SDGR is the only UN official report that monitors global progress on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Key highlights of the Report
Goal 1: No poverty |
|
Goal 2: Zero hunger |
|
Goal 4: Quality education |
|
Goal 5: Gender equality | Globally, women occupy less than a third of managerial positions. |
Goal 8: Decent work and economic growth |
|
Goal 10: Reduced inequalities | In 2024, 57% of working-age people were employed worldwide, impacting the lives of 3.6 billion workers and their families. |
Goal 11: Sustainable cities and communities | Up to 3 billion people worldwide struggle to afford a place to live, and 1.12 billion live in slums or informal settlements. |
Goal 13: Climate action | 2024 marked the hottest year on record, at approximately 1.55°C above pre-industrial levels. |
Goal 16: Peace, justice and strong institutions | In 2024, nearly 50,000 lives were lost to conflict and 123.2 million people were forcibly displaced. |
Article Sources
1 sourceNIF launched by MoSPI reflects India’s commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and serves as the backbone for monitoring SDGs at the national level.
Key Progress Highlighted in the Report
Zero Hunger (SDG 2) |
|
Clean Water and Sanitation (SDG 6) |
|
Clean Energy (SDG 7) |
|
Decent Work and Economic Growth (SDG 8) |
|
Industry and Innovation (SDG 9) |
|
Reduced Inequality (SDG 10) |
|
Responsible Consumption (SDG 12) |
|
Life on Land (SDG 15) |
|
MoEFCC Issued Draft Emission Targets Rules for Industries Under Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS).
- Draft Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emission Intensity Target Rules, 2025 are issued under the compliance mechanism of CCTS.
About Draft Rules
- Defines Greenhouse gas emission intensity (GEI) as tonnes of CO2 equivalent emitted per unit of output or product.
- Proposes legally binding GHG emission targets for over 400 industrial units.
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) will determine the emission targets.
- Applies to sectors such as aluminium, iron and steel, petroleum refining, petrochemicals, and textiles.
- Failure to comply will result in financial penalties under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 (EPA 1986).
About CCTS
- Goal: Lower GHG emissions by promoting carbon pricing (i.e., imposes a cost on GHG emissions)
- Legal Backing:Energy Conservation Amendment Act (ECA), 2022 empowers the Central Government, in consultation with BEE, to specify the CCTS.
- Key elements:
- Compliance Mechanism (For Obligated Entities): Obligated entities that emit less than their target get Carbon Credit Certificates.
- Voluntary Offset Mechanism: Enables other sectors to register their projects for GHG emission reduction, removal, or avoidance, in exchange for the issuance of Carbon Credit Certificates.
- Administrator: BEE
- Regulator of Carbon Trading: Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC)
- Significance: Stepping stones for Indian Carbon Market and aligns with India’s obligations under UNFCCC and Paris Agreement.
World Bank’s “State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2025” report has recognized India’s growing role in shaping global climate finance and carbon pricing frameworks.
Article Sources
1 sourceUsing the power under Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, the MoEFCC has notified the Environment Protection (Management of Contaminated Sites) Rules, 2025.
- Rules will ensure that polluted sites are cleaned up (remediation) by those responsible.
- Contaminated sites are areas where hazardous waste has been previously disposed of, polluting the soil and water and posing risks to health and the environment.
Key highlights of the Rules
- Contaminants Covered: 189 hazardous substances as per Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016.
- Exclusions: Contamination from radioactive waste, mining, oil spills at sea, and solid waste dumps (governed by separate legislation).
- Response levels: Different response levels are set for agricultural, residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
- Contaminated Site Management
- Site Identification: Local bodies/District Administrations must report suspected sites twice a year to State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs)
- Site Assessment: SPCBs shall inspect the suspected sites and list of probable contaminated sites and inform to the CPCB on the centralised online portal.
- Polluter Identification: SPCBs identify the polluter. If land is sold, the new owner is liable.
- Clean-Up Plan: Polluter must carry out a clean-up plan using an approved agency, and pay for it.
- However, in case the polluter is not identified, SPCB execute clean-up plan.
- Funding for assessment and remediation: Initial assessment costs may be covered by the Central Government from the Environmental Relief Fund under Public Liability Insurance Act, 1991 and also by the State Government.
- If the polluter is found, these costs must be repaid within 3 months.
- Penalties: The State Board may impose fines for failure to clean up, especially if health is at risk.
Rules address the legal vacuum around the remediation of legacy pollution sites while also providing provision for voluntary remediation.
The report was released by Secretariat of the Ramsar Convention.
Key Highlights
- Coverage: Inland freshwater, coastal, and marine wetlands extend over 1,800 million hectares.
- Wetland Degradation: 22 per cent of the world’s wetlands have been lost since 1970.
- More wetlands are reported as being in poor condition for lower income/lower middle income countries (LICs/LMICs).
- Africa's wetlands are among the most degraded globally.
- The Ramsar Convention’s strategic goals align with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KM-GBF) Targets.
- KM-GBF is a non-binding framework adopted at the 15th Conference of Parties (COP) to the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- Threats faced by Wetlands includes unplanned urbanisation, rapid industrial and infrastructure development.
Best Case Studies
- Regional Flyway Initiative, a US$3 billion partnership across Asia, is restoring more than 140 wetlands critical to migratory birds and nearly 200 million people.
- Seychelles issued the world’s first sovereign “blue bond”.
Way Forward
- Integrating wetlands into national planning: Embedding wetlands into good natural capital accounting.
- Recognising their central role in the global hydrological cycle.
- Embedding and prioritising wetlands in innovative financial solutions: Like debt instruments (such as green bonds, blue bonds) results-based financing instruments.
The survey aims to formulate a long-term strategy to protect the popular hill towns in the district from increasing pressure due to unregulated tourism, mounting vehicular traffic, population pressure, among others.
- Previously, in September 2024, National Green Tribunal directed the state government to classify the Nainital district based on carrying capacity and environmental sensitivity.
What is Carrying Capacity?
- It refers to the maximum threshold of population an area can bear in relation to the available resources.
- It depends on both biotic (e.g. vegetation, hydrology) and abiotic (e.g. terrain, climate) factors.
- Two major approaches for assessing Carrying Capacity:
- Planetary boundaries approach: Applied in the context of environmental crises such as global warming, land degradation, pollution, water stress.
- Biocapacity Overshoot approach: It is sustainability metric about the demand humans put on the earth systems by consuming total annual productivity of natural systems within a few months every year. e.g., Earth Overshoot Day.
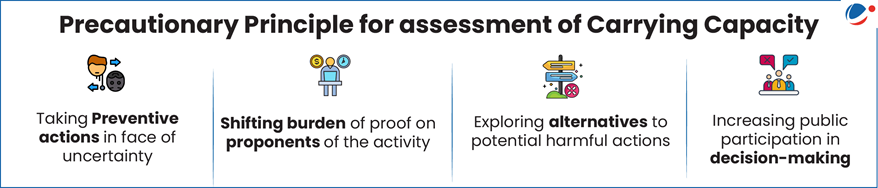
- Significance of carrying capacity in planning for sustainable development: Carrying capacity assessment based on precautionary principles (refer infographic) provides the option to practically deal with the tussle between ‘developmental governance’ and ‘sustainability of development’.
Proactive regulation, backed by scientific evidence and adaptive planning as per precautionary principles, can help balance economic aspirations with ecological limits. Institutionalizing such foresight can guide sustainable tourism models, prevent irreversible damage, and serve as a template for governance in other environmentally fragile regions.
The case on global responsibilities toward climate action, especially to protect vulnerable Small Island States (SIDS) was led by the Pacific Island nation of Vanuatu and supported by more than 130 countries.
- In 2023, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution requesting the ICJ to issue an advisory opinion on:
- States’ obligations under international law to protect the environment
- Legal consequences for failing to meet these obligations
Key Highlights of ICJ Ruling
- Clean, Healthy, and Sustainable Environment is Human Right: States are bound by treaties like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and must act on climate change to protect these rights.
- States Obliged to Limit Emissions: States must prevent harm from greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and ensure meeting the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- Consequences for Non-Compliance: If states fail to meet obligations, they:
- incur legal responsibility and may be required to cease the wrongful conduct, and
- may be required to offer guarantees of non-repetition, and make full reparation depending on the circumstances.
Some countries, like the US and Russia, have opposed any court-mandated emission cuts. But ICJ’s opinion adds growing legal pressure.

Assistance in Deploying Energy Efficient Technologies in Industries & Establishments (ADEETIE) scheme can help Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) reduce energy consumption by 30–50%, improve power-to-product ratio, and support creation of green energy corridors.
About ADEETIE
- Ministry: Ministry of Power.
- Eligible Enterprises: MSMEs with Udyam ID.
- Entities must demonstrate 10% energy savings of the implemented technologies.
- Implementation: Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- Scheme Duration: 3 years (FY 2025-26 to FY 2027-28).
- Budgetary outlay: ₹1000 crore.
- Target Sectors: Covers 14 energy-intensive sectors like Brass, Bricks, Ceramics, Chemicals, Fishery, Food Processing, etc.
- Implementation Approach:Phased roll-out, First phase with 60 industrial clusters, and additional 100 clusters in the second phase.
- Scheme components
- Interest Subvention: 5% for Micro and Small Enterprises and 3% for Medium Enterprises on loans.
- Streamlined Project Implementation: Support for Investment grade energy audits and preparation of Detailed Project Reports, etc.
- Support Provided: Technical handholding, financial incentives, Assistance in conducting Investment Grade Energy Audit, etc.

Patterns of floods in terms of magnitude, size and intensity undergoing changes reveals IIT Study.
- IIT Delhi and IIT Roorkee have found that riverine floods in India are changing over the past 40 years (1970–2010) based on data from >170 monitoring stations across the country.
Key highlights of the study
- Decline in Flood Magnitude: 74% of stations showed decreasing flood magnitude trends whereas 26% showcased increasing trends. Larger catchment experienced reduced flood magnitudes
- Region Specific:-
- West and Central Ganga basin: 17% decline per decade in monsoon floods (due to declining precipitation and soil moisture)
- Narmada basin: Consistent decrease in magnitude of floods(mainly on account of dam construction)
- Marathwada region: River flows are decreasing by 8% during monsoon and 31% in pre-monsoon season
- Region Specific:-
- Rise in Pre-Monsoon Flood Intensity: Malabar Coast -Increase of 8% per decade in pre-monsoon flood intensity (due to rising pre-monsoon rainfall). It affects rivers such as Chaliyar, Periyar, Bharathapuzha etc.
- Shift in Flood Timing: Upper Ganga (delayed floods), Central India (earlier floods), Southern India (generally sees later floods).
C-FLOOD will act as a unified system integrating flood modelling outputs from national and regional agencies, offering a comprehensive decision-support tool for disaster management authorities.
- Over 40 million hectares (mha) (~12% of total area) out of 329 mha is flood prone in India.
About C-FLOOD
- It is a web-based platform providing 2-day advance flood inundation forecasts up to village-level.
- It uses advanced 2-D hydrodynamic modelling to simulate flood scenarios.
- It offers flood inundation maps and water level predictions to aid disaster preparedness.
- Jointly developed by:
- Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune.
- Central Water Commission (CWC), nodal organisation entrusted with the task of flood forecasting & early flood warnings in the country.
- the Department of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) has also collaborated in its development.
- Execution: Under the National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- NSM was launched in 2015 with the aim to empower India in supercomputing capabilities.
- Jointly steered by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) and Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Present Coverage: Mahanadi, Godavari, and Tapi river basins. Planned to expand to cover all river basins across India.
- Forecasts to be integrated with the National Disaster Management Emergency Response Portal (NDEM).
Article Sources
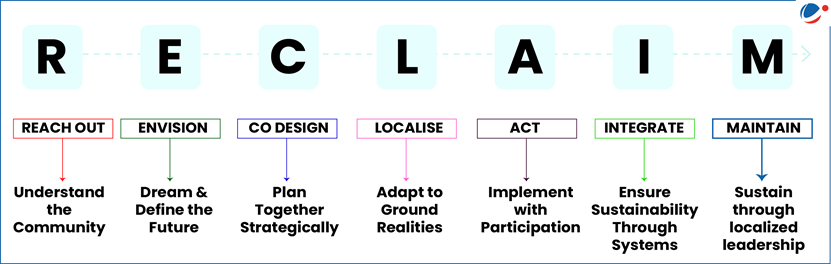
1 sourceCoal Ministry has launched the RECLAIM framework - A Community Engagement and Development Framework for Mine Closure and Repurposing.
Reclaim Framework
- Developed by: Coal Controller Organisation under the Ministry of Coal in partnership with the Heartfulness Institute.
- Objective: serves as a structured guide for inclusive community engagement and development throughout the mine closure and post-closure phases.
- It recognizes that mine closures significantly impact both landscapes and local livelihoods.
- Special emphasis is placed on gender inclusivity, representation of vulnerable groups, and alignment with Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- Framework (Refer Infographic)
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia is set to launch its first weather derivatives, with National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange Ltd (NCDEX) partnering with India Meteorological Department (IMD) to develop rainfall-based derivative products.
- These instruments will help farmers and allied sectors hedge against risks like irregular rainfall, heatwaves, and unseasonal weather.
- Using historical and real-time weather data from IMD, these derivatives will offer location-specific, seasonal contracts backed by statistically verified datasets.
About weather derivatives
- Unlike traditional derivatives based on financial assets, weather derivatives utilise meteorological parameters, such as rainfall and temperature, as the underlying asset, tied to a predefined weather index.
- Since these have no inherent market value, weather derivatives are considered part of an incomplete market.
- Globally, over-the-counter trading in such products began in 1990s, and India now takes its first significant step forward.
A recent study revealed that dam construction has shifted Earth’s rotational axis by over 1 meter since 1835 i.e., they have driven True Polar Wander (TPW).
What Is True Polar Wander (TPW)?
- Definition: TPW, or planetary reorientation, is the rotation of the solid Earth (crust and mantle) about the liquid outer core.
- It helps the Earth maintain rotational balance due to mass redistribution.
- Natural Factors driving TPW: Traditionally, TPW has been linked to natural processes such as glacial melting, Ice sheet melt, tectonic plate shifts, and ocean swell.

How Dams Are Driving TPW?
- Reservoirs trap large volumes of water that would otherwise remain in oceans.
- This redistributes Earth’s mass inland, causing shifts in the planet’s rotation.
- The study also revealed that the shift was not smooth—it varied depending on the size and location of dams built over time.
Effects of Shifting Poles
- Navigation Problems: Shifting poles can affect satellites and space telescopes, which depend on Earth’s rotation for accurate positioning.
- Longer Days: The days on Earth are growing slightly longer, and this change is accelerating.
Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) completes 10 years of dedicated research into North India’s dense winter fog and its impact.
About WiFEX
- It is one of the world’s few long-term open-field experiments focused solely on fog.
- Institutions: Led by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
- Objective: To develop better now-casting (next 6 hours) and forecasting of winter fog.
Article Sources
1 sourceUninhabited Kariyachalli island has sunk significantly over the past few decades due to rapid erosion and rising sea levels.
About Kariyachalli island:
- Location: Between Rameshwaram and Thhothukudi in the Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park region, Tamil Nadu.
- Tamil Nadu Sustainably Harnessing Ocean Resources (TNSHORE) project will try to restore the reefs around the island with artificial modules, planting seagrass beds and reviving marine life.
The forest advisory committee has granted ‘in-principle’ approval for diversion of forest land for construction of Sawalkot HEP on Chenab River.
- Sawalkot HEP is one of the six strategic hydropower developments aimed at optimising India’s use of Indus waters.
About Chenab River
- Origin is Bara Lacha Pas.
- Two streams namely Chandra and Bhaga rise on the opposite sides of the pass and join to form Chenab.
- Chenab valley is a structual trough formed by the great Himalayan and Pir Panjal ranges.
- Tributaries include Miyar Nalla, Sohal, Thirot, Bhut Nalla, Marusudar and Lidrari.
- It was known to Indians in the Vedic period as Chandrabhaga, also Ashkini or Iskmati.
More than 1,000 earthquakes have rattled the Tokara Islands in southern Japan.
- Japan is one of the world’s most seismically active countries, sitting on top of four major tectonic plates along the western edge of the Pacific “ring of fire”.
About Tokara Island
- It is an archipelago in Japan, south of Kyushu and north of Amami Islands.
- Toshima (Japan’s longest village) is located here.
Lakshadweep administration is considering acquisition of Bitra for defence purposes.
About Bitra Island
- It is the smallest inhabited island in the territory of Lakshadweep having a land area of 0.105 sq km.
- Location: Near the Agatti Island, Arabian Sea.
- Climate: Categorised as 'Aw' i.e., tropical savannah according to the Köppen-Geiger system of climate classification.
- The average rainfall received is ~1600 mm a year.
About Lakshadweep
- It is India’s smallest Union Territory.
- Lakshadweep Island consists of 36 coral islands, located in the Arabian Sea. Atoll, lagoon and reefs are the three main geographical features.






