Why in the News?
Recently, Karnataka's State Legislative Assembly passed the Karnataka Platform-Based Gig Workers (Social Security and Welfare) Bill, 2025, to protect the rights of workers.
More about the bill
- Establishment of Welfare Board: It will oversee registration of workers and aggregators, create social security schemes, monitor the schemes, etc.
- Establishment of Social Security and Welfare Fund:Consists of welfare fee (Levied on transactions b/w worker & aggregator or on overall turnover of company) & contributions from Union and State governments.
- Others: Aggregators will register gig workers, share work terms, and explain how automated systems affect their conditions.
- Rajasthan and Bihar have passed laws in this regard in 2023 and 2025, respectively.
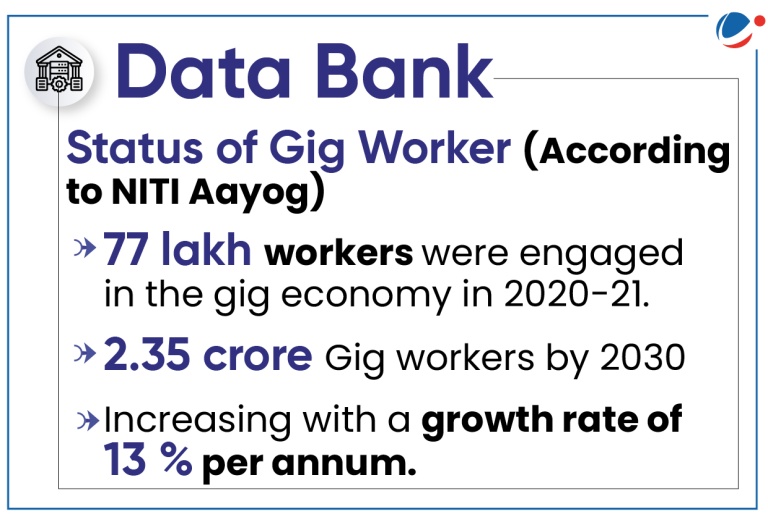
About Gig workers
- Definition: The Code on Social Security, 2020, defines a gig worker as a person who works outside a traditional employer-employee relationship.
- Types: platform and non-platform-based workers.
- Platform workers are those whose work is based on online apps or digital platforms. E.g., Ola, Uber, Zomato, Swiggy, Urban Company, etc.
- Non-platform gig workers are generally casual wage workers and own account workers in the conventional sectors, working part-time or full time.
Reasons for growth: Demographic dividend (65 % of Indians are in age group of 15-64 years), Rapid urbanisation, boost to the remote work during COVID-19, Adoption of smartphones and internet (In India, 85.5 % of households possess at least one smartphone), etc.
Significance of the gig economy
- For government
- To utilise demographic dividend: By ensuring employability, business that serves the gig economy account for 56 % of all new jobs created in India.
- Economic growth: By 2030, India's gig economy might see $250 billion in transactions or 1.25 % of GDP (NITI Aayog).
- For society
- Empowering the vulnerable section: According to ILO, digital platform's flexible employment benefits women, youth, and physically disabled.
- Micro-Entrepreneurship: Platforms like Airbnb and Urban Company let people monetize their skills, assets, and time while lowering entry barriers such as high startup costs.
- For workers
- Flexible Employment: Remote work, on-demand and task-based arrangements, flexible work hours, etc.
- Skill development: The gig economy imparts a range of skills, such as digital literacy, self-management, communication, problem-solving, etc.
- For consumers
- Access to the Global Market: e.g. Airbnb, and Amazon.
- Greater convenience: Via personalised and cheaper products.
Challenges for Gig Workers
- Lack of social security: More than 82.5 % of gig workers are informal employees (NITI Aayog).
- Health and Safety Concerns: Due to the nature of the job, e.g., tight delivery schedule can cause accidents.
- High Working hours: 60 % of platform workers work 7 days a week, while 47% of the workers work for more than 12 hours a day (Tata Institute of Social Science).
- Income uncertainty: According to Fairwork India, around half of the gig workers did not receive the statutory minimum wage
- Algorithmic Asymmetry: Platforms use algorithms to manage work. However, reliance on this leads to various imbalances such as
- Information Access: Platform aggregators have access to worker's personal information raising privacy concerns.
- Transparency: Rating Systems, task distribution and wage based on data etc are often guided by algorithms which are opaque, increasing the possibility of unfair calculations.

Conclusion
A comprehensive framework can be brought for gig and platform workers that ensures fair wages, social security, safe workplaces, gender inclusion, and protection from discrimination. It should mandate transparency, algorithmic accountability, and the right to unionize while promoting training, grievance redressal, and access to finance.







