Why in the News?
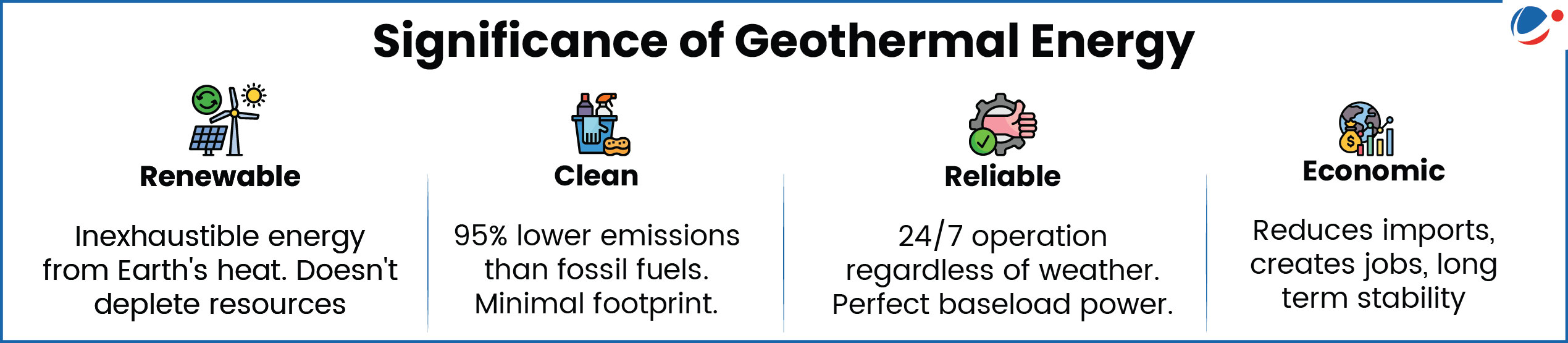
The Union Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) notified National Policy on Geothermal Energy (2025), India's first such Policy to reinforce efforts for an energy transition.
About Geothermal Energy
- It harnesses heat stored within the Earth's crust.
- Key Sources and applications-
- High-enthalpy (~200°C) resources: Like volcanic regions, geysers and hot springs suitable for electricity generation.
- Low- to medium-enthalpy (100–180°C) resources: Like hot rocks and shallow ground layers suitable for direct-use applications like heating and cooling, agri-food, aquaculture and geothermal heat pumps.
- Estimated Potential in India: 10,600 MW (Geothermal Atlas of India, 2022)
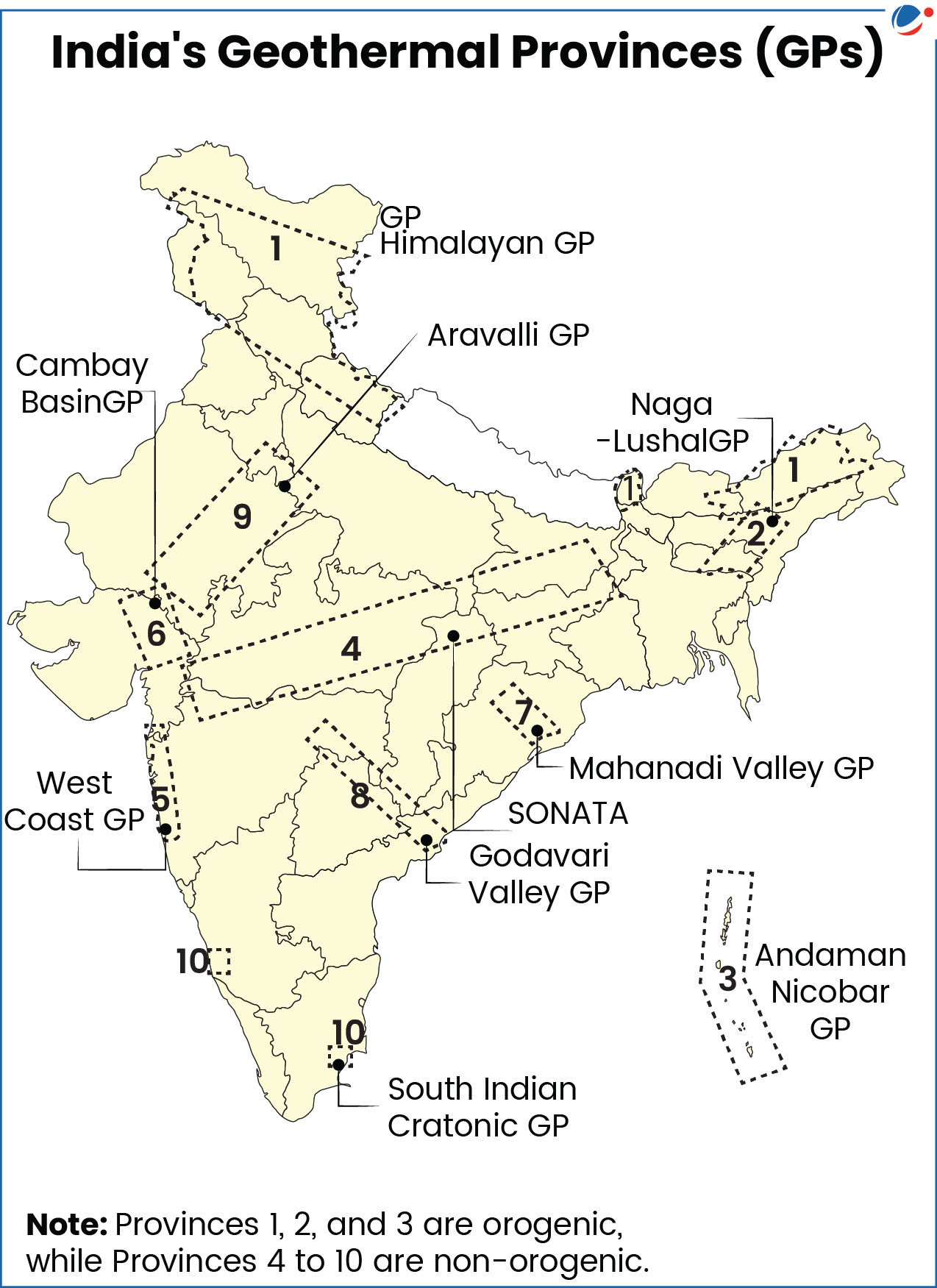
- GSI identified 381 hot springs and 10 geothermal provinces (see infographic)
Challenges related to development of Geo Thermal Energy in India
- High Upfront Cost: Exploration and drilling are capital intensive.
- High investment risk: Due to uncertainty of finding commercially viable reservoirs which deter private players.
- Exploration & Data Gaps: Limited deep drilling assessment and data with geological complexity (Himalayas, volcanic zones) making resource assessment more difficult.
- Lack of Commercial Projects: Only one 20 kW pilot plant (Manuguru, Telangana) exists and no utility-scale projects are established yet.
- Technology & Skill Gaps: India lacks indigenous drilling and reservoir management technology and expertise.
- Environmental & Social Concerns: Risks of land subsidence, seismicity, and water contamination if reinjection is not managed.
About National Policy on Geothermal Energy (NPGE, 2025)
- Vision: To establish geothermal energy as a major pillar of India's renewable energy mix, achieving net zero carbon emission by 2070.
- Nodal Ministry for implementation of GE based projects: MNRE
- Goals of NPGE, 2025
- Improve research on GE development and deployment, advanced exploration, drilling techniques, reservoir management & cost-effective power generation
- Collaborate with Ministries, international geothermal development bodies and national research institutes to incorporate global best practices
- Deploy geothermal heating and cooling solutions, and other direct-use applications to decarbonize buildings, agriculture, industries, etc.
- Build an enabling ecosystem with public-private partnerships, capacity building, and knowledge sharing.
Key features of the Policy
- Scope of policy:
- Geothermal Resource Assessment, Power Production systems, Direct use, Ground (geothermal) Source Heat Pump (GSHP) etc.
- Emerging Innovative Technologies such as Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS), Advanced Geothermal Systems (AGS), geothermal energy storage, offshore geothermal wells etc.
- Extracting GE from abandoned oil and gas wells.
- Mineral by-products such as silica, borax, cesium, lithium, etc. subjected to rules and payment of royalty under MMDR Act.
- Creation of a geothermal resource data repository: Through Intergovernmental/inter-agency collaboration, e.g., with Ministries of Mines, Earth Sciences etc.; institutes like Geological Survey of India (GSI), National Data Repository (NDR), etc.
- Operators/developers will be permitted to conduct geothermal resource assessment surveys for R&D, assessment etc.
- Developmental Model
- Preference to indigenous geothermal technologies: By encouraging local innovation.
- Economic feasibility models: like revenue sharing, milestone based payment etc.
- Central funding assistance: To Northeastern Region and special category states.
- Joint ventures: Between oil and gas companies, mineral companies, and geothermal developers
- Repurposing oil and gas production facilities: like pipelines, etc.
- Pilot projects and Centres of Excellence (CoEs) for R&D and training.
- Sustainability
- Promotion of Technology for safe, non-polluting use of geothermal fluids or by-products.
- Developing Environmental & Social Impact Assessment guidelines for geothermal projects.
- Financing Mechanisms
- Renewable Energy Research and Technology Development Programme (RE-RTD) provides up to 100% financial support to Government/non-profit research organizations and upto 70% to Industry, start-ups, private Institutes, entrepreneur, and manufacturing units
- Long-term concessional loans, Sovereign Green Bonds, Viability Gap Funding (VGF), etc.
- Fiscal incentives: GST/Import duty exemptions on equipment, services; Tax holidays etc.
- Support mechanisms: Inclusion in Indian Carbon Credit Trading Scheme; Inter-State Grid Access; Open Access charges waiver; eligibility for Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) etc.
- Guidelines for States and Union Territories
- Responsible for granting geothermal exploration/development permit and land lease
- Exploration leases may be granted for 3 to 5 years.
- Lease for development for power generation or direct-use applications for up to 30 years.
- Single-window clearance mechanisms managed by designated state nodal agencies.
- Ensure stakeholder consultations and adequate compensatory measures, particularly in tribal and remote areas.
- Responsible for granting geothermal exploration/development permit and land lease
Conclusion
The NPGE, 2025 directly addresses sector challenges by streamlining approvals, encouraging R&D and partnerships, and providing fiscal incentives and financial support. With mechanisms for local innovation, stakeholder consultation, and dedicated pilot projects, the policy creates a strong foundation for sustainable, reliable geothermal growth.






