Why in the News?
India and the UK signed the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA), marking a major milestone in their partnership.
More in the News
- Major developments apart from CETA:
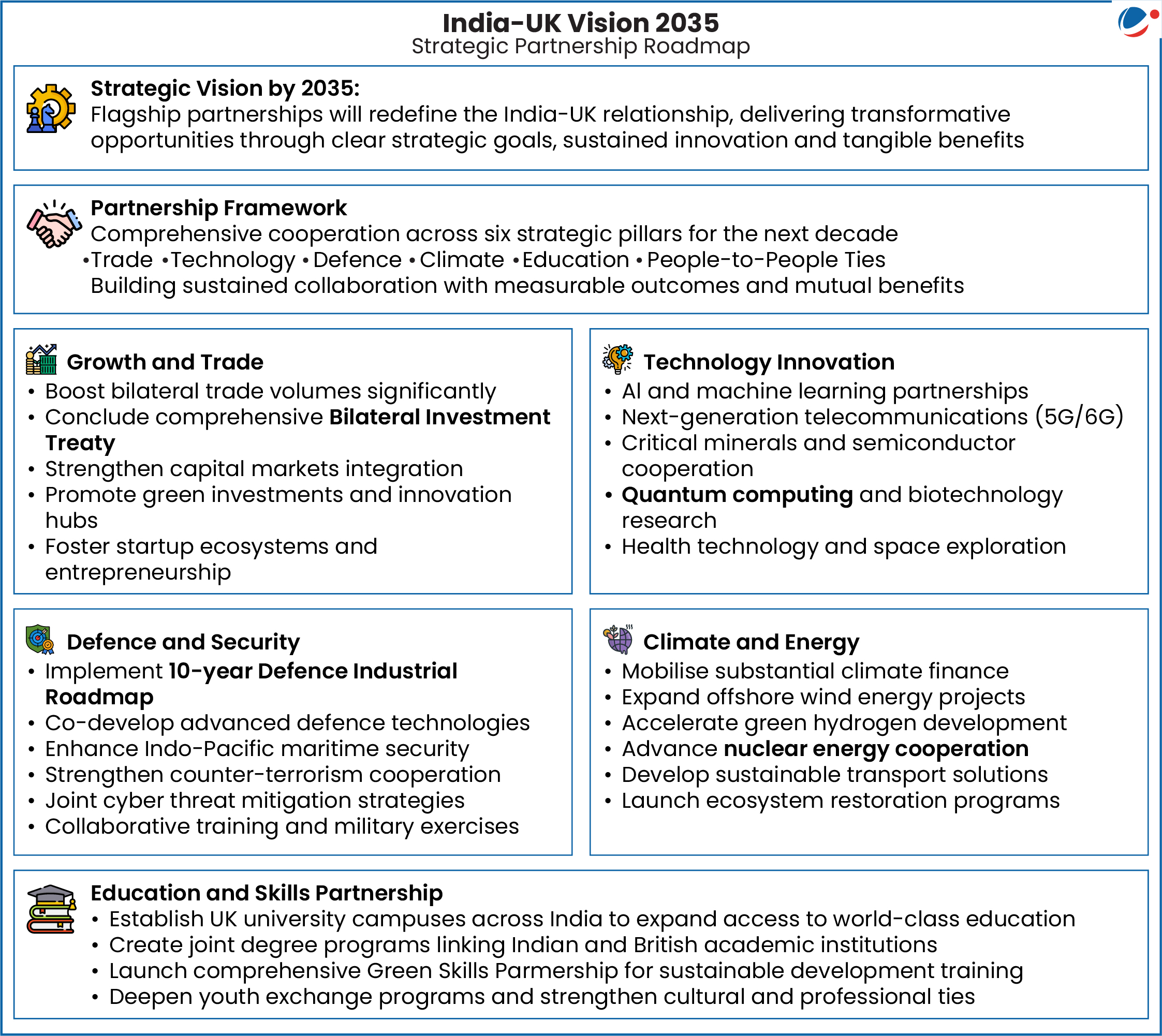
- India-UK Vision 2035 was adopted to guide cooperation for the next decade in the economy, technology, defence, climate, health, and education.
- Defence Industrial Roadmap adopted for co-design, co-development, and co-production of defence products.
Key Highlights of the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement
- Comprehensive Tariff Elimination and Market Access
- Tariff Elimination: Over 99% of tariff lines will be eliminated, covering almost India's entire trade basket.
- Meanwhile, India has opened 89.5% of its tariff lines, covering 91% of UK exports.
- Sensitive Sector Safeguards: India has safeguarded sensitive sectors like dairy, cereal, millets, gold, jewellery, lab-grown diamonds, etc.
- Bilateral Safeguards: Measures to control sudden import surges that could hurt domestic industries.
- Services
- Deep Market Access: Wider entry for Indian IT, finance, education, and healthcare services.
- Comprehensive Commitments: India has secured wide-ranging commitments from the UK, covering all 12 major service sectors.
- Mutual Recognition and Professional Mobility
- Mutual Recognition Agreement: Both countries will recognise professional qualifications in areas like nursing, accountancy, and architecture within a year, easing mobility and reducing barriers.
- Temporary Entry for Professionals: UK allows Indian business visitors, intra-corporate transferees, service suppliers, independent professionals, and investors to stay from 90 days to 3 years, with possible extensions.
- Double Contribution Convention (DCC): It exempts Indian workers and their employers from social security contributions in the UK for up to three years when on temporary assignments.
- Simplified Rules of Origin: Exporters can self-certify product origin, small consignments under £1,000 need no documents, and Product Specific Rules of Origin (PSRs) align with India's current supply chains for key sectors such as textiles, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and processed food.
Significance of CETA for India
- Export growth: Expected 20-40 per cent rise in exports in key sectors such as textiles, jewelry, machinery, etc.
- Geographical Indication protection: Protection for Indian Geographical Indication (GI) products like feni, toddy, and Nashik wine.
- Market Access: The agreement opens the UK's $37.5 billion agricultural import market to Indian producers, with over 95% of agricultural and processed food items gaining duty-free access.
- Worker Benefits: CETA upholds labour rights, ensuring awareness, access to fair tribunals, and transparent enforcement.
- Women workers will gain from provisions on non-discrimination and gender equality in the workplace.
- MSME and regional growth: Trade boost will benefit key hubs like Tiruppur (textiles), Kolkata (leather), and Surat–Bharuch (chemicals).
Significance of India-UK Relations
- Economic Cooperation: Bilateral trade stands at USD 56 billion, with the goal of doubling it by 2030.
- Investment: The UK is the 6th largest inward investor in India, with a cumulative equity investment of US $ 35 billion till September 2024.
- Geo-Political: Cooperation in multilateral forums such as the UN, UNSC, G20, Commonwealth, and the Indo-Pacific enhances mutual interests.
- The UK supports India's bid for a permanent seat in the UN Security Council.
- Defence Cooperation: India and the UK hold regular military exercises, including Konkan (naval), Cobra Warrior (air), and Ajeya Warrior (army).
- Indian Diaspora: The UK has a large Indian diaspora of 1.864 million as per the 2021 UK Census.
- Education cooperation: Several UK universities plan to open campuses in India, with the University of Southampton's Gurugram campus being the first under the New Education Policy.
- Around 170,000 Indian students are currently studying in the UK.
- Health Cooperation: E.g., The joint research and development of the COVID-19 vaccine, under a licensing agreement between UK-based AstraZeneca and Serum Institute of India.
- India-UK Framework agreement for collaboration on health care workforce supports recruitment and training of Nurses, Allied Health Professionals, etc.
Concerns in India-UK Relations
- Divergent Foreign Policy Positions: For example, their stances on the Russia-Ukraine conflict are different.
- UK's Domestic Politics: UK political debates over Kashmir and comments on India's internal matters have occasionally created friction, influencing diaspora relations.
- Khalistan Separatism: India is concerned over the activities of pro-Khalistan elements in the UK, which it sees as a threat to its sovereignty.
- Extradition hurdles: Despite an extradition treaty, legal delays keep high-profile fugitives like Vijay Mallya in the UK, straining bilateral trust.
Conclusion
The CETA, anchored within the India-UK Vision 2035, marks a pivotal milestone in bilateral ties, expanding cooperation in trade, technology, defence, climate, and education. With the UK's global influence as a P5, G7, and Five Eyes member, and India's position as the fastest-growing major economy, both nations stand at a strategic inflection point. By leveraging synergies in a volatile global order and advancing joint initiatives under Vision 2035, India and the UK are poised to elevate their partnership to unprecedented levels while addressing long-standing challenges.




