Why in the News?
RBI's push for internationalization of INR through SRVAs, UPI linkages, currency swap agreements etc., aims to reduce dependence on foreign currencies and contributes to global de-dollarization.
What is De-dollarization?
- It aims to reverse dollarization (historical domination of US dollar in global market) causing a significant reduction of its use in world trade, reserves and financial transactions.

Key reasons for De-dollarization
- Asymmetry of shrinking US economic weight and growing dominant role of the dollar: While the US share of world GDP has decreased from around 45% post-World War II to approximately 25% currently, the dollar still carries disproportionate share.
- Weakening credibility of Dollar: The US government's high debt burden and instances like the 2023 debt ceiling standoff have weakened this credibility.
- Spillover effects of US monetary policy: Actions by the Federal Reserve, such as hiking interest rates (2023), have led to currency depreciation, significant increases in debt service costs, and inflation in many countries.
- Weaponization of US dollar and payment clearance systems: Currently, approximately 40 countries are under US sanctions, which have become more systemic, impacting central governments and policy making.
- Aspiration for a new and more democratic international economic order: De-dollarization efforts are also a reflection of a desire to shift away from a unipolar world towards a multipolar New International Economic Order (NIEO).
- Positive developments outside U.S.: Enhanced credibility of alternative currencies, like economic and political reforms in China.
Challenges with De-dollarization
- Transition Costs: Moving away from the U.S. dollar requires heavy spending on updating financial systems, adjusting contracts, and renegotiating trade agreements.
- Market Volatility: The shift to new currencies can trigger uncertainty and market instability, affecting global trade and investment flows.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Reducing reliance on the U.S. dollar may spark political frictions and be seen as a challenge to American economic influence.
- Reserve Diversification Challenges: Holding reserves in alternative currencies or assets like gold brings new risks, including currency depreciation or commodity price swings.
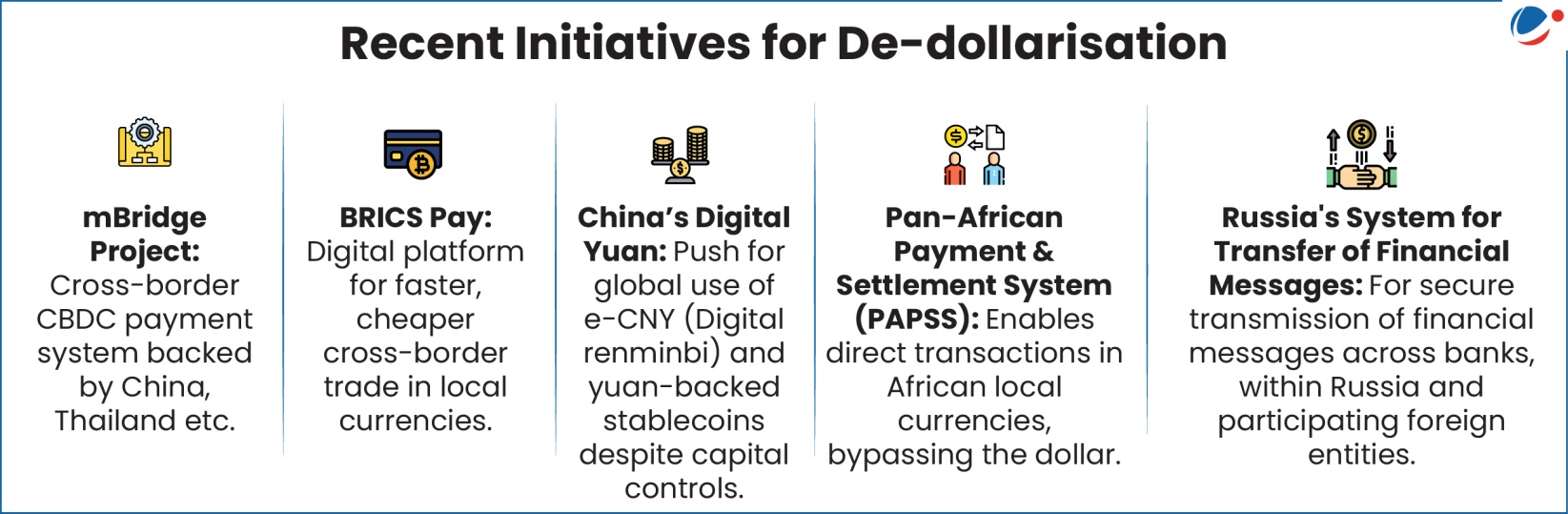
Conclusion
In case of India, de-dollarization can be complemented with internationalization of Rupee—rupeefication, that would provide complete freedom over buying or selling of the rupee by an entity.






