Why in the News?
In his Independence Day address, the Prime Minister announced the launch of a High-Powered Demography Mission aimed at addressing the challenge of illegal immigration.
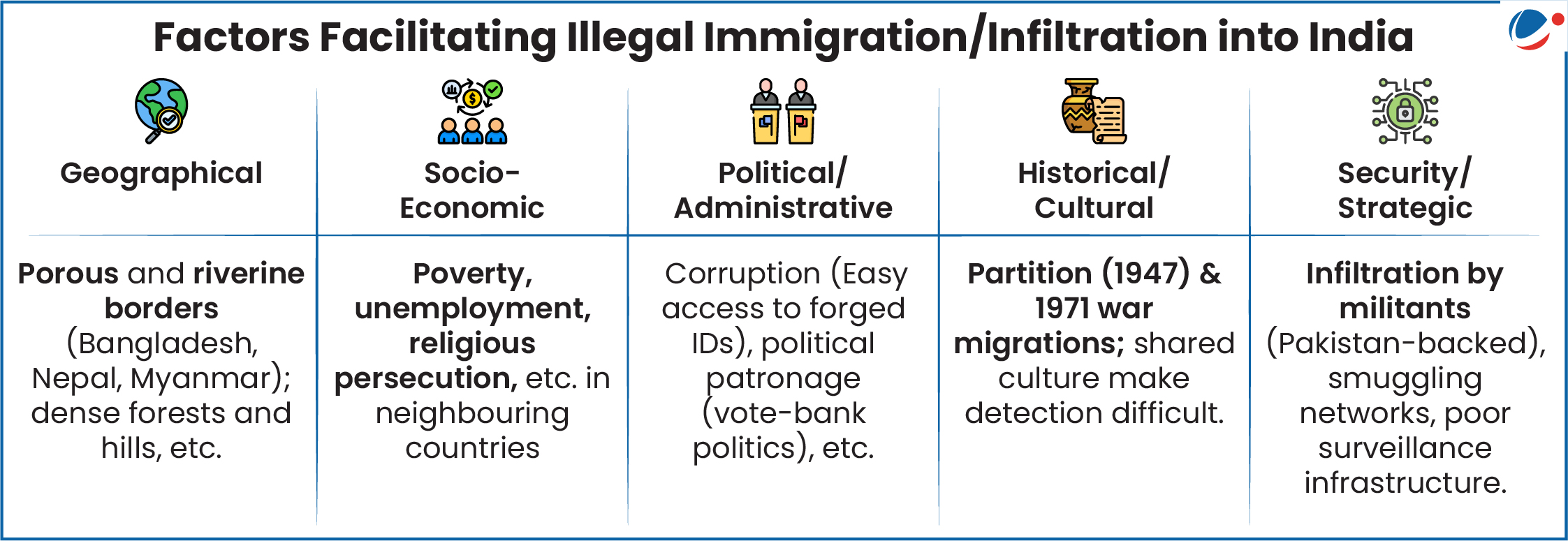
More on the News
- Illegal immigrants are those who enter the country without valid travel documents in a clandestine and surreptitious manner.
- There is no officially verified estimate regarding the number of illegal immigrants currently residing in India.
- In 2016, government had informed that there are around 20 million illegal Bangladeshi migrants staying in India.
Key concerns associated with Illegal Immigration and Infiltration
National Security Threats
- Terror Links and Radicalisation: Extremist groups may exploit Illegal Immigrant, such as the Rohingya, for recruitment.
- India's border also faces threats from smuggling, human trafficking, and other cross-border criminal activities.
- Demographic Shifts and Social Cohesion: States bordering Bangladesh, such as Assam, have experienced significant demographic changes due to the influx of illegal immigrants.
- Presence of immigrants may lead to ethnic/religious friction. E.g. Threat to Assamese identity due to illegal migration from Bangladesh.
Socio-Economic Burdens
- Strain on Public Services/Overburdening of Welfare Schemes: E.g., healthcare, housing, etc.
- Distortion in the Labour Market: Displacing local workers and disrupting wage structures (often work at lower wages).
- Other: Illegal settlers encroach on agricultural and forest lands, etc.
Initiatives taken to Curb Illegal Immigration/ Infiltration in India
- Legislative and Policy Measures
- Immigration and Foreigners Act, 2025: Empowers authorities to detect, detain and deport illegal immigrants.
- National Register of Citizens (NRC): Updated in Assam under Supreme Court supervision.
- Other: Citizenship (Amendment) Act (CAA), 2019, etc.
- Border Management Initiatives
- Border Fencing & Floodlighting (along Indo-Bangladesh and Indo-Pakistan borders)
- Comprehensive Integrated Border Management System (CIBMS), use of smart technologies (radars, sensors, drones)
- Institutional and Administrative Measures
- Foreigners Tribunals (FTs): These are quasi-judicial bodies established through the Foreigners (Tribunals) Order of 1964 under Section 3 of the Foreigners' Act of 1946 to decide cases of illegal immigration and nationality.
Way Forward: Measures to curb Illegal Infiltration/Immigration
- Security & Intelligence Strengthening: E.g., Integrated Intelligence Grid, seamless coordination among IB, BSF, state police, and local intelligence units.
- Strengthen Border Management: E.g., Specialized floating Border outpost, UAV monitoring in river stretches, etc.
- Enacting a National Refugee Law: India needs a national refugee law to legally distinguish between genuine refugees and illegal economic migrants.
- India is not a signatory to the 1951 UN Refugee Convention or its 1967 Protocol.
- Formal Bilateral Repatriation Agreements: Facilitates the return of their nationals residing illegally.
- Other:
- Involve international organizations like the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) for support in managing illegal immigration.
- Expeditiously issue National Identity Cards (NIDs)
- Maintaining Biometric Records of Illegal Immigrants/ Refugees
Conclusion
The High-Powered Demography Mission is a timely step to counter the long-standing challenge of illegal infiltration. Its success will depend on stronger border fencing and surveillance, faster Foreigners Tribunal decisions, bilateral repatriation agreements, and robust national ID systems.



