The Philippines and India formally elevated their bilateral ties through a declaration on establishing a Strategic Partnership guided by the Plan of Action (2025-2029).
More on the news
- The strategic partnership marks 75 years of diplomatic ties (established in 1949), further strengthened by India’s Look East (1992) and Act East (2014) Policies.

Convergence of India-Philippines Relations
- Defense Partnership: Growing trust and defense cooperation exemplified by India’s arms exports, like $375m BrahMos missile deal with Philippines (1st foreign buyer).
- China Factor: Increasing Chinese assertiveness in the South China Sea threatens Philippine sovereignty and also India’s maritime trade routes, bringing both towards closer cooperation.
- Maritime Security: India backs the Philippines’ stance on the 2016 arbitration ruling, reinforcing a rules-based order under UNCLOS.
- India calls a rules-based order and freedom of navigation in the SCS region.
- Indo-Pacific Vision: India's Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific outreach have Philippines as a key player.
Conclusion
India-Philippines relations are becoming more strategically deep through collaboration in cyber, economics, maritime, and defense. The partnership promotes a rules-based Indo-Pacific and enhances India's Act East Policy. By working together, both countries can guarantee shared prosperity, stability, and security in the region.
India launched projects with the UN under Global Capacity Building Initiative for Asia, Africa and Caribbean countries.
About Global Capacity Building Initiative
- Genesis: India and the United Nations jointly launched it in September 2023 .
- Objective: Share India’s development experiences, best practices, and expertise with Global South nations through capacity-building and training programs for accelerating progress on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Implemented through the new UN India SDG Country Fund as well as the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation Programme (ITEC).
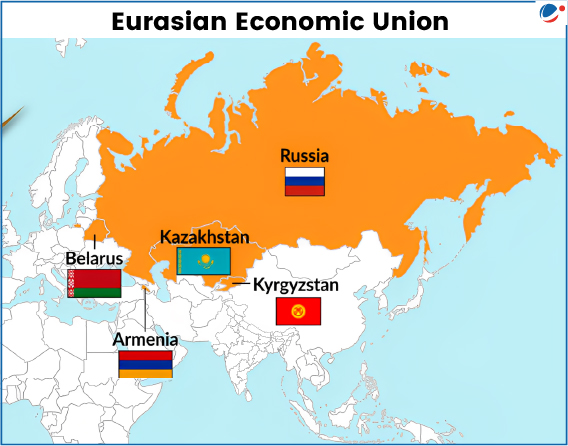
India and Eurasian Economic Union recently signed Terms of Reference for trade deal. Signing of Terms of Reference marks the formal commencement of Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations with the goal to establish a long-term framework for trade cooperation.
Potential Benefits of FTA with EAEU
- Economic Benefits
- Trade expansion: It will unlock untapped trade potential, increase investments and establish a stronger, durable India–EAEU economic partnership.
- Bilateral Trade turnover stood at USD 69 billion in 2024 (7% rise from 2023).
- Market access: It will open wider opportunities for Indian exporters amid increasing US tariffs and support diversification into new sectors and geographies.
- Enhance competitiveness: It will strengthen India’s position against non-market economies.
- It will significantly benefit Indian Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Energy partnership: EAEU offers abundant natural resources and energy crucial for India’s growth.
- E.g. Russia now accounts for 35-40% of India’s total oil imports by volume.
- Trade expansion: It will unlock untapped trade potential, increase investments and establish a stronger, durable India–EAEU economic partnership.
- Strategic Benefits: Strengthening ties with Russia led bloc will reinforce India’s policy of multialignment.
About Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)
- Overview: It is an international organization for regional economic integration.
- Genesis: Established by the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (2014).
- Benefits: Provides for free movement of goods, services, capital, and labour, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceRussia officially end commitment to 1987 Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty. Russia cited recent US military actions as key reason including the US order of repositioning two nuclear submarines closer to Russian shores and deployment of Typhon missile system in Philippines.
About INF Treaty
- Signed between the United States and the Soviet Union in 1987, the treaty required destruction of all ground-launched ballistic and cruise missiles with ranges of 500–5,500 km.
- It was the first major agreement to reduce nuclear arsenals, remove an entire class of weapons, and allow on-site inspections for verification.
- INF Treaty had already weakened after the US withdrew in 2019.
Implications on nuclear arms control
- Breakdown of Arms Control Frameworks: Eroding trust and hindering efforts towards future nuclear disarmament movements.
- Negative impact on nuclear disarmament: Major powers accelerating nuclear modernization, while non-nuclear states are reconsidering their non-proliferation commitments, heightening global instability.
- Return to Cold War Politics: Collapse of treaty has stoked fears of a replay of Cold War-era European missile crisis.
- Increasing Security Risk: Such weapons take less time to reach targets, raising the likelihood of a global nuclear conflict over a false launch warning.

Article Sources
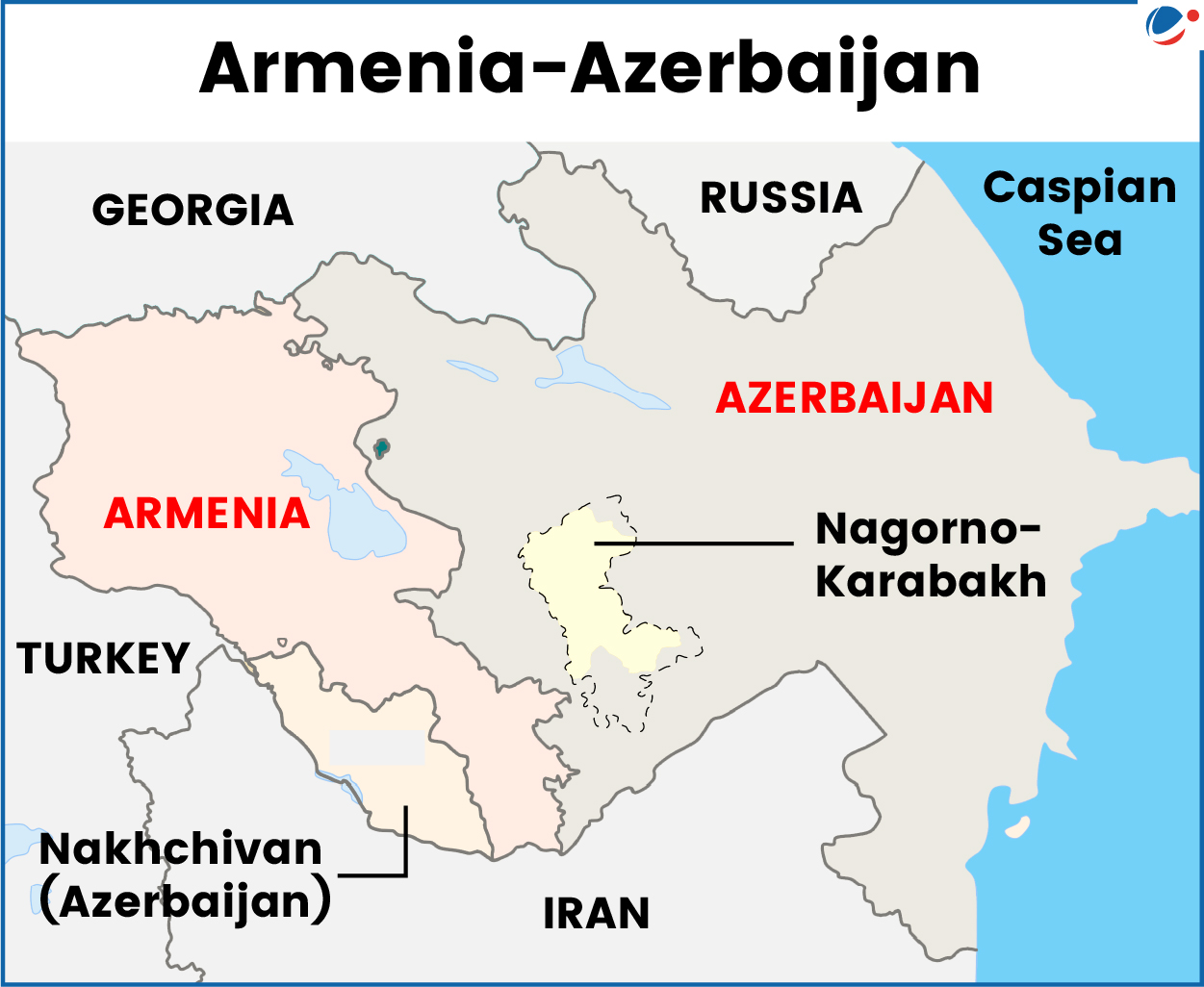
1 sourceThe deal aims to bring an end to decades of conflict between the two South Caucasus countries.
Key Provisions of the deal
- Cessation of Hostilities: Both nations agreed to end armed conflict, establish diplomatic relations.
- Trump Route for International Peace and Prosperity" (TRIPP): New transit route linking Azerbaijan to its exclave Nakhchivan through Armenian territory.
- US has exclusive development rights.
- US Cooperation Deals: Both countries also signed separate agreements with the United States to enhance cooperation in energy, technology, and the economy.
Background of the Conflict
The Armenia–Azerbaijan conflict is mainly over Nagorno-Karabakh, a mountainous region inside Azerbaijan but predominantly populated by ethnic Armenians.
- 1980s: Nagorno-Karabakh broke away from Azerbaijan with Armenia’s support.
- 1991: Both countries gained independence from the Soviet Union, but the dispute continued.
- 2023: Azerbaijan regained full control, causing nearly 100,000 Armenians to flee to Armenia.
India’s Interest
India supports the peace deal, calling it an “important achievement” for dialogue and diplomacy. The deal is important for India as:
- Armenia is the only country in the region with which it has a Friendship and Cooperation Treaty (signed in 1995).
- Azerbaijan falls on the International North-South Transport Corridor route, connecting India with Russia through central Asia.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe President of USA and Russia met in Alaska regarding Ceasefire in Russia-Ukraine war.
- About Alaska
- It is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of the North American continent.
- It was bought by the USA from Russia as per Alaska Treaty 1867.
- Maritime Boundaries: Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean (North), Gulf of Alaska and Pacific Ocean (South), Bering Sea (West), Chukchi Sea (Northwest)
- The Northern Lights or Aurora Borealis, are visible across much of Alaska
- Nearly one-third of the state lies within the Arctic Circle, and about 85% of Alaska is underlain by permafrost.
India has been elected as the Chairman of the Executive Board of AIBD at 23rd General Conference in Thailand.
About Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development
- Genesis: Founded in 1977 under the auspices of UNESCO, AIBD is a unique regional inter-governmental organization.
- Secretariat: Kuala Lumpur.
- Mandate: To achieve a vibrant and cohesive electronic media environment in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Members: It currently has 92 member organizations from 45 countries.
- India is a founding member of AIBD, and Prasar Bharati India’s public service broadcaster represents the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting in the organization.
Article Sources
1 sourceAreas In Conflict | Reason | Key Geographical Features | Map |
Gaza (Khan Yonis, Rafah, Jabalia, Dier al-Balah). | UN officially declared famine in August 2025, with half a million people at risk of starvation due to Israel's prolonged blockade and restricted aid entry post Hamas attack on Israel. |
| 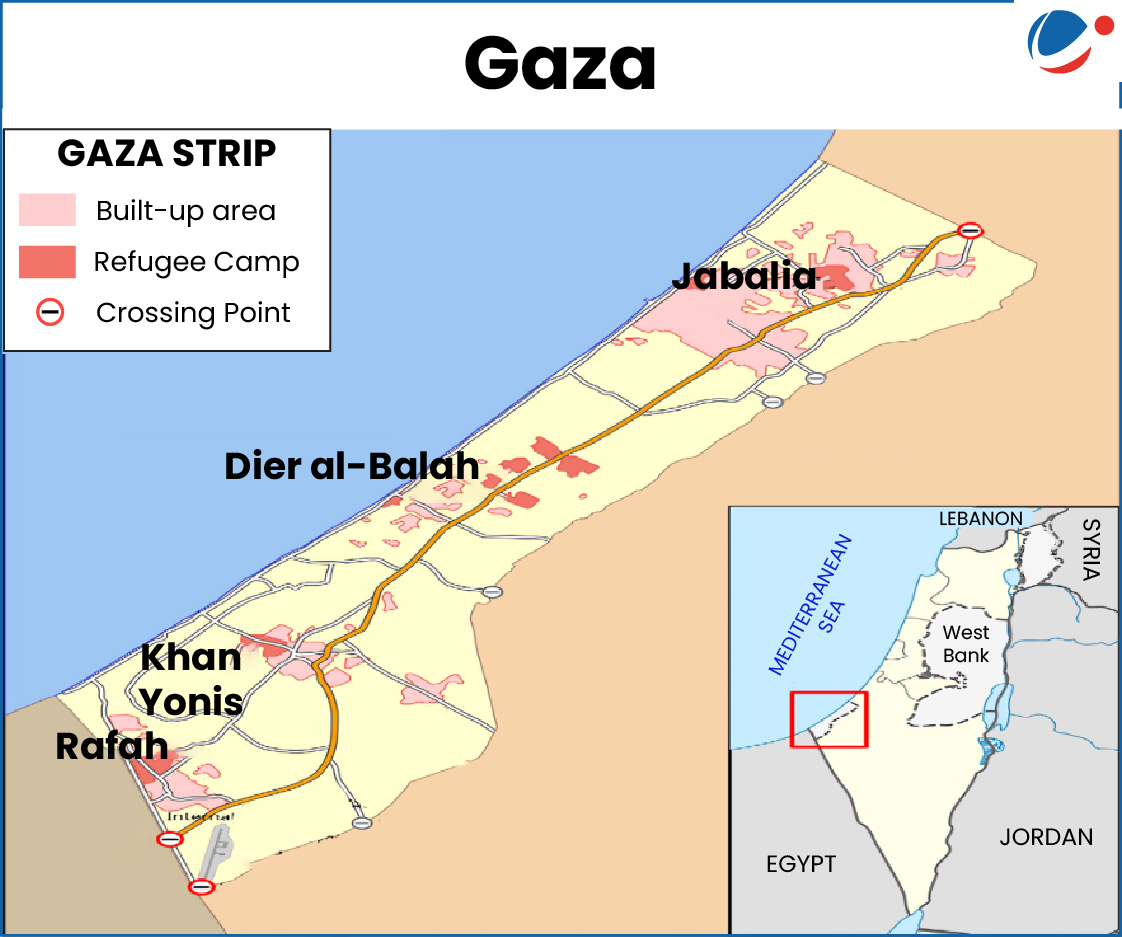 |
Sudan (Darfur, Khartoum, South Kordofan, Blue Nile States). | Sudan plunged into a civil war in April 2023 after a vicious power struggle broke out between its Army and a powerful paramilitary group, the Rapid Support Force (RSF). |
| 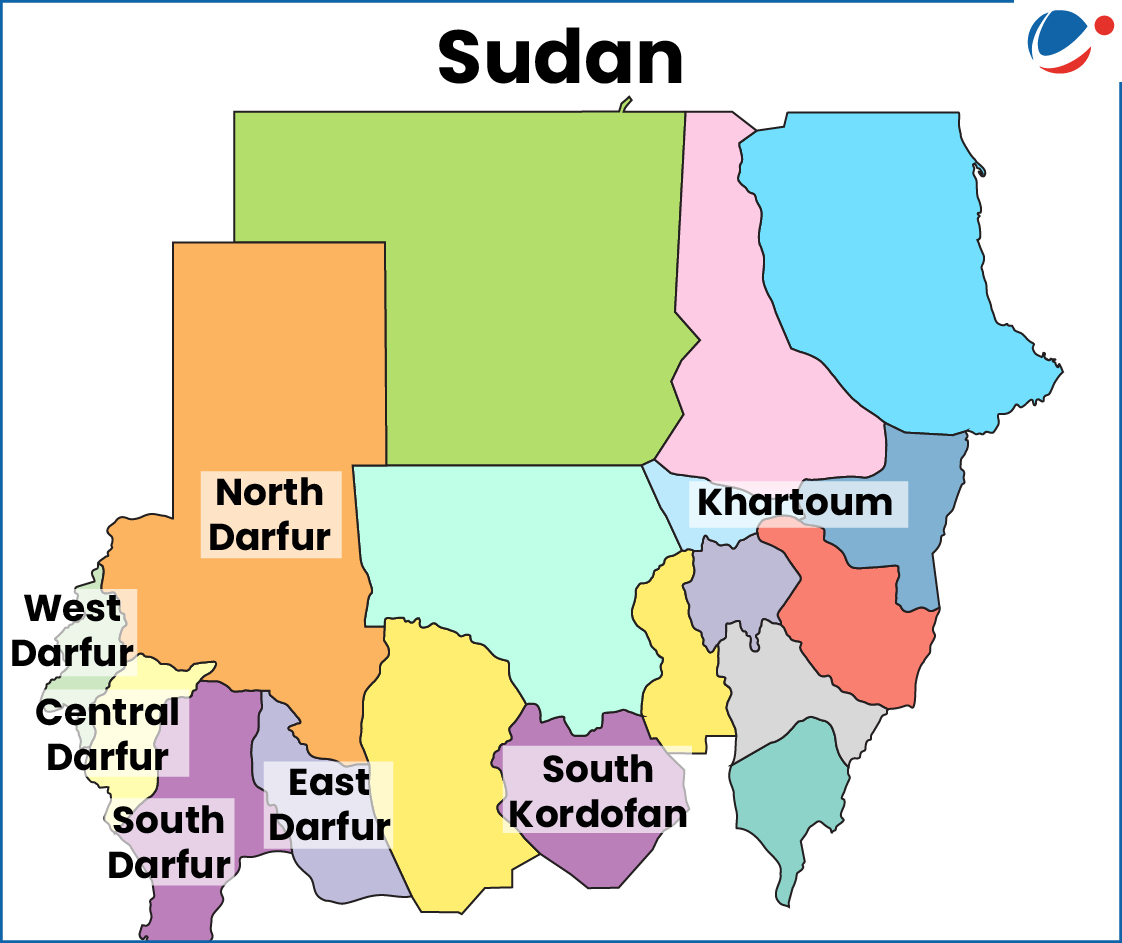 |
Ukraine (Kyiv, Donetsk, Zaporizhzhia, Cherkasy and Chernihiv, and Kharkiv). | Worsening humanitarian conditions in Ukraine amidst wave of Russian missile and drone strikes.
|
| 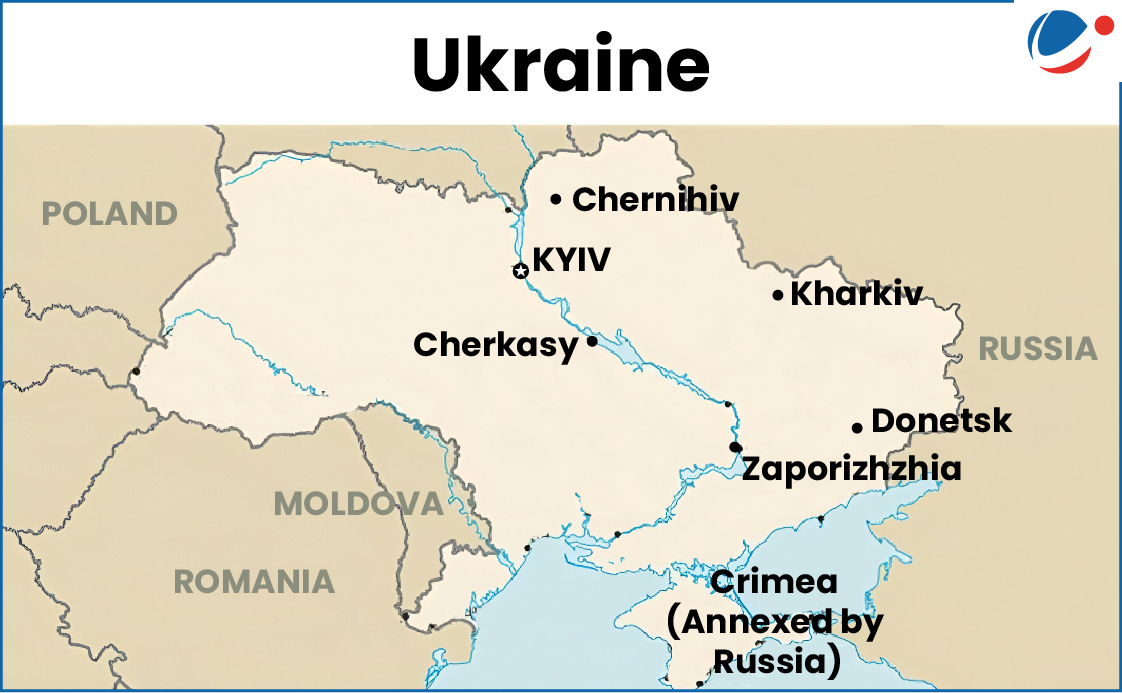 |
Democratic Republic of Congo (North Kivu, Ituri province). | Congo has been facing a long cycle of wars in the east, shaped by ethnic tension, weak governance, and the struggle for its mineral wealth. |
| 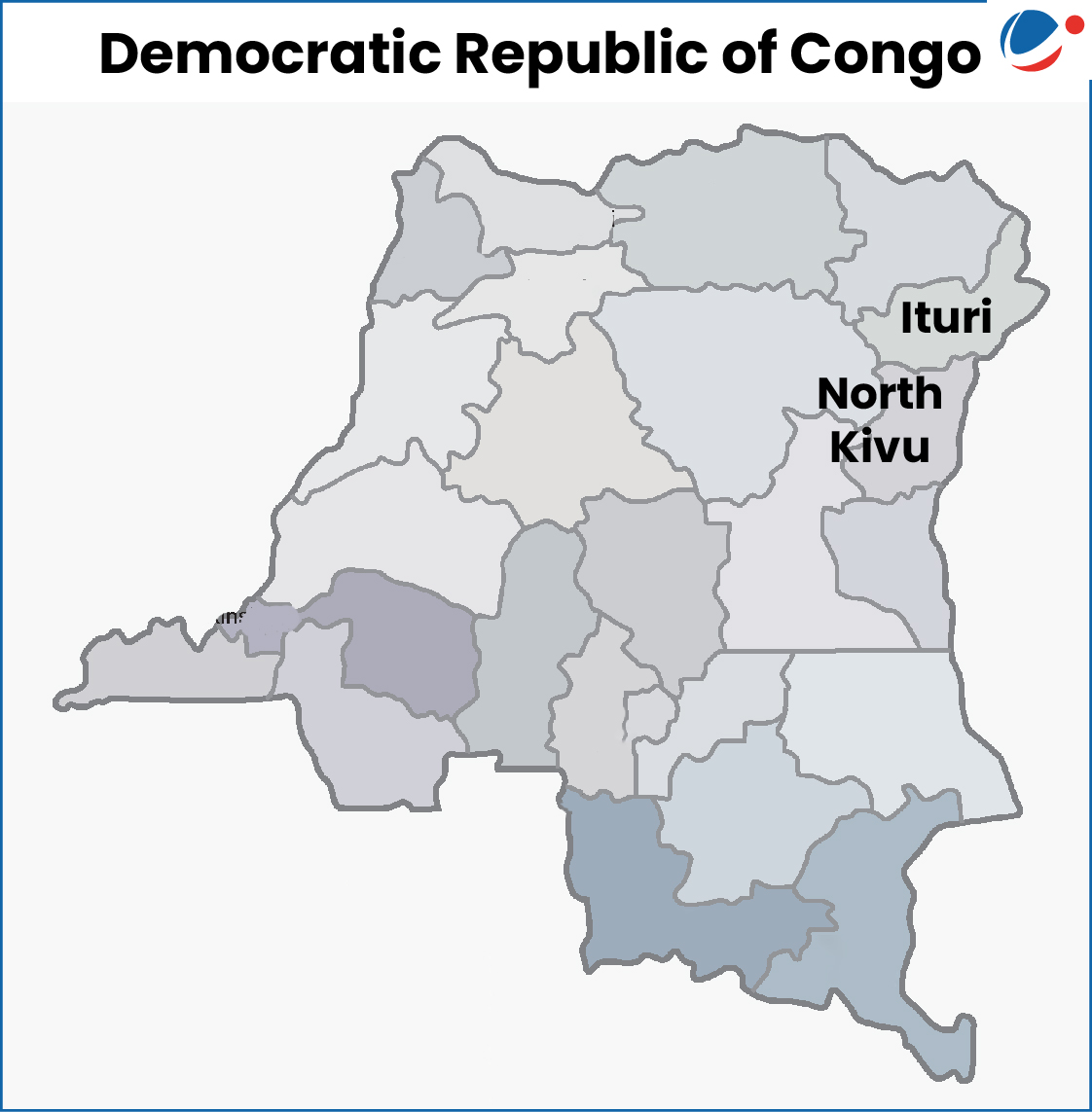 |





