Why in the News?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) recently completed five years.
About the National Medical Commission
- Establishment: A statutory body constituted under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019; came into force on 25 Sept 2020.
- Replaced the Medical Council of India (MCI), and the Board of Governors was dissolved.
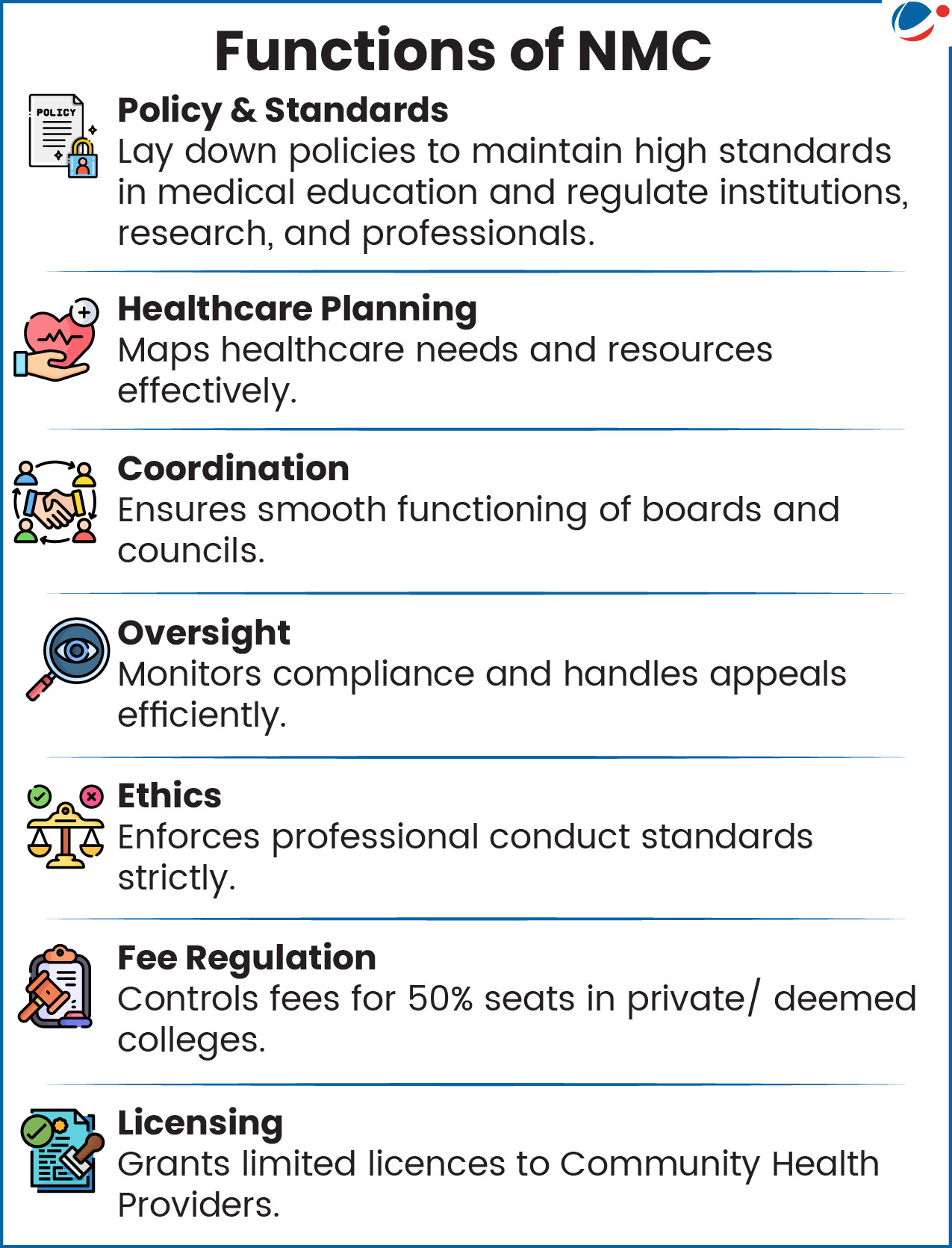
- The Commission consists of the following persons to be appointed by the Central Government, namely
- a chairperson
- ten ex officio Members
- twenty-two part-time Members
- Four Autonomous boards under NMC:
- Undergraduate Medical Education Board
- Post-Graduate Medical Education Board
- Medical Assessment & Rating Board
- Ethics and Medical Registration Board.
Issues With NMC
- Governance Gap: Weak accountability due to a body dominated by doctors; it lacks public health experts, social scientists, or citizen voices.
- NMC also allows appeals only from registered medical practitioners, systematically rejecting patients' complaints despite no legal bar.
- Fee Regulation: Controls fees for only 50% of private seats; others remain prone to exorbitant charges, excluding poor students.
- Ethics Oversight: Misconduct cases handled without judicial expertise or timelines, raising concerns of impartiality.
- National Medical Register (NMR): The process for updating and verifying the credentials of practicing doctors in the NMR has been very slow, leading to concerns about unqualified individuals practicing medicines.
Conclusion
While the NMC marks a step towards modernizing medical governance in India, addressing concerns of accessibility, ethical oversight, and inclusivity remains vital to build a transparent, accountable, and globally competitive healthcare system.






