Why in the News?
India's first National Biofoundry Network was launched on August 25, 2025, which also marked the first anniversary of India's BioE3 Policy.
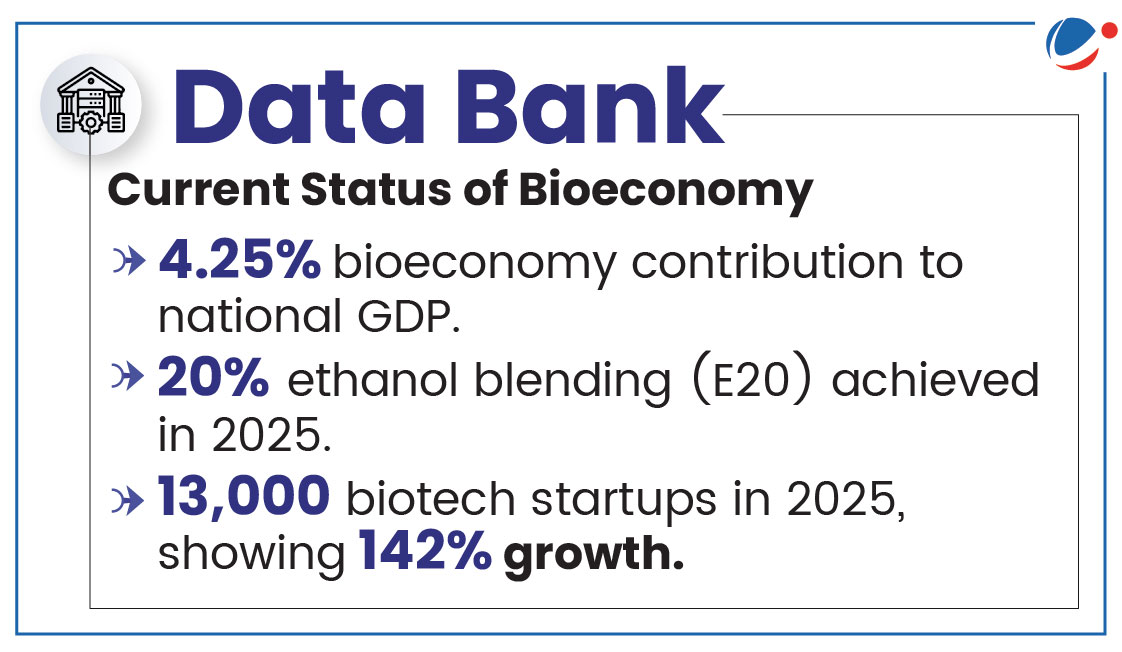
About National Biofoundry Network
- Objectives: To aid in the scale-up of proof-of-concept projects into viable technologies.
- Proof of Concept (POC): A demonstration to test if an idea is feasible and viable, not to assess market demand or production methods.
- Component of: BioE3 Policy and categorized as Bioenablers.
- Biofoundry: It is an automated facility that rapidly designs, builds, and optimizes engineered organisms by integrating DNA synthesis, gene editing, and high-throughput biomanufacturing workflows.
- Functions:
- Scaling up research activities across various thematic areas. Examples:
- International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB) working on engineering microbial strains for first and second-generation biofuels,
- IIT-Madras advancing animal-free production of hyaluronic acid.
- The network offers shared infrastructure for startups, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), industries, and academic institutions.
- It also provides training and internships to build human resources with the necessary interdisciplinary and cross-functional technical skills for biomanufacturing.
- Scaling up research activities across various thematic areas. Examples:
About BioE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) Policy
- Approved in 2024, as India's first policy in Biotechnology.
- Ministry: Department of Biotechnology (DBT), under the Ministry of Science & Technology.
- Objectives:
- To revolutionize biomanufacturing for enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and quality, while accelerating the development and production of high-value bio-based products.
- Biomanufacturing includes sectors like precision biotherapeutics, carbon capture and utilisation, functional foods and smart proteins, etc.
- To double India's bioeconomy to US$300 billion by 2030.
- To revolutionize biomanufacturing for enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and quality, while accelerating the development and production of high-value bio-based products.
- Key Features of BioE3 Policy:
- Innovation-Driven R&D & Entrepreneurship: Provides strong support to foster research and startups.
- Technology Development & Commercialization: Accelerates progress through Biomanufacturing, Bio-AI hubs, and Biofoundries.
- Green Growth Models: Prioritizes regenerative and circular bioeconomy practices.
- PPP-Based Implementation: Leverages Public-Private Partnerships to boost industry participation, expand skilled workforce, and generate employment.
Key Achievements of BioE3 Policy
- Infrastructure: Established 21 advanced BioEnabler facilities, BRIC National Agri-Food Biomanufacturing Institute (BRIC-NABI).
- Inter-Ministerial Cooperation: DBT- ISRO MoU for space biotechnology, leading to life sciences experiments on the International Space Station.
- Centre-State Partnerships: Initiated a partnership with the Government of Assam to leverage regional biodiversity for biomanufacturing.
- Human Capital Development: BioE3 Youth Challenge launched for grassroots innovation for healthcare, agriculture, environment, and industry.
- Gene-Edited Crops: India became the first country to develop gene-edited rice varieties for nutritional security and climate resilience.
Challenges of BioE3 Policy
- Lack of Milestones: Difficulty in tracking policy progress.
- Human Capital Gaps: Critical expertise shortages, particularly in microbial strain engineering and bioprocessing, requiring stronger hands-on training and interdisciplinary programs.
- Scale-up Bottlenecks: The "valley of death" challenge between discovery and commercialization due to limited funding and developmental stalls.
- Commercialization Barriers: High capital investment for Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) units, limited local supply chains for raw materials, dependence on costly imported materials, and fragmented logistics hinder the growth prospects.
- Biosafety and Public Trust: Ongoing debates over biosafety concerns for gene-edited crops and the need for proactive, responsible science communication to build public trust.
Conclusion
The BioE3 Policy, with the National Biofoundry Network, marks a pivotal step in India's journey towards building a sustainable, self-reliant, and green bioeconomy. With an ambitious target of reaching a US$300 billion bioeconomy by 2030 and potentially US$2.7 trillion by 2050, India is poised to emerge as a global bioeconomy powerhouse, playing a critical role in achieving national and international net-zero carbon emission goals.





