Twitter Co-Founder shared details of Bluetooth Messaging App, Bitchat.
- Bitchat is a new peer-to-peer messaging app that communicates without a centralised server or phone network.
- Bitchat relies on Bluetooth Low Energy Mesh Networking to enable communication
What is Bluetooth Mesh Networking?
- It relies on Bluetooth clusters or Mesh network created by devices in a range.
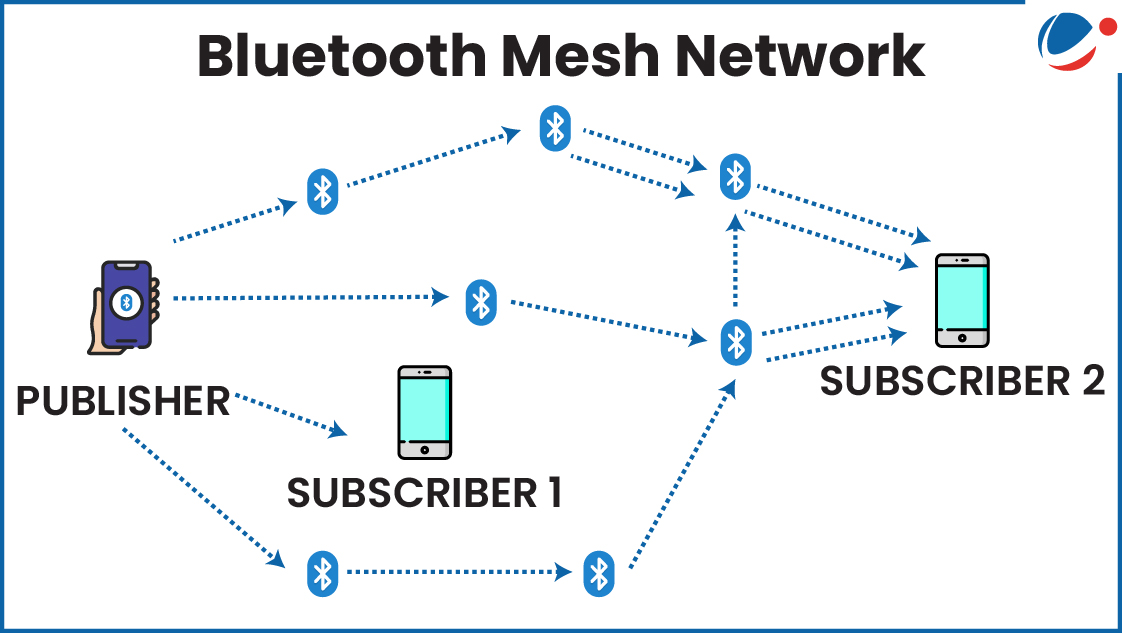
- Mesh network, also known as “multi-hop network”, is a networking topology.
- In it, data can travel from any device to all others, achieving many-to-many communication.
- Even if one device fails, the network keeps working.
- Messages are broadcast and relayed by nodes until they reach the intended destination.
- When a Bluetooth device joins a Mesh network, it becomes a node
Potential Benefits of Bluetooth Mesh Networking
- No central database: the messages are stored entirely on users’ devices and are deleted after a short period.
- This design is created to prioritise users’ privacy.
- Also, Messages are end-to-end encrypted and do not leave the network.
- No registration required: Users are not required to create accounts using their email or phone number, making the communication anonymous.
- Other: Low Power Consumption, etc.
Key Limitations: high latency, Complex network management, low data transfer rates, etc.
The Digital India Foundation (DIF), a founding member of the AIANET, has objected to the membership application of Pakistan's AI Technology Centre (AITeC) to AIANET.
- Digital India Foundation (DIF) is a not-for-profit think-tank aiming to foster digital inclusion and adoption, and the use of the Internet and related technologies for the developmental process.
About AIANET
- About: It is an informal voluntary network and community for its Members to exchange views, share information and expertise.
- Aim: Accelerate the development and deployment of AI technologies to enhance sustainable long-term prosperity, social and economic development
- Members: 17 including India.
- Administered by: AI Alliance Russia.
Initiative aims to raise prices of any or all of three unhealthy products tobacco, alcohol, and sugary drinks by at least 50% through health taxes by 2035.
- Launched initiative can mobilize an additional US$ 1 trillion in public revenue globally over next decade.
- This Initiative functions as a collaborative alliance with coordinate efforts from coalition of development partners, civil society, academic institutions, and national governments.
What is Health Tax?
- Levied on products that have a negative public health impact e.g. Tobacco, Alcohol etc.
- WHO recommends taxation as one of the most cost-effective tools for addressing population levels of obesity and other related non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
Need for Health Tax

- Health Impact: Consumption of tobacco, alcohol, and sugary drinks fuels the NCD epidemic which accounts for over 75% of global deaths.
- Economic Impact: These products create negative externalities (costs to others) and internalities (hidden costs to consumers).
- Tobacco use alone costed the global economy US$ 1.4 trillion in 2012.
- Revenue Generation: 50% tax can generate up to US$ 3.7 trillion in new revenue globally within five years, or an average of US$ 740 billion per year – equivalent to 0.75% of global GDP.
- Promote Equity: As NCDs impact lower-income populations disproportionately.
Steps taken in India for curbing consumption of Unhealthy Products
- Aerated beverages in India are taxed at 28% GST and an additional 12% Compensation cess.
- High-fat sugar Salt (HFSS) foods in India are taxed at a 12% GST rate.
- FSSAI limits Trans-Fatty Acids (TFA) in food products to 2% by mass of total oils and fats.
WHO/UNICEF 2024 Estimates show significant progress on Immunization in India.
- The data provides the world’s largest and most comprehensive dataset on immunization trends for vaccinations against 14 diseases.
Key Findings
- Global: In 2024, 89% of infants globally received at least one dose of the diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTP) containing vaccine.
- India: It reduced its number of zero-dose children by 43% in 2024 (from 1.6 million in 2023 to 0.9 million in 2024).
- Zero-dose children are those who have not received a single vaccine.
Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) of India
- Genesis: Initially launched in 1978 as the Expanded Programme on Immunization, it was rebranded as the UIP in 1985.
- Coverage: Provides free immunization against 12 diseases:
- Nationwide (9): Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, Measles, Rubella, Childhood Tuberculosis, Hepatitis B and Meningitis & Pneumonia.
- Region-specific (3): Rotavirus diarrhoea, Pneumococcal Pneumonia, and Japanese Encephalitis.
- Under the National Rural Health Mission, the UIP has become a central component of India's public health efforts.
- Under this, a child is considered fully immunized after receiving all vaccinations as per the national schedule within the first year of life.
- Achievements: Polio-Free India (2014), Neonatal tetanus elimination (2015).
- Key Initiatives: Intensified Mission Indradhanush 5.0 (IMI 5.0) campaign with special focus on improvement of Measles and Rubella vaccination coverage, U-WIN Portal etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceNational Biobank inaugurated at the CSIR-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (IGIB).
- The newly launched facility marks a significant stride towards building India’s own longitudinal health database
- It will enhance India’s capabilities in precision medicine and biomedical research.
About National Biobank
- Launched under: Phenome India Project.
- It is based on the UK Biobank model, but customized for Indian diversity.
- Purpose: It will aid in early diagnosis, improve therapeutic targeting, and bolster the fight against complex diseases such as diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular ailments, and rare genetic disorders.
- It will generate high-resolution data that can power AI-driven diagnostics and gene-guided therapies.
- Coverage: It will collect comprehensive genomic, lifestyle, and clinical data from 10,000 individuals.
About Phenome India Project
- It is officially called as Phenome India-CSIR Health Cohort Knowledge base (PI-CheCK).
- Launched by: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) in 2023.
- Objective: It is designed to be a long-term, data-rich study tracking the health trajectories of individuals over several years.
What is Phenome?
- Phenome is the entire set of phenotypes in a cell, tissue, organ, organism or species.
- Phenotype refers to the observable physical characteristics of an organism.
- These include the organism's appearance, development, and behavior.
- An organism's phenotype is determined by its genotype (set of genes the organism carries) as well as by environmental influences upon these genes.




