Cyclone rain-triggered landslides in the Northeast spotlights need for building resilience to multi-hazard disasters.
About Landslides
- It is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope under the direct influence of gravity.
- Landslides are generally classified by type of movement (slides, flows, spreads, topples, or falls) and type of material (rock, debris, or earth).
Causes
- Natural: Rainfall, snowmelt, changes in water level, stream erosion, earthquakes, volcanic activity, etc.
- Human activity: Agriculture, construction, deforestation, irrigation, encroachment in vulnerable terrain, etc.
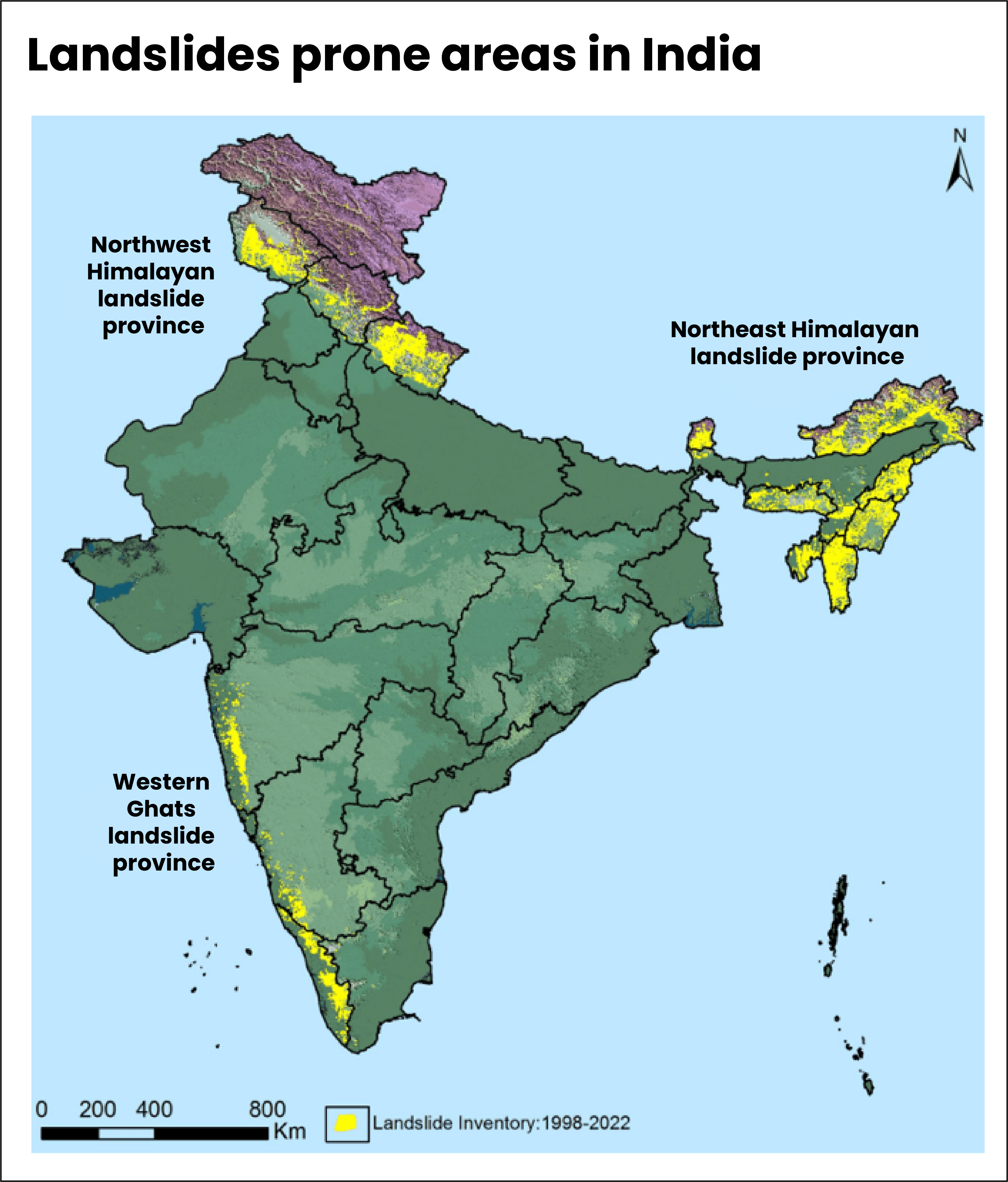
Landslides prone areas in India
- The Northwest Himalayas contribute- 66.5% of landslides in India, followed by the Northeast Himalayas -18.8% and the Western Ghats - 14.7%.
- Western Ghats: Laterite exposed along plateau edges, growth of roots along the opening of fractures, etc. are some of the significant causes of landslides in the region.
Initiatives taken for Landslides reduction
- National Landslide Risk Management Strategy (2019): comprises hazard mapping, monitoring and early warning system etc.
- National Landslide Susceptibility Mapping (NLSM) Programme: for landslide prone areas in the country.
- Landslide Risk Mitigation Scheme (LRMS): to provide financial support for site specific Landslide Mitigation Projects.