Why in the News?
Recently, FICCI in collaboration with PWC released a report titled 'Charting the path forward in city gas distribution: Emerging trends and insights'
About CGD
- Pipeline Network: CGD network is an interconnected system of underground natural gas pipelines for supplying Piped Natural Gas (PNG) and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG).
- Natural gas is a relatively clean-burning fossil fuel which mainly comprises Methane (CH4) with a small percentage of other higher hydrocarbons
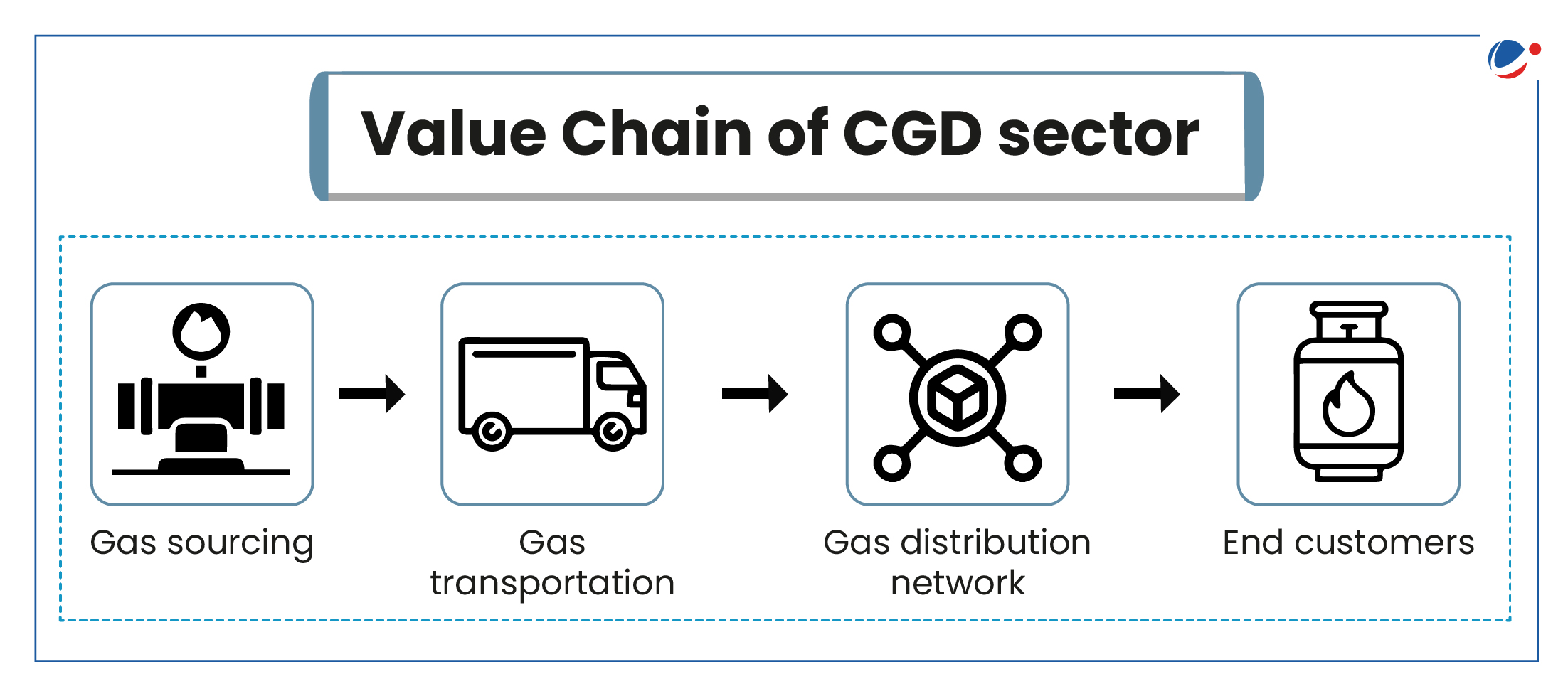
- 4 distinct segments: CNG is predominantly used as auto-fuel, and PNG is used in domestic, commercial and Industrial segments.
- Regulation: Under the PNGRB Act 2006, PNGRB grants authorization to the entities for developing a CGD networkin specified geographical areas (GAs).
- Coverage: Over 33,753 Kms of natural gas trunk pipelines are authorized in the country out of which around 24,623 Kms of pipeline are currently operational
- After the latest (12th) bidding rounds, coverage is expected to nearly reach 100% soon, excluding only the Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands.
- Growth: The Government of India plans to raise the share of natural gas in the energy basket from around 7% at present to 15% by 2030.
Relevance of CGD Network
- Clean Energy Transition: Transitioning to a gas-based economy is expected to support India's climate action commitment of
- net zero emissions by 2070,
- reducing emissions intensity by 45% and
- cutting total carbon emissions by 1 billion metric tonnes by 2030
- Natural Gas as Transition Fuel: Natural gas serves as a bridge between traditional and renewable energy sources in India.
- It acts as a critical energy source during the transition period, complements renewables and helps meet growing energy demands.
- Equitable Energy Access: It will ensure adequate availability and equitable distribution of natural gas across the country.
- Economical and Safe: The natural gas pipeline infrastructure provides an economical and safe method for transporting natural gas from production sources to consumption markets.
- Benefits of CNG: Very low levels of emissions, unlikely to ignite due to high ignition temperature, lowest injury and death rate per vehicle mile etc.
- Benefits of PNG: Safe and assured supply, convenient to use, no wastage, no hassle for replacement of cylinder or cylinder booking etc.
Challenges in the CGD Sector
- Complex Policy Framework: Companies in the CGD sector face challenges like navigating complex regulations and balancing innovation with safety norms.
- e.g., Involvement of multiple agencies such as Directorate General of Hydrocarbons, Oil Industry Safety Directorate, etc., in Supervision of safety standards.
- Infrastructure: High costs, complex technology integration, and regulatory delays hinder development.
- Competition: Gas, making up only 2% of power generation, faces strong competition from cheaper, cleaner alternatives like renewables.
- Import Dependence: With 48% of LNG imported, reliance on costly imports hampers growth, especially since domestic production is sluggish.
- It also makes the sector sensitive to price volatility.
- Technological and digitalisation Lag: The gas infrastructure lacks modern technologies for extraction, transport, and storage. Also, managing large volumes of data requires significant storage and processing capabilities.
Initiatives Taken to Promote CGD Network
- Market Exclusivity to CGD companies: Market exclusivity for a period of 8 years, extendable up to 10 years is given to companies selected in bidding for developing CGD network.
- Infrastructure Status to Gas pipelines: The status accorded by RBI facilitate financing from commercial banks and other financial institutions.
- Priority for Gas Sourcing: The government prioritizes domestic gas supply for households (PNG) and transport (CNG).
- Unified Tariff Reform: It will help achieve the objective of "One Nation, One Grid and One Tariff".
- Financing: Government has set an objective to invest $67 Billion in the natural gas sector in the next six years.
Way Forward for Promoting CGD Networks
- Government and Regulators: Developing a unified regulatory strategy is crucial to streamline the CGD sector.
- Addressing issues like skilled personnel shortages, slow approvals, and volatile gas prices can build trust and improve processes.
- CGD Companies: Companies need to shift towards customer-led strategies to meet market demands and build loyalty.
- Preparing for market changes, including the rise of EVs and alternative energy sources, will help manage future demand fluctuations.
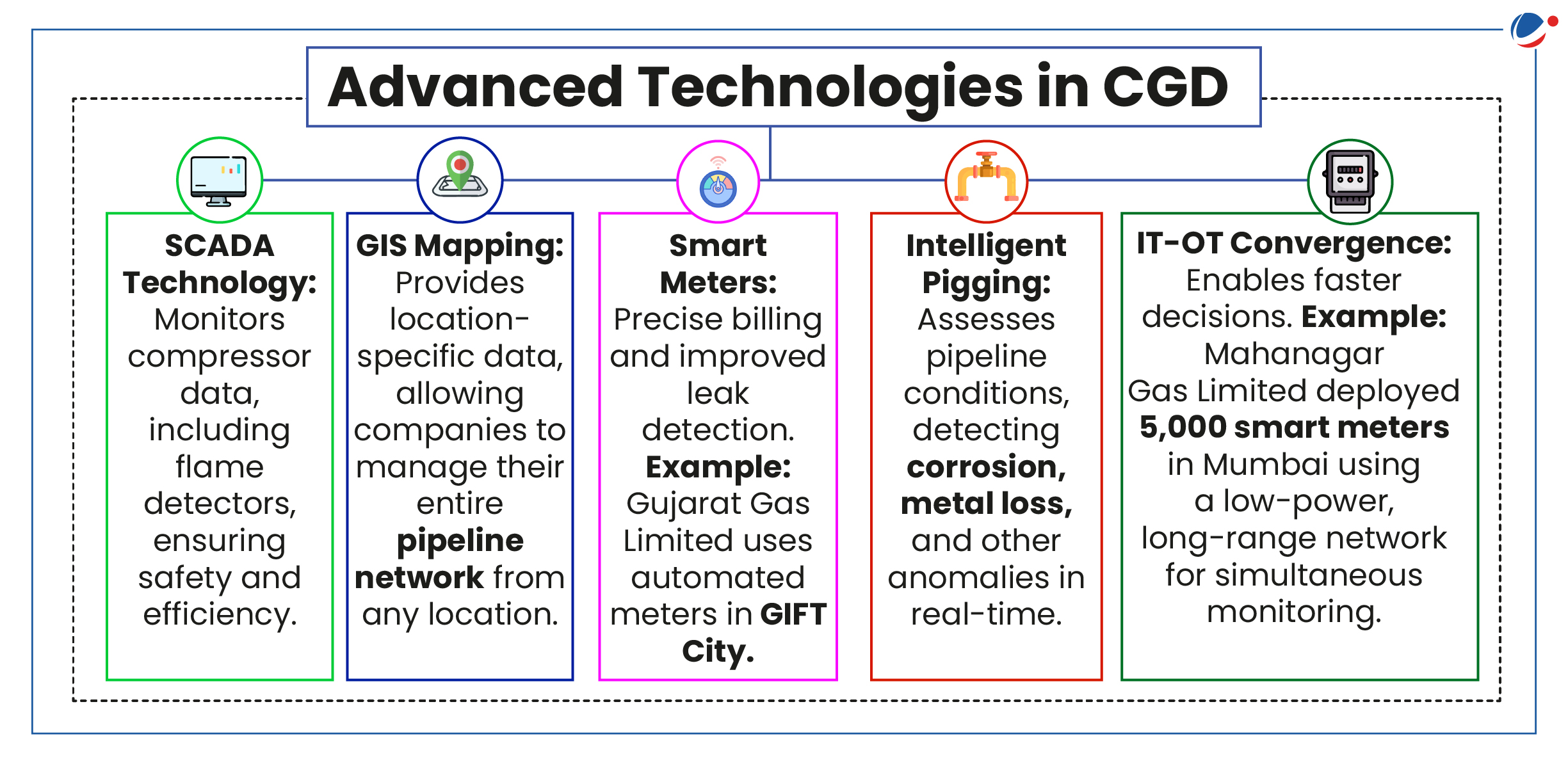
- Technology Companies: Tech firms should focus on developing advanced solutions like smart meters and GIS mapping.
- Collaboration with CGD companies is essential to integrate these technologies, improving efficiency and safety standards.
- Financial Institutions and Investors: Investors must identify promising CGD projects and develop strategies to mitigate risks from volatile market dynamics.
- Prioritizing investments in infrastructure expansion and technologies like SCADA, cloud computing, ML, and AI is crucial.
- All initiatives should align with the UN's 17 sustainable development goals.





