RBI has issued revised guidelines capping investment by Regulated Entities at 20% of the corpus of an AIF scheme.
About Alternative Investment Fund (AIF)
- Any fund established or incorporated in India which is a privately pooled investment vehicle which collects funds from sophisticated investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investing it in accordance with a defined investment policy for the benefit of its investors.
- AIFs are regulated by the SEBI, as per the SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
Categories of AIFs
- Category I AIF: Invest in start-ups, early-stage ventures or sectors considered socially or economically beneficial.
- E.g. Venture Capital Funds, Angel funds, SME Funds, Infrastructure Funds
- Category II AIF: They do not use leverage or debts other than to cover their day-to-day operational expenses.
- E.g. Private Equity Funds, Debt Funds, Real Estate Funds.
- Category III AIF: It may use leverage including through investment in listed or unlisted derivatives.
- E.g. Hedge Funds, Private investment in public equity (PIPE).
The Indian digital payment landscape has witnessed over 65,000 crore digital transactions amounting to more than Rs. 12,000 lakh crores in the last 6 Financial years.
About DPI
- RBI has developed the DPI (published Semi-annually) to measure the extent of digital payment adoption across India.
- DPI comprises these broad parameters: Payment Enablers; Payment Infrastructure – Demand-side factors & Supply-side-factors; Payment Performance; Consumer Centricity.
- The latest RBI-DPI indicates over fourfold growth in digital payment penetration since 2018.
A study of RBI has proposed the construction of a FCI for India to track market trends with daily frequency.
About Financial Conditions Index (FCI)
- It assesses the degree of relatively tight or easy financial market conditions with reference to its historical average since 2012.
- The chosen indicators represent five market segments: money market, G-sec market, corporate bond market, forex market, and equity market.
- A higher positive value of the FCI indicates tighter financial conditions.
The World Bank report titled ‘Global Findex 2025’ released reflecting achievements in digital and financial inclusion.
India specific Highlights
- India has account ownership at or close to 90 percent.
- 16 percent of account owners do not have an active account, the average for all other low- and middle-income economies is 4 percent.
- The share of both women and men with only inactive accounts decreased between 2021 and 2024.
- The primary barrier to mobile phone ownership is the cost of the device, and lack of reliable mobile network coverage.
Article Sources
1 sourceGENIUS Act has been enacted in the US to establish a regulatory framework for stablecoins.
- Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency whose value is linked to that of another currency, commodity, or financial instrument. E.g., Tether (USDT), is pegged to the US dollar
- They have the potential to bring efficiencies to payments.
Why has the use of Stablecoins increased?
- Linked to an underlying asset: Due to this, they can maintain a steadier value, making them a more reliable medium of exchange than other volatile cryptocurrencies like bitcoins.
- Underlying assets are backed by an identifiable issuer, unlike many unbacked crypto assets.
- Issuers could be banks, nonbank financial entities, and large technology conglomerates.
- Regulation: Decisions for stablecoin arrangements are usually taken by a governance body.
Regulation of Cryptocurrency or Cyrpto Assets in India
- Currently, Crypto Assets are unregulated in India.
- However, Government, through the Finance Act, 2022, brought a comprehensive taxation regime for the transfer of Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs).
- It imposed a 30% tax on capital gains from VDAs.
- The Income Tax Act 1961 defines VDA as any information or code or number or token, generated through cryptographic means or otherwise; transferred, stored, or traded electronically. E.g. cryptocurrencies, Non-fungible token (NFT), etc.
- In 2023, VDAs were brought under the purview of the Prevention and Money-laundering Act, 2002.

Article Sources
1 sourceThis initiative is part of digital innovations in agriculture for fostering financial resilience.
About CROPIC (Collection of Real Time Observations & Photo of Crops) initiative
- It is a mobile app launched by The Ministry of Agriculture under Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY).
- To take geotagged pictures of crops four-five times during their cycle.
- It will use an AI-based cloud platform for photo analysis and information extraction, and a web-based dashboard for visualisation.
- Funding: Through Fund for Innovation and Technology (FIAT) under PMFBY.
Article Sources
1 source- Released By: OECD and FAO.
- Provides a comprehensive assessment of the ten-year prospects for agricultural commodities (Including fish) and their markets at national, regional, and global levels.
- Global Market Trends (2024) according to the report
- Biofuels: Its demand is projected to grow at 0.9% annually, led by India, Brazil and Indonesia.
- Cotton: Global use increased; India is set to overtake China as the top producer.
Article Sources
1 source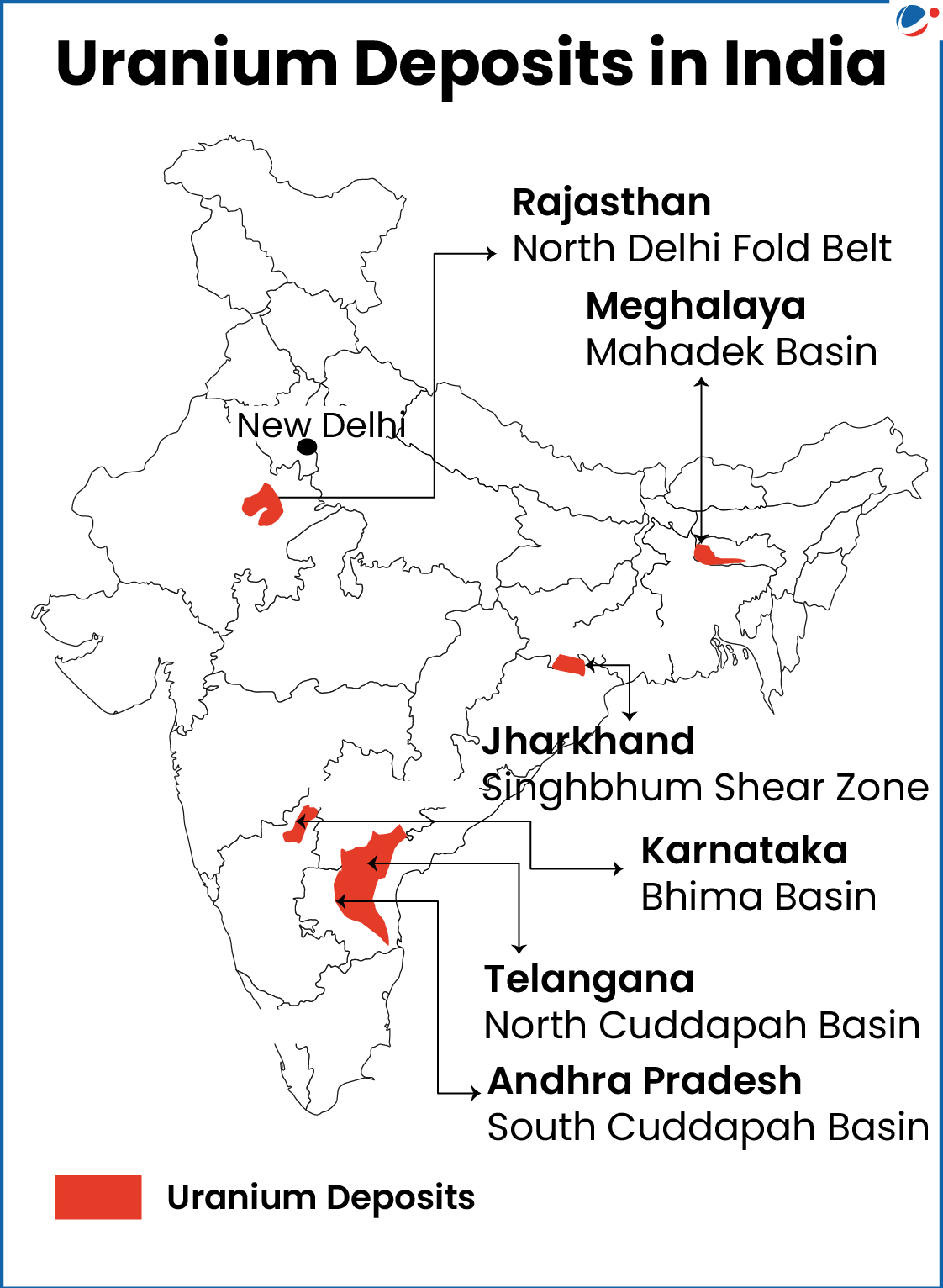
These rules are notified in accordance with the provision of the Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002.
About the Rules
- Objective - To regulate the exploration and mining of atomic minerals like uranium and thorium in offshore areas
- Rules will only apply if concentration of atomic minerals above a certain minimum level.
- Under the rules entities nominated by Govt can be granted exploration licences or production leases.
- In case of foreign entities, undertaking exploration operations, prior approval shall be obtained from the Government authorities.
Key Atomic Minerals in India
- Uranium
- Key Reserves: Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Meghalaya, Rajasthan etc.
- Jaduguda (Jharkhand) is the first mine in the country to produce uranium ore on a commercial scale.
- Other Important Mines: Lambapur-Peddagattu (AP), Bagjata mine (Jharkhand), etc.
- Most of uranium deposits in India small and of far lower grade compared to those in the leading uranium-producing countries in the world.
- Thorium
- India has a limited resource of uranium but a large resource of thorium.
- Monazite contains about 8 – 10% thorium.
- The beach sands of Kerala and Orissa have rich reserves of monazite.
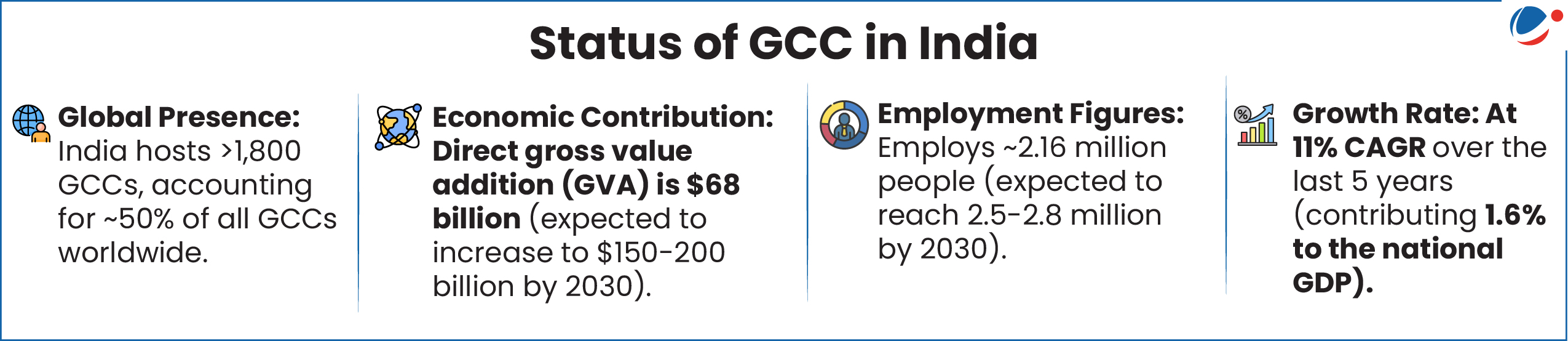
The Finance Minister urged industry & government to work together to boost the setup of GCC and attract more Fortune 500 companies which are yet to establish their presence in India. (On an average 1 new GCC per week was set up in the year 2024)
About GCCs
- It is also known as global in-house centres or captives (GICs).
- GCCs are offshore centres established by global firms to provide various services to their parent organisations.
- E.g. IT services, Research and Development (R&D), customer support
- They operate within the internal organization structure of the global corporate organization.
- Major Drivers in India: Cost efficiency, Digital and Policy Readiness (e.g Smart Cities, Digital India), Talent availability (Highly skilled & cost-effective workforce with english proficiency), Large Consumer Market etc.
Challenges in development of GCCs in India: Limited availability of skilled workforce (in Tier-II and III cities), Infrastructure gaps (physical and digital connectivity), Complex regulatory structures, cybersecurity threats.
Strategic Interventions Required
- Embrace Next-Gen Technologies: e.g. AI, automation, cloud computing etc.
- Navigate Geopolitical Complexities: Adopt agile governance models to respond swiftly to complex geopolitical scenarios and resulting regulatory uncertainty.
- Redefine Workforce Strategies: Upskilling of talent, adoption of new-age skills and hybrid work models.
- Sustainability: Aligning GCCs with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals.
Article Sources
1 sourceNTP-2025 seeks to build on progress made under National Digital Communications Policy 2018.
- It addresses emerging challenges by next-generation technologies such as 5G/6G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Quantum Communications, Satellite Network, and Blockchain.
- It positions India to become “Nation of Choice” for Telecom Technology, under the vision of “Bharat – A Telecom Product Nation”.
About NTP-2025
- Vision: transform India into a digitally empowered economy by ensuring universal and meaningful connectivity, building secure and sustainable telecommunications networks.
- Mission: It outlines six strategic missions:
- Universal and Meaningful Connectivity: Expand telecom networks, improve service quality, and integrate technologies to ensure inclusive digital participation.
- Innovation: Promote research, startups and strengthen industry -academia -government.
- Domestic Manufacturing: Boost economic growth through skilled workforce, investments, and design-led manufacturing.
- Secure and Trusted Telecom Network: Enhance security, promote cyber hygiene, and build a resilient, trustworthy telecom ecosystem.
- Ease of Living and Ease of Doing Business: Simplify telecom access, foster digital inclusion, and create a business-friendly environment.
- Sustainable Telecom: Promote green technologies, circular economy, and renewable energy to reduce telecom’s environmental impact.

Article Sources
1 sourceCentral Government recently unveiled Aluminium and Copper Vision Documents.
About Vision Document
- Provides a long-term strategy to meet growing domestic demand while ensuring raw material security.
- Copper Vision Document: Anticipates a six fold increase in demand by 2047 and outlines plans to add 5 Million Tonnes Per Annum (MTPA) of smelting and refining capacity by 2030.
- Aluminium Vision Document: Outlines a strategic roadmap to scale up aluminium production six fold by 2047 and aims to expand bauxite production capacity to 150 MTPA.
Distribution of Copper and Aluminium
Aluminium/Bauxite
- India
- Reserve: Odisha (41%) followed by Chhattisgarh and Andhra Pradesh for bauxite.
- Odisha is leading producing State (73%).
- World
- China is the leading producer of aluminium (58%) which is followed by Australia,Brazil and India.
Copper
- India :
- Reserves: Rajasthan (52.25%) followed by Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- Production: Madhya Pradesh was the leading producer (57% of the production during 2022-23), followed by Rajasthan (43%).
- World
- Chile has the largest share (19% of world reserves) followed by Peru and Australia (10%).



