Why in the News?
The 'Report of India's G20 Task Force on DPI' was released by 'India's G20 Task Force on Digital Public Infrastructure for Economic Transformation, Financial Inclusion and Development'.
About the Report
- The Task force was established in 2023 under India's G20 Presidency to facilitate priorities on DPI and Financial Inclusion, and supplement efforts towards the adoption of DPI globally.
- The report defines DPI and outlines a three-part framework for global DPI advancement.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- It is a set of shared digital systems that-
- Should be secure and interoperable,
- can be built on open standards and specifications to deliver and provide equitable access to public and / or private services at societal scale ,
- are governed by applicable legal frameworks and enabling rules to drive development, inclusion, innovation, trust, and competition and respect human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- What is 'Not' DPI?
- Interventions which are complementary to DPI: E.g., connectivity infrastructure that improves individuals' access to mobile & internet via physical infrastructure.
- Digital processes that may not enable private innovation: E.g., digitizing existing physical processes or workflows to create a government portal.
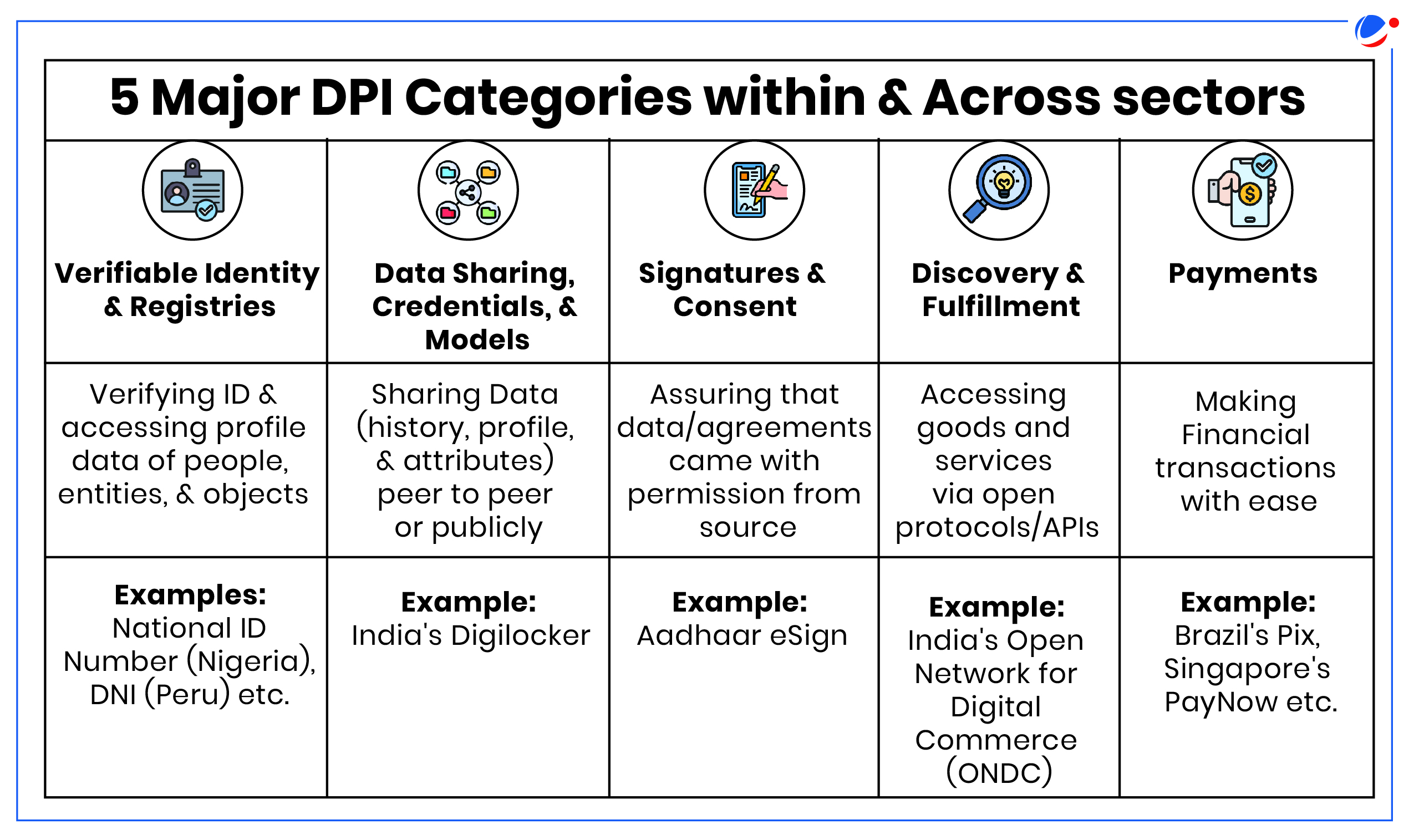
Significance of DPI
- Accelerate Development: It has a high multiplier on economic growth.
- E.g., with its DPI India achieved in less than a decade financial inclusion levels that would have otherwise taken 5 decades.
- Spurs Innovation: By reducing transaction costs, maintaining competition through interoperability, and attracting private capital.
- E.g., PhonePe's (fintech company) growth of $12 Billion is largely due to DPI.
- Inclusive development: DPI inclusively enables vulnerable groups (such as physically remote populations, women, SMEs etc/) to access services, helping close inter- group disparities.
- E.g., Number of Bank accounts opened in India tripled from 147.2 million in 2015 to 508.7 million in 2023 in which women own 55 % of these accounts
- Effective Public Service Delivery: E.g., DPI enabled effective direct benefit transfer across several Central Government Schemes leading to $ 41 billion savings in India.
- Resilient: E.g., During the COVID-19 pandemic, countries worldwide were able to leverage digital vaccination certificates.
- Empowers Individuals: By protecting individuals with economic mobility and key digital rights such as control over their money and data.
- Other factors that highlight DPI's significance:
- Fiscally prudent as it uses a mix of public & private financing.
- Enables maintaining control over critical national infrastructure.
About India's DPI
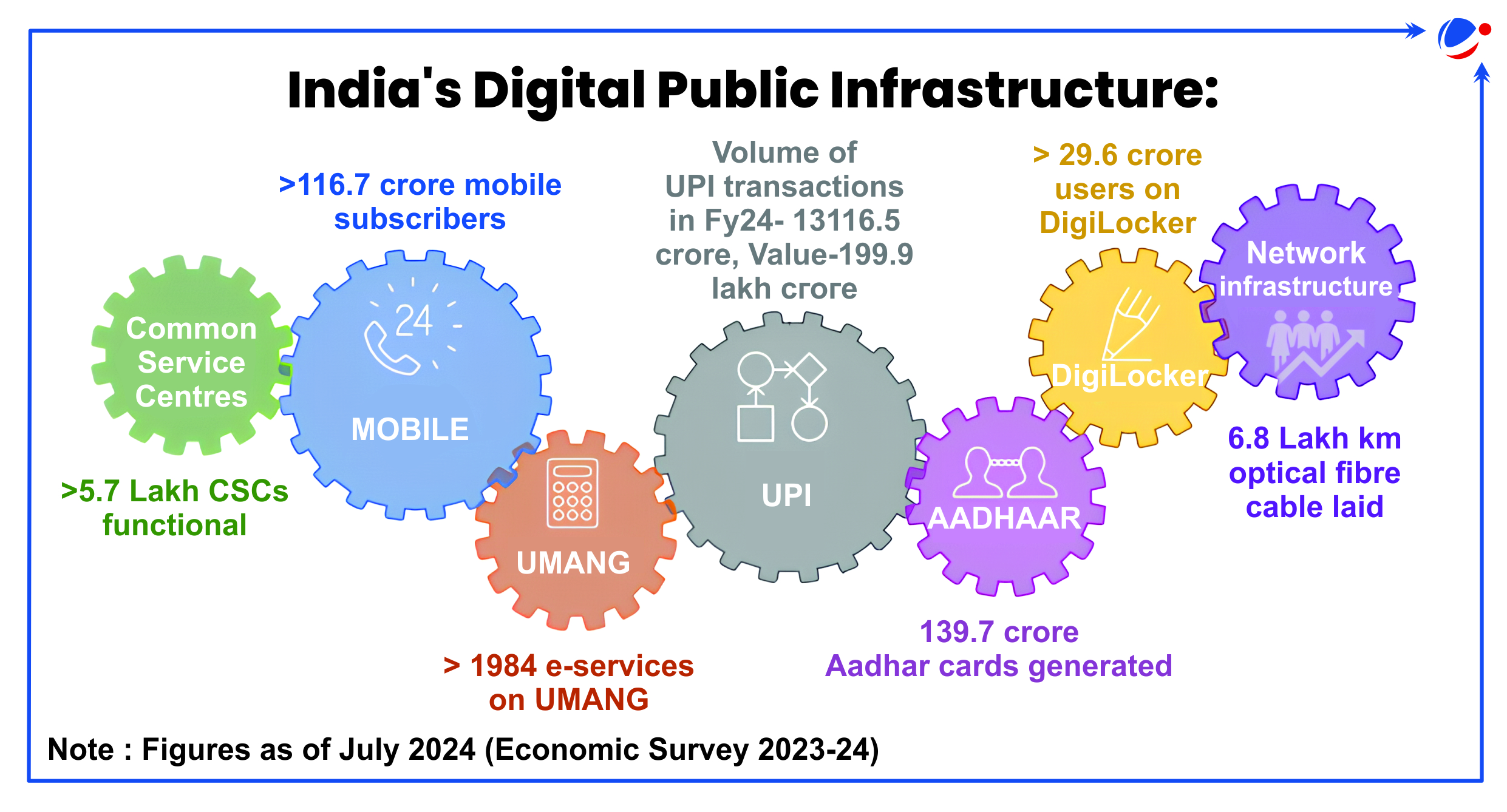 |
Global efforts for DPI
- Digital Economy Working Group (DEWG): First consensus on DPI approach was formally accepted by countries on any international forum.
- One Future Alliance: It's a voluntary initiative proposed by G20 India Presidency, aimed to build capacity, and provide technical assistance and adequate funding support for implementing DPI in Low and Middle-Income Countries.
- Global DPI Repository (GDPIR): Announced the launch at the G20 virtual leaders' summit in 2023 to establish a focused institution working on DPI.
- Social Impact Fund (SIF) was also announced for accelerating DPI implementation across global south nations.
- EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC): India and the European Union agreed to take steps to accelerate the development and deployment of DPI in other countries.
Way Forward
- Adopting 3 pillared DPI Approach suggested by the report.
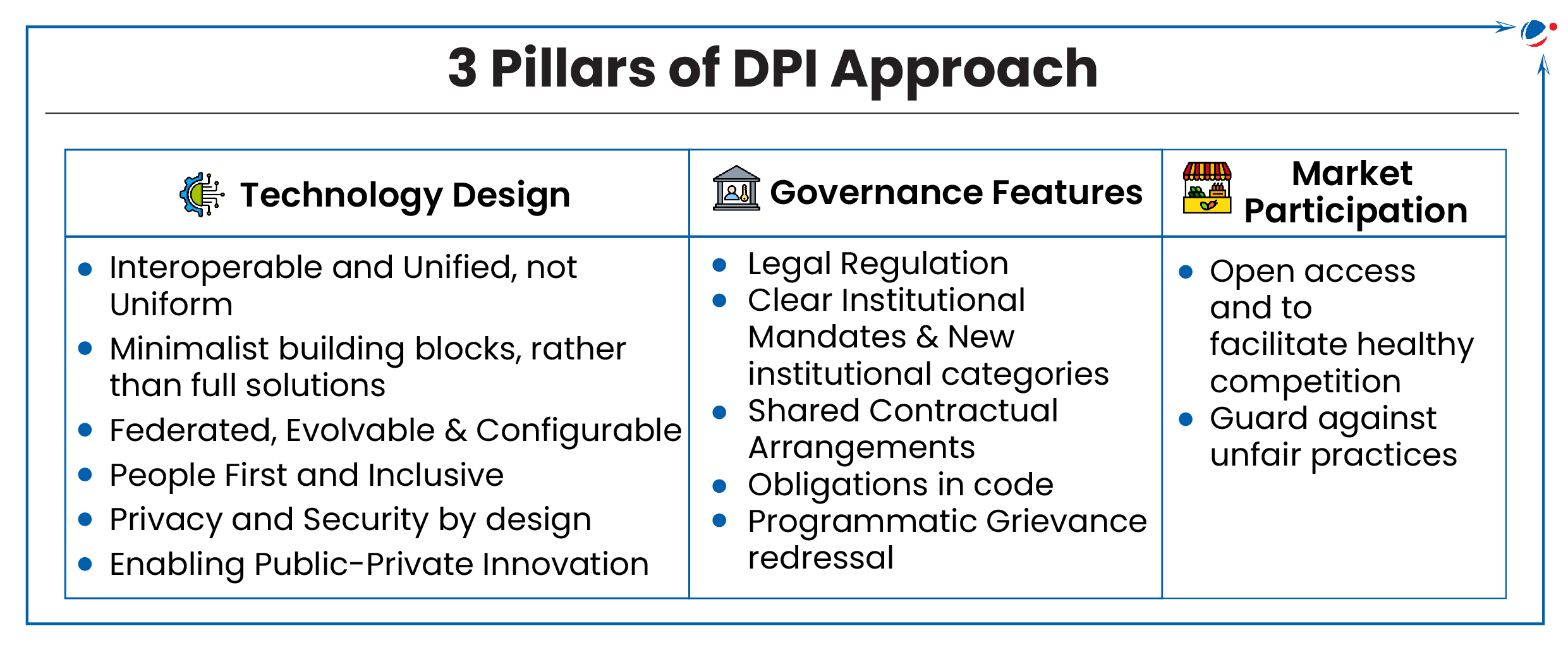
- Comprehensive and Phased Approach informed by in-depth research and analysis of the global digital infrastructure landscape.
- Supporting open & reusable technology frameworks.
- For instance, reusable managed services models can be explored to allow countries to plug and play in order to deploy certain DPI, whilst ensuring countries' sovereignty and data ownership.
- Creating Dialogue and Alignment through an annual DPI forum to share their experiences with deploying DPI.
- Countries of the Global South may come together to establish Global South Forum to discuss and deliberate matters on DPI particularly to their needs and requirements.
- Bilateral or Multilateral Engagement among countries to jointly offer to deploy DPI within the recipient country.
- Focused Institution to work on policy dimensions, formulation and implementation of strategies with appropriate technical and academic expertise.
- Leveraging AI for making DPIs more effective and efficient.
- E.g., AI can help overcome the challenge of limited data availability in Indian languages by enabling language localization using India's Bhasini, a Natural Language Processing (NLP) model







