Why in the News?
Recently, Jammu division of the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) has been witnessing a rise in terrorist incidents.
More on the News
- While terror incidents have been relatively common in Kashmir Valley, resurgence of militant activity in Jammu region, which remained free of such incidents in past two decades, raised concerns among the security establishment.
- Terrorist incidents in Jammu remain far fewer than the Kashmir Valley, yet the frequency and nature of attacks, targeting pilgrims and security forces, is worrying.
Reasons for recent rise in terrorism in Jammu
- Reactivation of proxy-war: Pakistan wants to re-establish its relevance, which was severely diminished after abrogation of Article 370 by the Parliament of India on August 5, 2019.
- Thinning of Security Grid in Jammu: Post-2020 Galwan clashes in eastern Ladakh, large contingent of forces were pulled out of Jammu and deployed along the border with China, making the area vulnerable.
- Security situation in Kashmir: Heightened state of alert provides little scope state-sponsored terrorism in the Kashmir Valley whereas it is convenient to launch terror attacks in Jammu where the guard is relatively down.
- This may also provide militants space to stabilise cadres in the Kashmir Valley.
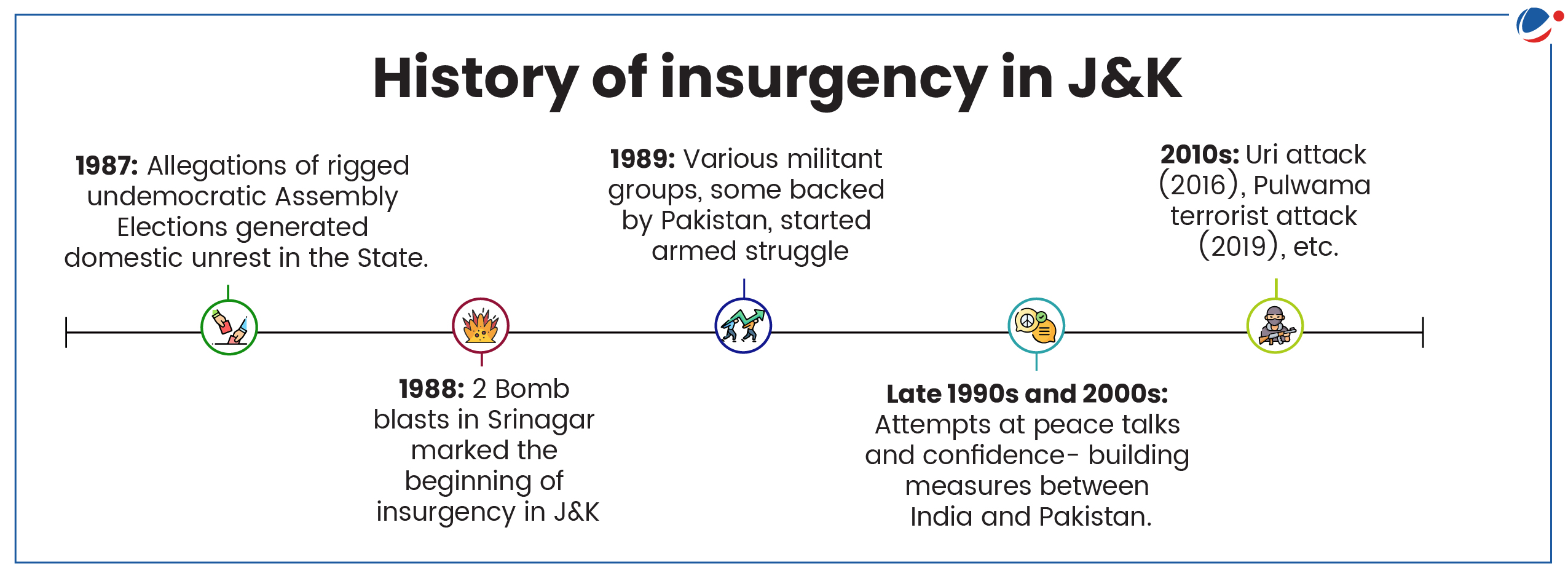
Reasons for persistence of terrorism in J&K
External
- State-sponsored terrorism: Pakistan has been accused of providing logistical support, training, and safe havens to terrorist groups operating in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Porous borders facilitating infiltration: Challenging terrain along the LoC and international borders makes it difficult to completely seal the border, allowing for movement of militants and weapons.
- Ideological influence from global extremist groups: International terrorist organizations have influenced local groups, providing them with ideological frameworks and operational tactics.
Internal
- Political instability: Frequent changes in governance, periods of President's Rule, and absence of democratically-elected popular governments created a power vacuum that terrorist groups exploit.
- Religious and ethnic tensions: Diverse religious and ethnic makeup of the region, including Muslims, Hindus, and various tribal groups, often provide opportunities to terrorist groups to flare up communal tensions.
- State highhandedness and alienation of people: State highhandedness marked by imposition of AFSPA, internet shutdowns, arbitrary detentions, etc., resulted in alienation of local population.
- Over Ground Workers (OGWs): OGWs play significant role in sustaining militancy through fund management, recruitment, propaganda and misinformation, etc.
- OGWs are individuals/ groups who provide logistical support, intelligence, and other non-combat assistance to militant groups without directly participating in armed activities.
- OGWs are difficult to counter due to blurring of lines between civilians and combatants, their community ties, technological adaptation such as use of encrypted communications, etc.
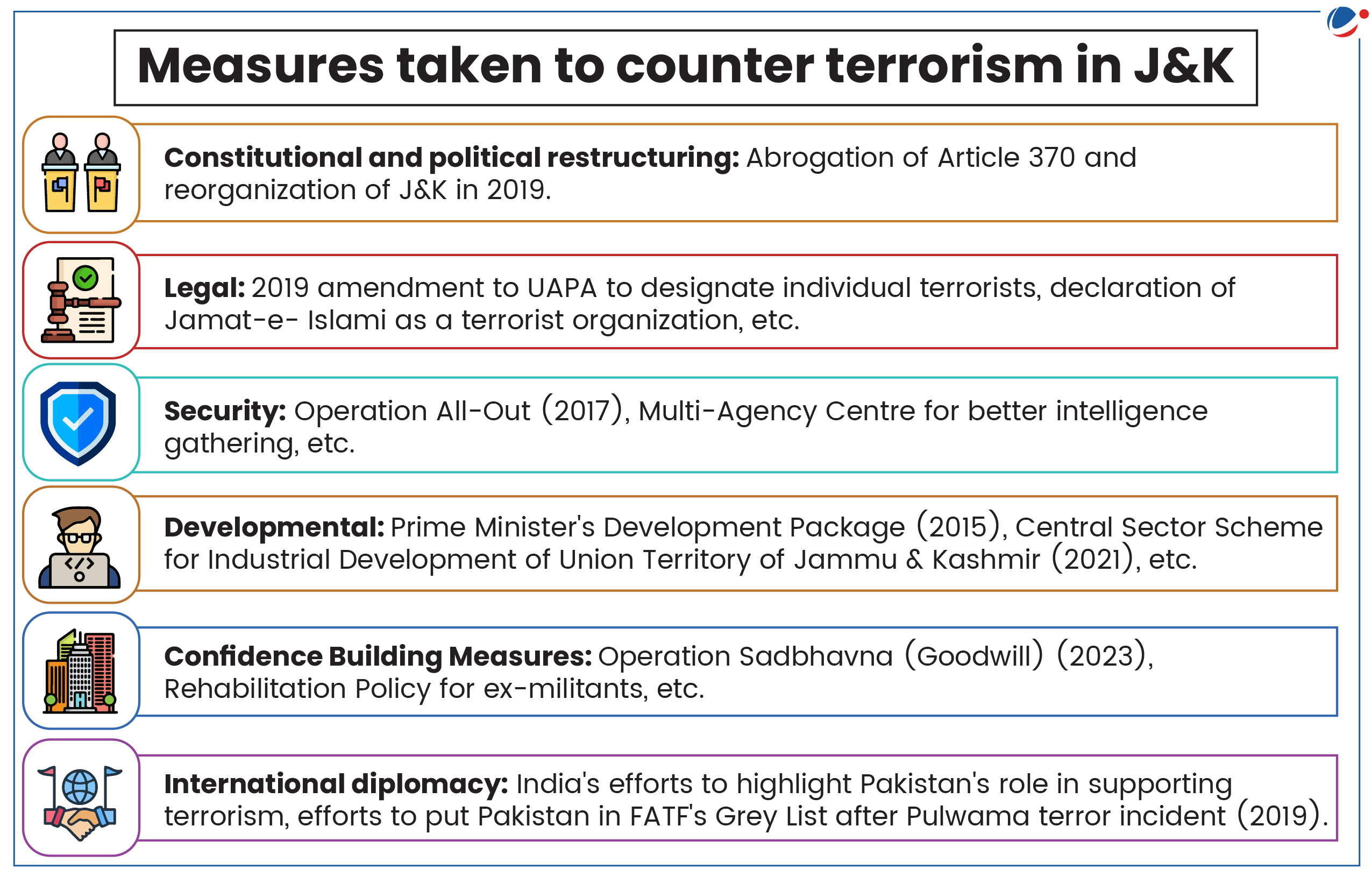
Way Forward
- Political: Ensure conduct of free and fair elections to restore faith of local population in the democratic processes.
- In this regard, recent announcement of assembly election in J&K by the Election Commission of India in September and October 2024 is a step in right direction.
- Strengthening local governance by empowering local bodies and Panchayats can improve transparency and accountability of administration resulting in restoration of faith in institutions.
- e.g., Successful conduct of District Development Council elections in J&K in 2020.
- Security and Intelligence: Army can leverage its strengths to dominate the heights, increase vigilance along the LoC, and tighten border security.
- Enhance intelligence gathering and analysis capabilities with strategies to reinforce HUMINT (Human Intelligence) to complement TECHINT (Technological Intelligence).
- Border Management: Strengthen border infrastructure, strategic deployment of forces, effective use of technology for protection of borders, etc., as per recommendations of the Madhukar Gupta Committee to prevent infiltration.
- Development: Enhanced investment in infrastructure, education, skill development, and promotion of local entrepreneurship to create jobs and opportunities of locals.
- e.g., Jammu & Kashmir Industrial Policy 2021-30 envisions transforming J&K from an aspirational to an industrialized society.
- Confidence Building Measures (CBMs) and counter-radicalization: Undertaking CBMs such as civilian-military cooperation, rehabilitation of former militants, effective grievance redress mechanism, etc.
- Village Defence Guards in the Jammu region are good example of effective civilian-military cooperation.
- Develop community-based programs with involvement of local religious leader to counter extremist narratives and proactively monitor and counter online radicalization.
- Diplomatic: Proactive engagement with the international community to isolate terrorist groups and their sponsor states to seek cooperation in curbing terror financing and cross-border terrorism.
- e.g., India's diplomatic efforts at FATF to highlight Pakistan's role in supporting cross-border terrorism.
To know more about the India's approach towards terrorism, refer to Article 4.2 on India's Anti-Terrorism Approach in October 2023 Monthly Current Affairs Magazine.







