Why in the News?
Government approved Mutual Credit Guarantee Scheme to Strengthen MSME Manufacturing Sector, fulfilling the budget announcement of 2024-25.
Key Features of Mutual Credit Guarantee scheme for MSMEs
- Guarantee Coverage: Offers 60% guarantee coverage by National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Limited (NCGTC) (a wholly owned company of Department of Financial Services) to MLIs for loans sanctioned under MCGS-MSME.
- Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) are Financial Institutions such as Commercial Banks, NBFCs registered with NCGTC under the Scheme.
- Eligible Borrower: MSME with valid Udyam Registration; Not a Non-Performing Asset with any lender; Minimum 75% of project cost for equipment/machinery.
- Duration of the Scheme: Available for 4 years or until Rs 7 lakh crore in guarantees are issued, whichever is earlier.
- Repayment Terms:
- Loans up to ₹50 crore: Repayment period of up to 8 years, with a moratorium of up to 2 years on principal installments.
- Loans above ₹50 crore: Longer repayment schedules & moratorium periods can be considered.
Other Key Measures Announced for MSMEs in Union Budget 2025-26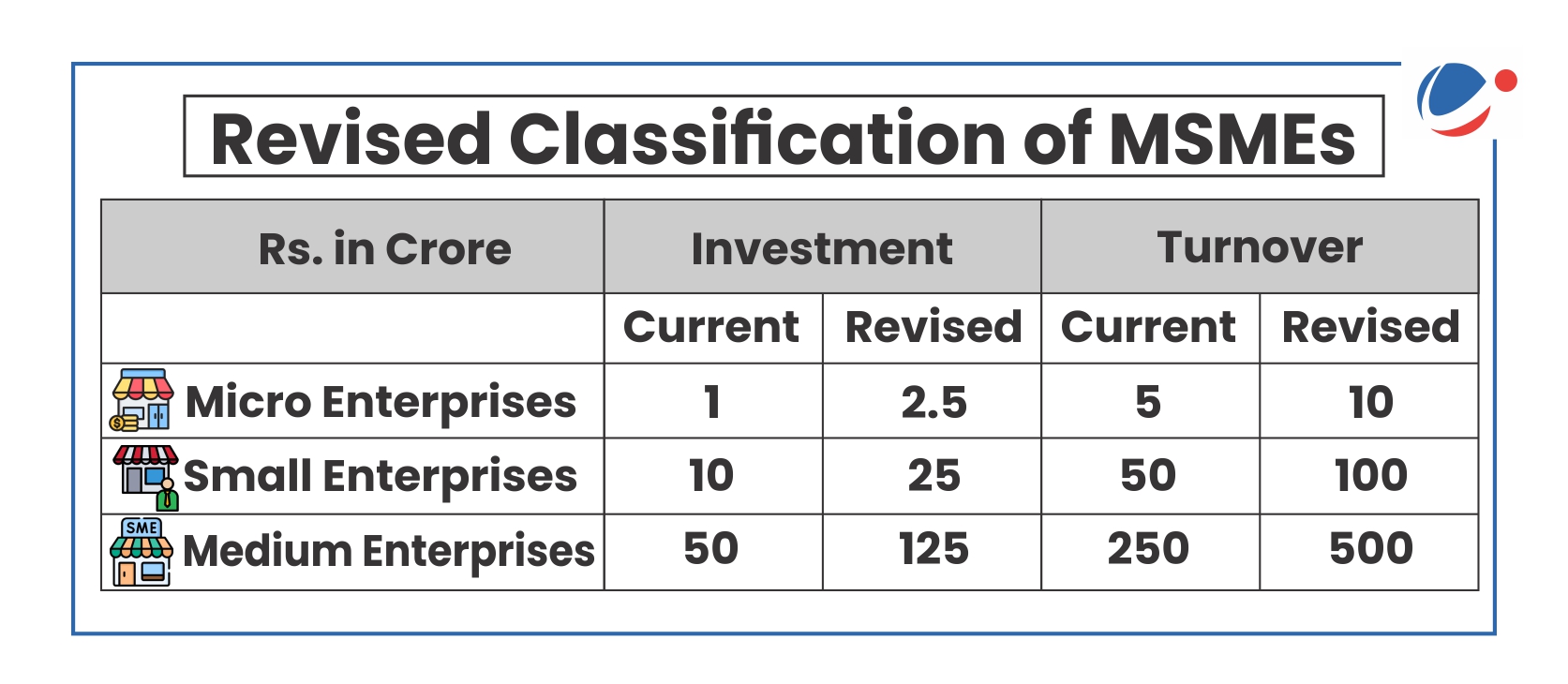
|
Significance of MSMEs for India
- Contribution to GDP: MSMEs contributes approximately 30 % of the country's GDP, 36 % to the country's manufacturing output.
- Employment: India has over 1 crore registered MSMEs, employing nearly 7.5 crore people.
- Foreign Currency: MSMEs contribute ~45% of India's total exports.
- Reduces Disguised Unemployment: Absorbing the surplus agricultural labour, they help to reduce the problem of disguised unemployment in rural areas.
- Disguised unemployment is a situation where more people are employed than are required for a job or role. It's also known as hidden unemployment or labor hoarding.
- Rural Development: Around 50% of the total MSMEs operate in rural areas and provide 45 % of total employment.
Challenges Faced by MSMEs
- Finance issues: Informal nature of MSMEs, credit assessment difficulties due to information gaps, absence of collateral etc. make it difficult for MSMEs to secure loans.
- Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Poor roads, unreliable power supply, and inadequate digital infrastructure hinder business operations.
- Delayed Payments: A large number of MSMEs are cater to the needs of large industries, both in public and private sector. But they face delayed payments, impacting cash flow and working capital.
- Regulatory & Compliance Burden: Complex taxation, labor laws, and frequent policy changes increase operational difficulties.
- Limited Integration of Technology: Affects productivity and competitiveness.
- Export issues: Inadequate infrastructure, Lack of Environmental, social and governance (ESG) reports by Indian MSMEs impacts exports competitiveness.
Initiatives Undertaken for MSMEs
|
Way Forward
- Policy Support: Consistent and supportive government policies that address the specific needs of MSMEs, including tax incentives and infrastructure development.
- Assist MSMEs embrace best business practices in line with the fast-changing business environment.
- Addressing Credit Gaps: Assess credit worthiness of MSMEs by utilising unexplored data sources like digital transaction trails & data generated through e-commerce sites to expedite lending.
- Technological Adoption and Digitalization: Providing training and resources for digital literacy, promoting e-commerce platforms, and encouraging the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Market Access and Expansion: Facilitating participation in trade fairs and exhibitions, promoting exports, and creating platforms for B2B networking.
- Simplification of Regulatory Framework: Reducing bureaucratic hurdles, streamlining compliance procedures, and creating a business-friendly environment.
- Integration with Global Value Chains (GVC): Being part of GVC would enable MSMEs to produce quality goods and services which will have greater acceptability in the global market.
- Promoting the formation of MSME clusters: To enhance collaboration, resource sharing, and collective bargaining power.







