The European Commission and the High Representative adopted a Joint Communication outlining a 'New Strategic EU-India Agenda', marking a significant milestone in the India-EU relations.
Key highlights of New Strategic EU-India Agenda
- Foundation: Strategic Partnership established in 2004.
- Aim: To enhance prosperity, security and tackle major global challenges together.
- 5 Core Pillars:
- Prosperity and Sustainability: Drives economic growth, job creation, industrial development, and decarbonization.
- Trade and Investment: Focusing on untapped potential in trade and investment, finalizing the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations by the end of 2025, concluding an Investment Protection Agreement (IPA).
- Economic Security and Supply Chains: Strengthening economic security within the Trade and Technology Council (TTC), creation of Blue Valleys as platforms for private-sector engagement in selected value chains.
- Advancing clean transition and resilience: Building on shared commitments – such as the EU’s 2050 and India’s 2070 net-zero pledges. E.g., creation of an EU-India Task Force on Green Hydrogen.
- Technology and Innovation: Focuses on emerging technologies for open, secure, human-centric innovation.
- Supporting Critical Emerging Technologies: E.g. Establish EU-India Innovation Hubs.
- Advancing a Conducive Digital Environment: E.g. Collaborate on Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for service delivery.
- Security and Defence: Addresses global security threats, geopolitical tensions, and counterterrorism and transnational crime. E.g. Coordinate on Indo-Pacific and promote rules-based maritime order.
- Connectivity and Global Issues: Strengthens regional connectivity, cooperation in third countries (such as Africa), and global governance. E.g. Collaborate via EU’s Global Gateway and India’s MAHASAGAR.
- Enablers across Pillars: Enhances skills mobility, knowledge exchanges, business engagement, and institutional cooperation.
- Prosperity and Sustainability: Drives economic growth, job creation, industrial development, and decarbonization.
The agenda highlights how closer EU-India cooperation is more important than ever in wake of ongoing weaponisation of dependencies, unilateral trade practices, and widening economic asymmetries across the globe.
Article Sources
1 sourceIsrael became first OECD country to sign bilateral investment agreement with India. The previous Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) signed between India and Israel in 1996 got terminated in 2017.
Key Features of India-Israel BIT
- Boost to Investment: Increased bilateral investments, which presently stands at a total of USD 800 million.
- Investor Protection: Balances investor protection with the State’s regulatory rights by ensuring a minimum standard of treatment.
- Dispute Resolution: Facilitating growth of trade and investments with dispute resolution mechanism through arbitration.
Evolving co-operation between India-Israel
- Economic: Bilateral trade was USD 6.53 billion (excluding defense) with India's exports surplus in FY 2023-24.
- Regional co-operation: I2U2 Partnership’s first summit held in 2022, with India, Israel, UAE, and US participation.
- Innovation & Science Technology: E.g., India-Israel Industrial R&D and Innovation Fund (I4F) for 5 years (2023–27).
- Defence: Co-developed the Barak-8 missile system, regular port calls in Haifa, etc.
- Other: Cultural Exchange Programme, cooperation in health and medicine, MoUs on agriculture and water resource management, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourcePrime Minister of Singapore paid an official visit to India.
The visit commemorated 60 years of India-Singapore diplomatic relations, reaffirming the shared legacy of friendship, trust, and mutual respect.
Key Outcomes: -
Both countries adopted a forward-looking and substantive roadmap for Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP) aims to deepen cooperation in eight critical areas:
- Economic Cooperation: · Both sides will continue to engage in dialogue and make progress on initiation of the 3rd review of Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and achieve substantial review of the ASEAN India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) in 2025.
- Supporting India's semiconductor industry, enhance India-Singapore capital market connectivity
- Space: Promote joint collaborations between Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) and the Office for Space Technology & Industry, Singapore
- Defence and Security Cooperation: Deepening defence technology cooperation in emerging areas like Quantum Computing, AI, Automation, and Unmanned Vessels.
- Reaffirmed strong commitments to combat terrorism, including cross-border terrorism and terror financing.
- Digitalisation: Strengthening of Digital Finance and Fintech cooperation, cybersecurity, and capital market linkages.
- Expanding and maximizing the potential of the UPI-PayNow Linkage for cross-border payments.
- Skills Development: Jointly developing a National Centre of Excellence in Advanced Manufacturing in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- Sustainability: Collaborating on green initiatives in multilateral frameworks like the International Solar Alliance and Global Biofuels Alliance.
- Step up cooperation in green hydrogen and ammonia production, exploring urban water management and civil nuclear domain cooperation.
- Connectivity: Supported the establishment of an India-Singapore Green and Digital Shipping Corridor (GDSC) between the Port of Singapore and ports in India.
- Healthcare and Medicine: Deepening collaboration in digital health, disease surveillance.
- People-to-People and Cultural Exchanges: Strengthening social, cultural, and people-to-people linkages.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe agreement aims to develop aspects of defence cooperation between the two countries and strengthen joint deterrence against any aggression.
- It states that “any aggression against either country shall be considered an aggression against both”.
Impacts of the Agreement
- Nuclear Warfare: It further raises the fears of nuclear warfare, as Pakistan extends its nuclear umbrella to Saudi Arabia, in the already tense region of West Asia.
- Shifting power dynamics: For Saudi Arabia, it strengthens defences against threats from Iran, Yemen’s Houthi militias and Israel.
- It signifies a move away from traditional role of US as security guarantor in the region due to US ally Israel’s war on Gaza and its strikes on regional neighbours.
- This could create a strategic vacuum for China to deepen its clout in the region.
- Implications for India: Pakistan may see the pact as strategic deterrence against India in future military confrontation, especially in response to cross border terrorism.
India-Saudi Arabia Relations
- Strategic partnership was formalised in 2010 via Riyadh declaration.
- Economic: India is the second largest trade partner of Saudi Arabia, whereas Saudi Arabia is the fifth largest trading partner of India.
- Bilateral trade in 2023 was 42.98 billion and India remained a net importer
- In 2024, Saudi Arabia contributed 6.7% of India's total inward remittances.
- Energy Partnership: Saudi Arabia is third largest crude oil supplier to India.
The four western nations, United Kingdom, Canada, Portugal and Australia, joined over 140 UN member states in recognizing Palestine as a state.
- India recognized the Palestinian State in 1988.
- Recently, India voted in favour of a resolution in the UN General Assembly endorsing the ‘New York Declaration’ on the peaceful settlement and implementation of the Two-State Solution.
Recognition of States
- The process in which a state acknowledges another entity as a state is known as recognition.
- Article 1 of the 1933 Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States defines the criteria for statehood: Permanent population, definite territory, government and capacity to enter into relations with other states.
- Effects of State Recognition
- It acquires the capacity to enter into diplomatic relations with other states.
- It acquires the capacity to enter into treaties with other states.
- The state is able to enjoy the rights and privileges of international statehood.
- The state can become a member of the United Nations organisation.
- Palestine is a UN “Permanent Observer State,” not a full member.

Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, UN General Assembly (UNGA) announced to establish two mechanisms within the UN to promote international cooperation on the governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- It builds on the "Pact for the Future" and the "Global Digital Compact," outlining a significant step towards international, non-military AI governance.
About the new mechanisms
- Independent International Scientific Panel on Artificial Intelligence: To promote scientific understanding of AI by issuing evidence-based scientific assessments synthesizing and analysing existing research related to the opportunities, risks and impacts of AI.
- Global Dialogue on AI Governance: To serve as a platform to discuss international cooperation, share best practices and lessons learned, and to facilitate open, transparent and inclusive discussions on AI governance.
Other UN Mechanisms for Global AI Governance
- Pact for the Future: Adopted at the Summit of the Future in September 2024 to chart a path toward achieving the SDGs and responding to emerging challenges and opportunities.
- Global Digital Compact: Annexed as part of the Pact for Future, it is a comprehensive global framework for digital cooperation and AI governance.
- AI for Good Global Summit (organized by ITU since 2017): Identified AI applications to advance on the SDGs and scale such applications for global impacts.
- Others: Adoption of the first global standard on AI ethics in 2021; UNESCO Recommendation on the Ethics of AI, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceReport of the UN-mandated Independent International Commission of Inquiry provided a legal analysis of Israel's conduct in Gaza concerning the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (Genocide Convention).
About Genocide Convention
- Defines Genocide as acts committed with the intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group.
- Genocide is a crime that can take place both in time of war as well as in time of peace.
- Membership: Signatories – 41, Parties - 153 States.
- India has signed the treaty in 1949 and ratified in 1959.
- International Court of Justice (ICJ) adjudicates cases related to the interpretation and application of the convention.
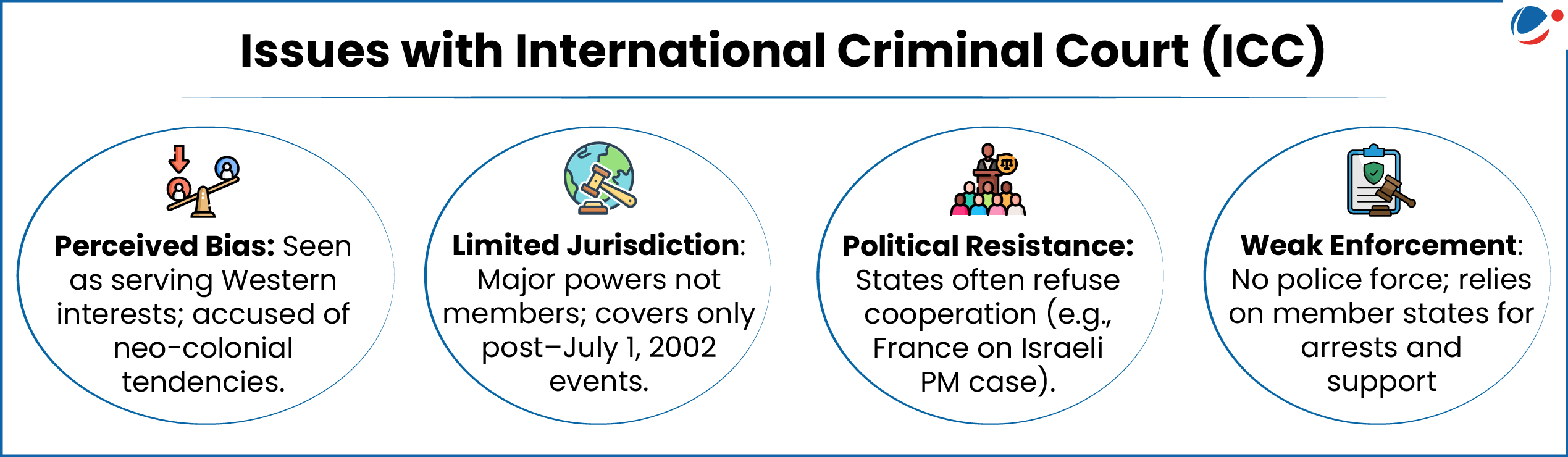
Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger recently withdrew from International Criminal Court (ICC).
In a joint statement, all three countries accused the ICC of being “a tool of neo-colonial repression controlled by imperialist powers.”
About ICC (HQ: Hague, Netherlands)
- It is the world’s first permanent international criminal court.
- Origin: Founded by Rome Statute (Adopted in 1998 and entered in force in 2002)
- Jurisdiction: investigate, prosecute, and try individuals (not groups or States) accused of committing serious crimes
- Crimes under ICC’s jurisdiction: Genocide, Crimes against humanity, War crimes, crime of aggression.
- Membership: 125 member countries
- India, Israel, the US, Russia and China are not parties to the Rome Statute.
- Funding: mainly by States Parties
- Enforcement: ICC's decisions are binding.
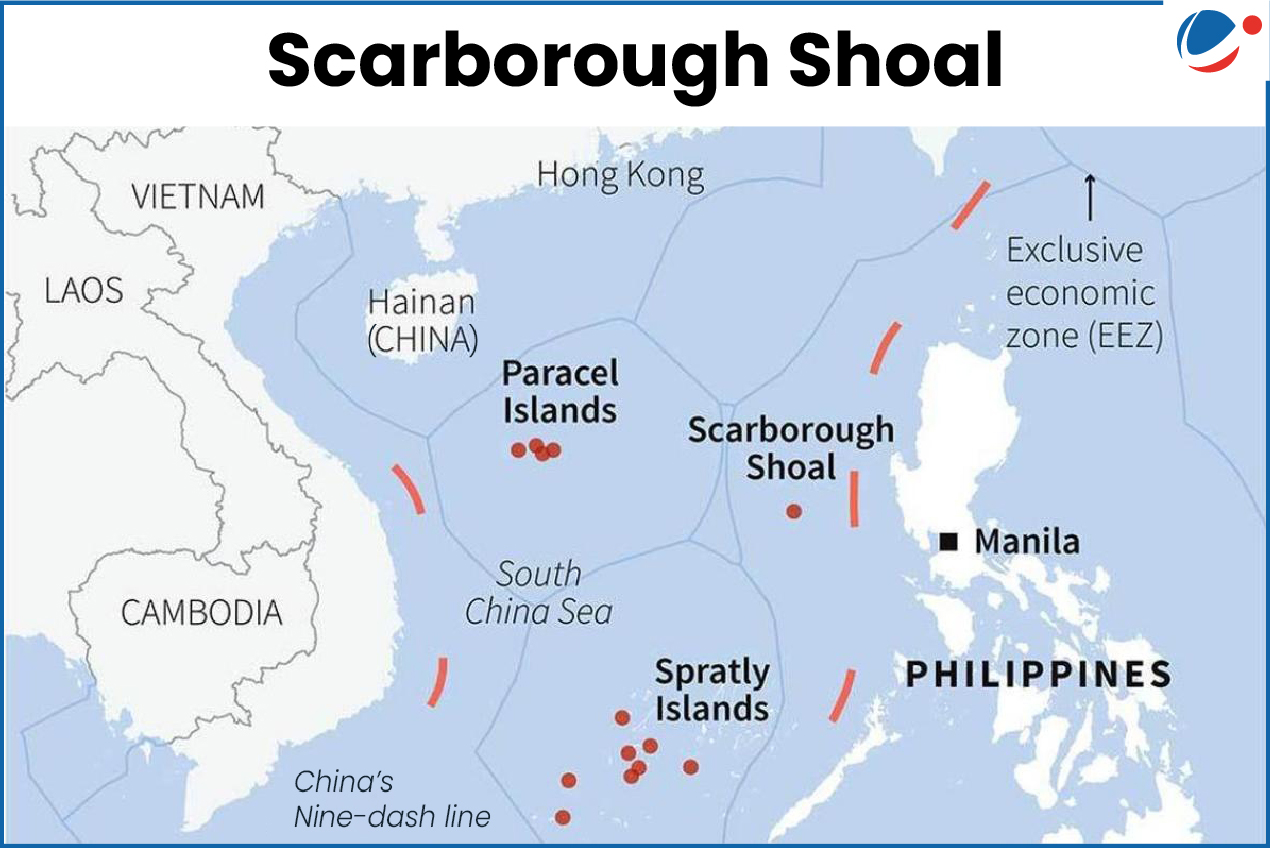
The Philippines strongly condemned China’s move to set up a nature reserve at Scarborough Shoal.
About
- Scarborough Shoal, also called Huangyan Island in China and Panatag Shoal in Philippines, is a small atoll in the South China Sea.
- Both China and the Philippines consider it part of their territory.
United States is in talks with Afghanistan to regain the control of the Bagram Air Base in Afghanistan.
About Bagram Air Base
- The largest air base in Afghanistan located north of the capital Kabul.
- Originally built by the Soviets in 1950s and after Soviet withdrawal in 1990s, it became a frontline in war between Taliban and Northern Alliance fighters.
- After 2001 terror attack on USA, it became the centre of US operations in their war against terror in Afghanistan.
- US and NATO troops pulled out of Bagram in 2021.






