Why in the News?
Recently, India offered aid to disaster-hit pacific Island Nation (Papua New Guinea) showcasing India's commitment to Forum for India–Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC) partnership.
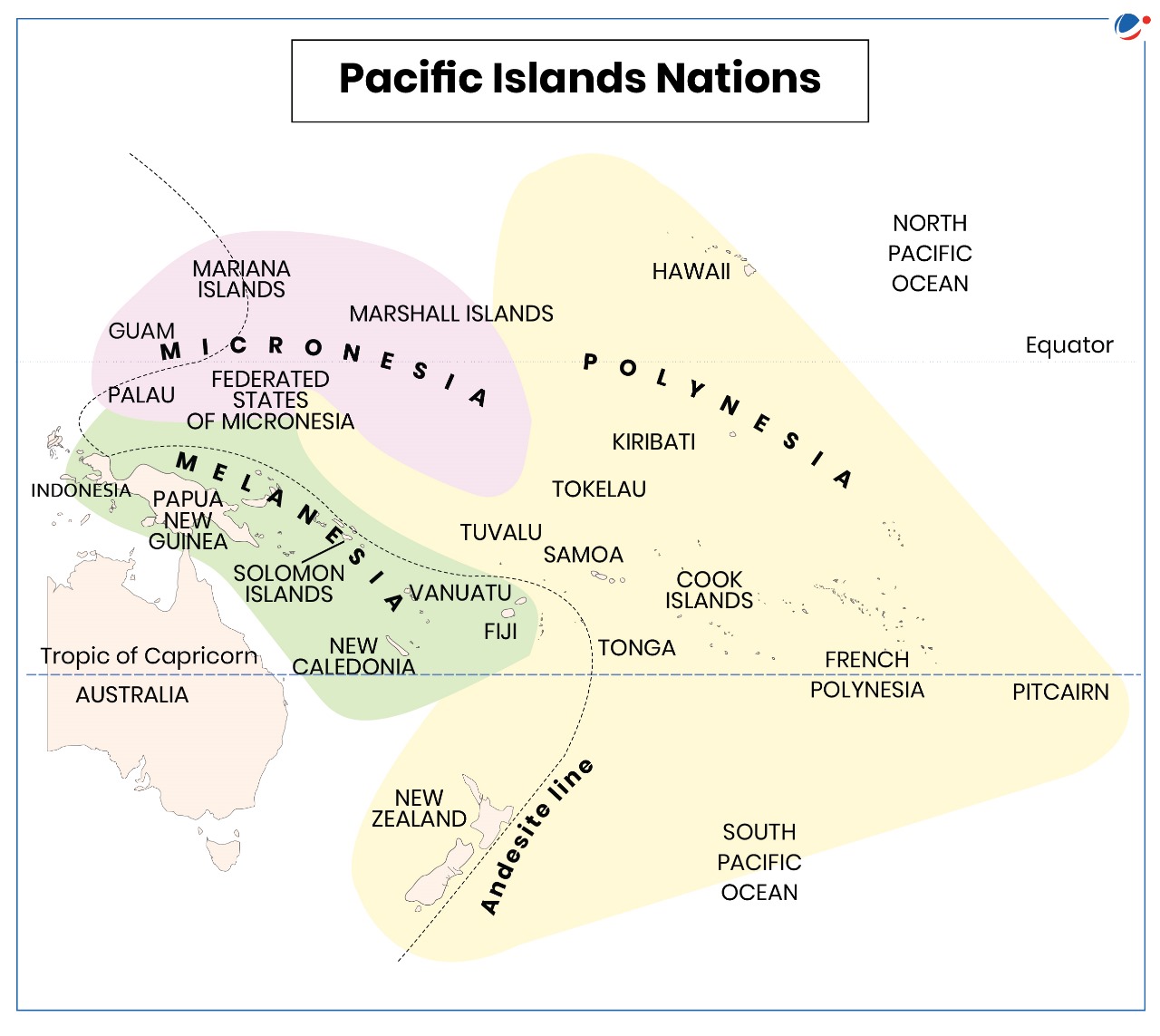
More on the News
- Papua New Guinea has been hit by a massive landslide which caused major destruction and loss of life.
- It is the largest nation by landmass and population among the Pacific Island Nations.
- Pacific Islands Nations are situated in Pacific Ocean and comprised of 3 groupings, i.e., Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia.
Significance of Pacific Islands Nations for India
- Geopolitical:
- Geostrategic Location: It offers India potential avenues for broader maritime strategies and military alliances as Indo-Pacific becomes the new area of Great War Game and Great Power Rivalry (E.g. China and USA).
- Enhance India's Global South Credibility: It provides India with opportunities to advocate for the concerns of developing nations in global forums such as the G-20 and G-7, while also strengthening South-South Cooperation.
- Strengthens India's Economic Leverage:
- Securing Maritime trade: Total trade between India and FIPIC was $571.66 million (2021-22).
- India's pursuit of Resource Security: Large Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) of pacific island nations offers ground for mutually beneficial partnerships in terms of Blue Economy.
- Reformed Multilateralism: These nations can play a major role in building collective stance on shared concerns at global level. E.g. India's permanent seat at UNSC.
- Indo-Pacific Strategy: The Pacific Islands are crucial to India's broader Indo-Pacific strategy, which aims to ensure a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
- India's International commitment to Climate Change: E.g. some of these nations have joined International Solar Alliance (ISA) and India has encouraged other nations to join Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Strong Diaspora Presence and Historical connections:
- Nations such as Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, share connection with India as former British colonies.
- More than 1/3rd of Fiji population are of Indian origin
About FIPIC
|
India's engagement with Pacific Island Nations
- Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI,2019): It is an open, non-treaty based global initiative, which seeks to manage, conserve, sustain, and secure the maritime domain in the region.
- Grant-in-aids and Concessional Line of Credits: For renewable energy and climate projects.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR): E.g. Supply of Vaccines during COVID-19.
- Facilitation in Election Processes: E.g. supply of indelible ink to Papua New Guinea
- Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC): E.g. Sagar Amrut Scholarship Scheme for 1000 training opportunities in FIPIC.
- India-UN Development Partnership Fund (2017: It provides assistance to Least Developed Countries (LDCs) and Small Island Developing States (SIDS)
- Community Development:
- E.g. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between India and Marshall Island to fund community development projects in the Marshall Islands.
- 12-Step Action Plan by India for healthcare support. E.g. Super Specialty Cardiology Hospital (Fiji).
Challenges in Cooperation
- Geopolitical Competition: Increased China's strategic foothold poses a challenge to India's influence in the region.
- E.g. China signed security pact with Solomon Islands (2022)
- Resource Constraints: India's need for domestic investment may restrict its ability to provide substantial international aid and deep global engagement.
- Large Geographical Distance: The vast geographical distance between India and the PINs makes regular diplomatic engagements and the implementation of joint projects difficult.
- Heightened Vulnerabilities: These nations face disproportionate impact in terms of vulnerability of coastal and commercial centres due to natural disasters, supply chain disruptions etc.
- Exclusion from policy discussions at global level: Although, crucial to great power competition these nations are frequently excluded from global policy discussions about the region. (E.g. QUAD, AUKUS)
Way forward
- Strengthening Diplomatic Engagement: Regular high-level dialogues and consistent outreach policies to increase diplomatic presence and ensure sustained engagement.
- Collaboration on Climate Resilience Projects: India can demonstrate its leadership in addressing climate change issues by offering technology and expertise.
- Maritime Cooperation: India can collaborate on issues like illegal fishing, piracy, and marine pollution, contributing to regional and global stability.
- Enhanced Economic Partnerships: Strategic resource allocation in infrastructure and sustainable development, along with a regular review mechanism, can strengthen economic ties and ensure progress.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Fostering people-to-people exchanges can deepen historical and cultural ties, building long-term relationships.
- Demand driven cooperation model: India can focus on demand-driven projects in IT, cyber security, desalination, and digital public goods, ensuring they meet the specific needs of Pacific Island nations.





