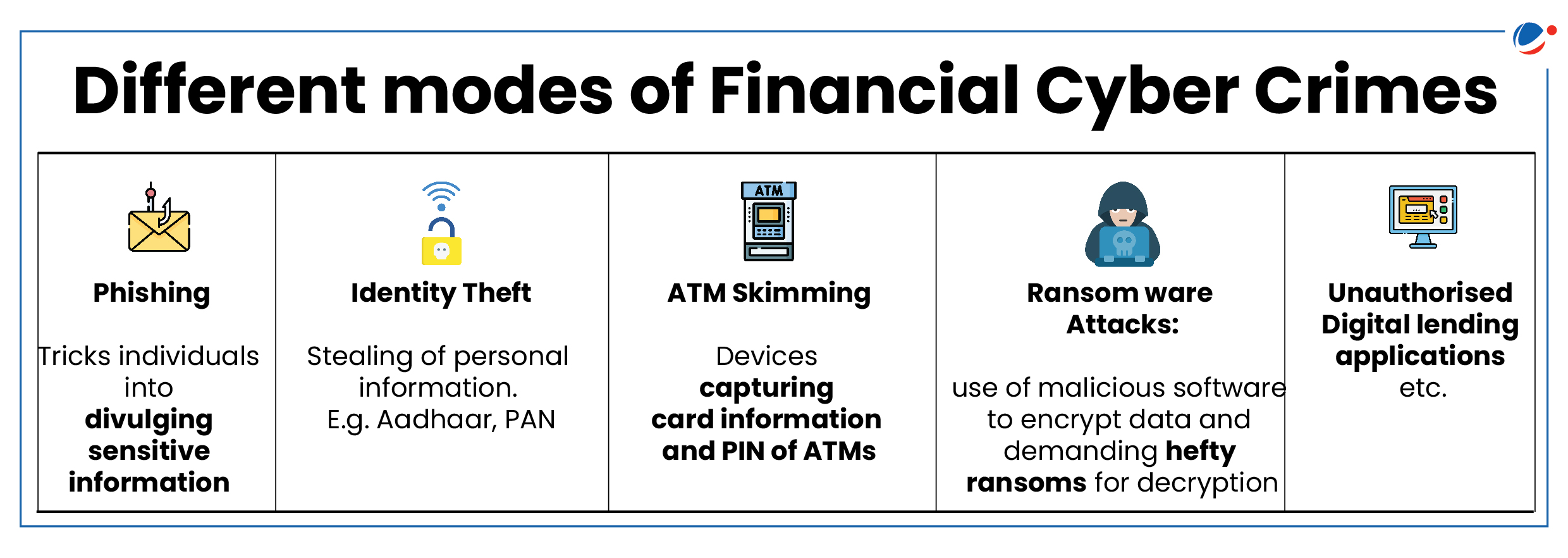
Impact of Cyber risks on Financial Systems
- Impact on macro-financial stability:
- Loss of confidence in the viability of the targeted institution may lead to instances of Cyber run and result in liquidity problems.
- Cyber run is deposit withdrawals (outflows ) from banks in large amount leading to liquidity crisis and default risk
- Lack of substitutes for a key institution or financial market infrastructure would lead to disruption in the financial system.
- E.g. A ransomware attack on payment systems, hacking of a central bank or electronic trading systems could lead to halts in trading, asset price volatility,
- Potential of systemic shock due to the interconnected nature of institutions through
- technological linkages (such as multiple firms using the same software) or
- financial linkages (e.g., interbank market and settlement systems)
- Loss of confidence in the viability of the targeted institution may lead to instances of Cyber run and result in liquidity problems.
- Affects government functioning as it disrupts the management of government debt and may give rise to sovereign risks etc.
- Credit and market losses due to loss of businesses, remittances, reputational damage, and increased investments in cyber security.
- Economic losses to the tune of 1 to 10% of the global GDP is caused by these frauds (IMF).
- Issues related to data integrity due to loss or compromise of data and its systems raising the problem of data confidentiality.

Challenges in dealing with Cyber Threats to Financial Systems
- Lack of regulatory and supervisory frameworks and cyber-security workforce: This leads to-
- Lack of effective oversight of third-party service providers.
- Gaps in national and financial sector cyber-security strategies and coordination among stakeholders.
- Technological innovations: Artificial Intelligence, quantum computing could further amplify cyber risks.
- Complex regulatory environment caused due to lack of seamless cooperation between regulators such as Reserve Bank India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) etc.
- Challenges related to legal framework: For instance, India lacks a dedicated legal framework or a dedicated court to deal with online financial frauds.
- Nature of Crime hindering investigation: Cybercrimes are conducted remotely and are Multi-state and Trans-border in nature, making police investigations costly.
- Also, the use of a mule account makes traceability harder.
- Other challenges: Procedural Hurdles and delays in cyber crime reporting; Lack of awareness to individuals; Resources constraint, etc.
Initiatives taken to curb Cyber Threats to Financial Systems
|
Way Forward
- Cyber legislation at the national level and better cyber-related governance arrangements at firms.
- This should also have central bank business continuity contingency plans covering cyber risk and provision of liquidity in case of crisis.
- Insurance by firms to protect against financial losses of cyber incidents
- Periodical assessment of the cyber-security landscape and identification of potential systemic risks from interconnectedness and concentrations, including from third-party service providers.
- Encouraging cyber "maturity" among financial sector firms, including board-level access to cyber-security expertise leading to better cyber-related governance may reduce cyber risk.
- Improving cyber hygiene of firm by enhancing online security and overall system health (such as antimalware and multifactor authentication.
- Capable cybersecurity workforce, and domestic and international information-sharing arrangements
- Prioritization of data reporting and collection of cyber incidents, and sharing information among financial sector participants to enhance collective preparedness.
Conclusion
Cyber incidents pose a global financial stability threat due to digitalization, technologies, and geopolitical tensions. Financial sector must develop capacity to deliver critical services during times of disruption and develop response and recovery mechanisms for crisis management.



