Commodity Dependence
The President of the United Nations General Assembly recently highlighted the issue of commodity dependence.
About Commodity dependence
- A country is dependent on the export of commodities (or “commodity-dependent”) when its merchandise exports are heavily concentrated on primary commodities (like crude oil, coal, iron ore, etc.).
- The source of commodity dependence can be linked to a country’s persistent or structural conditions, such as its resource endowment and factor composition, institutional framework, geographic situation, history among other factors.
Issues with Commodity dependence
- Exposes countries to shocks: Dependence can leave an economy highly exposed to shocks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, and price swings in international markets.
- Linked to lower human well-being: In 2021, 29 out of the 32 countries with low HDI scores were commodity dependent.
- More vulnerable to climate change: More than 60% of the world’s small island developing states – on the front lines of the climate crisis – are commodity-dependent.
- Profound social consequences: E.g., mining industry-dependent countries engage in trade but most of the benefits go to capital owners rather than the workers.
Way Ahead
- Developing a Diversification Strategy, promoting education and Skill Development, garnering support for commodity-dependent countries and encouraging strong national political will.
- Tags :
- Commodity dependence
- Merchandise Exports
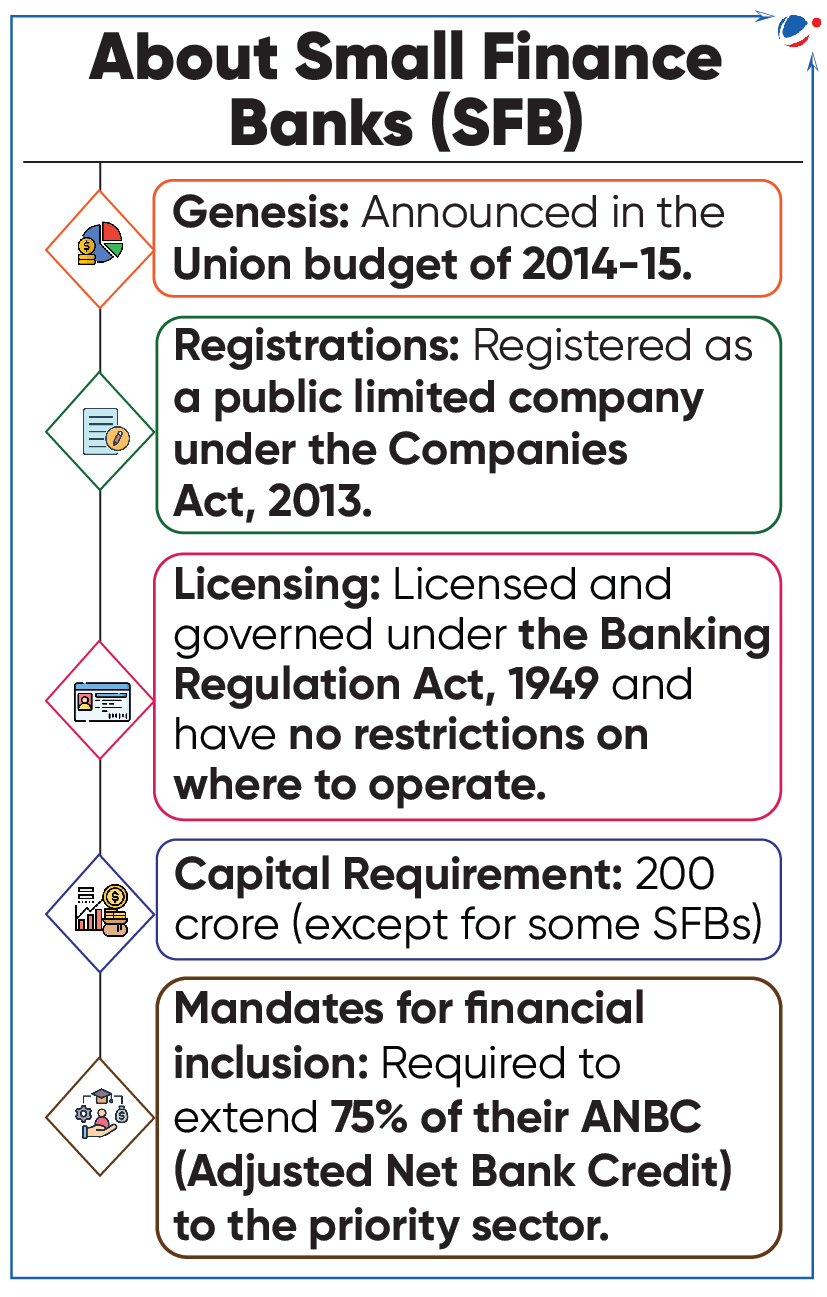
Eligibility for Universal Banking by SFBS
RBI set eligibility criteria for Small Finance Banks (SFB) to transit into universal banking under on-tap licensing.
- Universal banks (UBs) are banks that offer a wide range of financial services, beyond commercial banking and investment banking, such as insurance.
- Until now, SFBs were allowed to primarily undertake basic banking activities of acceptance of deposits and lending to unserved and underserved sections
- On-tap licensing: It was introduced in 2016 to allow banks to apply for banking licenses with the RBI throughout the year.
- Prior to this, banking licenses were granted upon invitation of applications by RBI to prospective players.
Eligibility for SFBs to transitioning into UBs
- Net Worth: SFBs must have a minimum net worth of Rs 1,000 crore.
- Status: SFBs must be scheduled banks with a satisfactory track record of performance for a minimum of 5 years.
- Financial Health:
- Profitability: Should have net profits in the last two Financial Years.
- Asset Quality: Gross non-performing assets (G-NPA) and net NPA (N-NPA) must be less than or equal to 3% and 1%, respectively, over the last two FYs.
- Stock Listing: Shares must be listed on a recognized stock exchange.
- Promoter Requirements: No addition of new promoters or changes to existing promoters are permitted during the transition.
- No changes are allowed to the promoter shareholding dilution plan previously approved by the RBI.
- Preference: SFBs with a diversified loan portfolio will be preferred.
- Tags :
- Small Finance Banks
- On-tap licensing
- Universal Banks
‘Five-Year Review of India's Merchandise Trade' Report
Report, released by Global Trade Research Initiative (GTRI), assesses impact of international disruptions and domestic hurdles and reviews market shifts in trade performances.
- Report also highlights varied impact of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) on India’s global trade dynamics.
About FTAs
- FTAs are treaties between two or more countries to reduce or eliminate certain barriers to trade and investment, and to facilitate stronger trade and commercial ties between participating countries.
- It can cover areas such as trade in goods, services, intellectual property rights (IPRs), etc.
Key findings of the report on India’s FTAs
- India's merchandise imports from FTA partners grew by ~38% whereas exports grew by just ~14.5%.
- FTA with Asean (signed in 2010), saw growth in imports at a faster pace than exports.
- Overall, India ranked 17th globally in merchandise exports whereas it is ranked 8th in merchandise imports.
Issues with India’s FTAs
- Lower FTA utilisation: India’s FTA utilization remains low at around 25%, as against 70-80% for developed countries.
- Higher compliance cost: Due to complex certification processes and rules of origin.
- Non-tariff barriers (NTBs): Persistence of stringent standards, sanitary and phytosanitary measures and technical barriers by partner countries like Japan.
- Limited awareness: Inadequate promotion and outreach activities about of FTA benefits among exporters.

- Tags :
- Free Trade Agreements
- Merchandise Trade
- Non-Tariff Barriers
India International Bullion Exchange (IIBX)
State Bank of India has become the first trading-cum-clearing member at IIBX.
- Bullion refers to physical gold and silver of high purity that is often kept in form of bars, ingots, or coins.
About IIBX
- Established at GIFT International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), Gandhinagar, Gujarat in 2022.
- Regulated by IFSC Authority (IFSCA).
- Promoted by India’s leading market infrastructure institutions like National Stock Exchange, Multi Commodity Exchange of India etc.
- Benefits
- Gateway to import bullion into India.
- Provide world class bullion exchange ecosystem to promote bullion trading, investment in bullion financial products and vaulting facilities in IFSCs.
- Tags :
- GIFT IFSC
- IIBX
India Volatility Index (VIX)
Recently, India VIX surged above the critical threshold of 21, indicating heightened volatility in India’s stock market.
About India VIX
- It is a measure of the amount by which an underlying Index is expected to fluctuate, in the near term (30 calendar days).
- Higher the India VIX values, higher the expected volatility and vice-versa.
- It is based on index option prices of NIFTY.
- Uses computation methodology of Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE).
- CBOE was first to introduce a volatility index for US markets in 1993.
- Tags :
- India VIX
- NIFTY
Cost Inflation Index (CII)
CBDT Notifies CII For Financial Year 2024- 25 for calculating long-term capital gains (LTCG).
- LTCG is the profit arising from the sale of a capital asset (i.e., Stocks, Bonds, jewellery, buildings, etc.) held for a duration of 12 to 36 months (based on the asset type)
About CII
- CII is notified under the Income-tax Act (1961) every year.
- It is used by taxpayers to compute gains arising out of sale of capital assets after adjusting for inflation.
- Tags :
- COST INFLATION INDEX (CII)
- Long-term Capital Gains (LTCG)
Paradox of Thrift (POT) Theory
This Economic theory was popularised by British economist John Maynard Keynes.
About PoT
- A rise in individuals’ savings, by reducing the amount of money spent on goods and services, can cause a fall in overall savings and investments.
- It believes that higher savings is bad for the wider economy and an economy can grow only by boosting consumer spending.
Criticisms of PoT
- It ignores the potential for saved income to be lent out by banks.
- It also ignores the potential of inflation and deflation in an economy.
- Tags :
- PARADOX OF THRIFT (POT)
- John Maynard Keynes
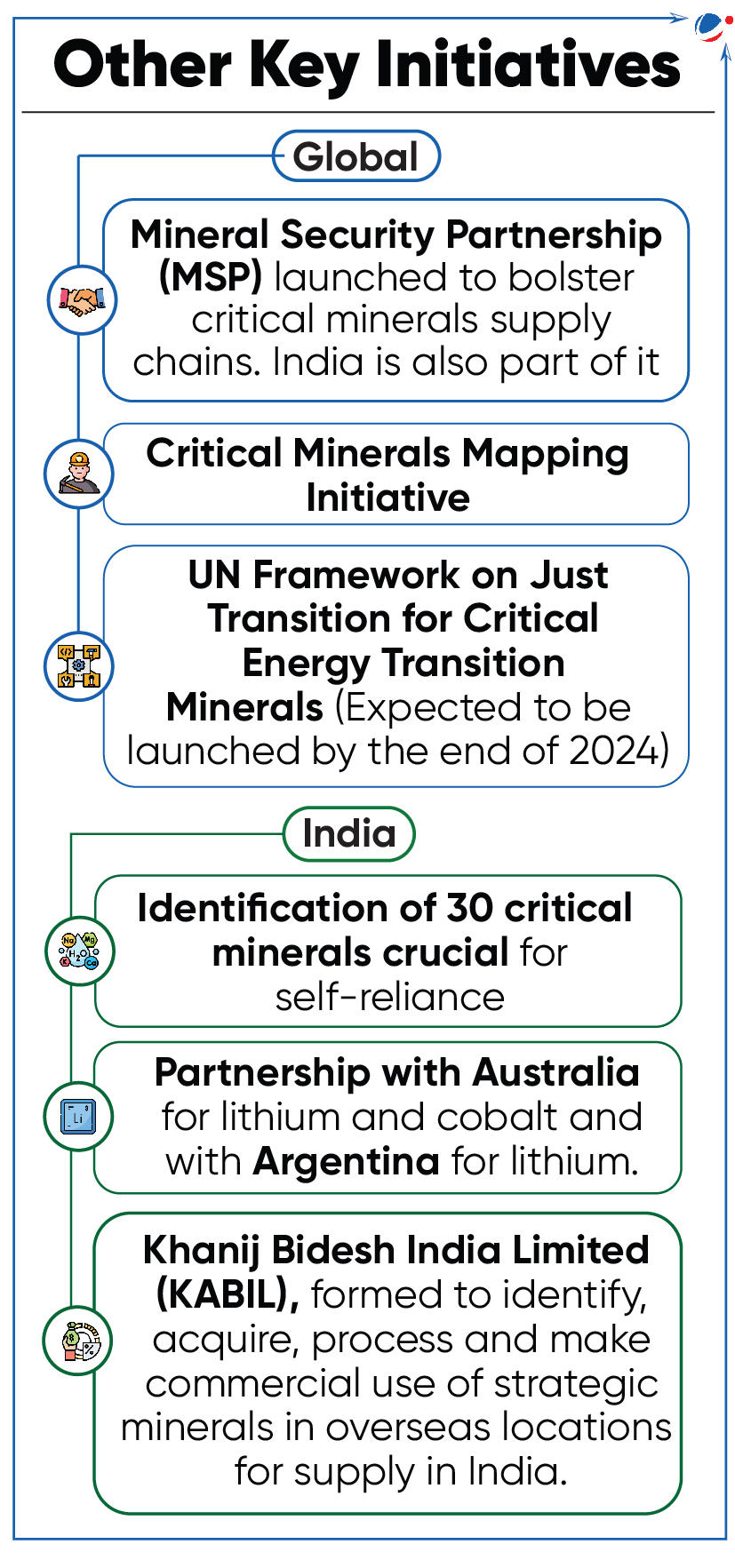
UN Panel for Critical Energy Transition Minerals
The United Nations (UN) appointed panel on Critical Energy Transition Minerals.
- The Panel aims to bring all stakeholders across the entire critical energy transition minerals value chain to develop a set of global common and voluntary principles for energy transition.
- It will address issues relating to equity, transparency, investment, sustainability and human rights.
- The panel comprises Government and intergovernmental actors including the European Union, African Union, Australia, Indonesia, Colombia, India, etc.
- Critical Energy Transition Minerals are essential components in many of today’s rapidly growing clean energy technologies, from wind turbines and solar panels to electric vehicles.
- E.g. copper, lithium, nickel, cobalt etc.
Challenges/Issues related to Critical Energy Transition Minerals
- Geographical concentration: Few countries have major reserves; it may exacerbate geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruption.
- E.g. Lithium triangle- consists of Argentina, Chile and Bolivia
- Unsustainable Mining and processing: It can lead to water pollution, destruction of ecosystems, etc., and human rights issues (such as child labour).
- Growing Demand: Mismatch in demand and supply.
- According to the International Energy Agency, demand of critical mineral is set to grow by three and a half times by 2030.
- Tags :
- Critical Energy Transition Minerals
- United Nations (UN)
Drip Pricing
The Department of Consumer Affairs has issued a warning against drip pricing.
About Drip Pricing
- It is a pricing technique in which firms advertise only part of a product’s price and reveal other charges later as the customer goes through the buying process.
- It is used as a tactic to attract customers into initiating the purchasing process
- It has been identified as a dark pattern under Guidelines for Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns, 2023.
- A Dark pattern refers to practices adopted by online platforms that mislead people into paying for items or services they did not intend to do originally.
- Tags :
- Drip Pricing
- Dark Pattern
Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI), 2024
Travel & Tourism Development Index (TTDI), 2024 was released by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
About TTDI, 2024
- TTDI measures the set of factors and policies that enable the sustainable and resilient development of Travel and Tourism.
- It is the second edition of an index that evolved from the Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Index (TTCI) series.
- TTCI is flagship index of WEF that has been in production since 2007.
- India's rank improved to 39 in 2024 from 54 in 2021.
- Tags :
- TTDI
ISHAN INITIATIVE
The Airports Authority of India (AAI) has started work on ISHAN (Indian Single Sky Harmonized Air Traffic Management) Initiative.
About ISHAN
- It involves Combining India's four Flight Information Regions (FIRs) into a single system overseen from Nagpur.
- Currently, Indian airspace is divided into 4 FIRs i.e. Mumbai, Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai, and a sub-FIR in Guwahati, each managed separately.
- Unifying these FIRs under a single authority in Nagpur is projected to improve efficiency, safety, and seamlessness in air traffic operations.
- Tags :
- ISHAN Initiative
- Airports Authority of India (AAI)



