It assessed the effectiveness of India’s measures to combat Money Laundering (ML), Terrorist Financing (TF), and proliferation financing.
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) places India in the ‘regular follow-up’ category, a distinction shared by only four other G20 countries.
- FATF is an intergovernmental organisation established in 1989 by G7 to examine and develop measures to combat ML.
- India became a member of FATF in 2010
About Money laundering
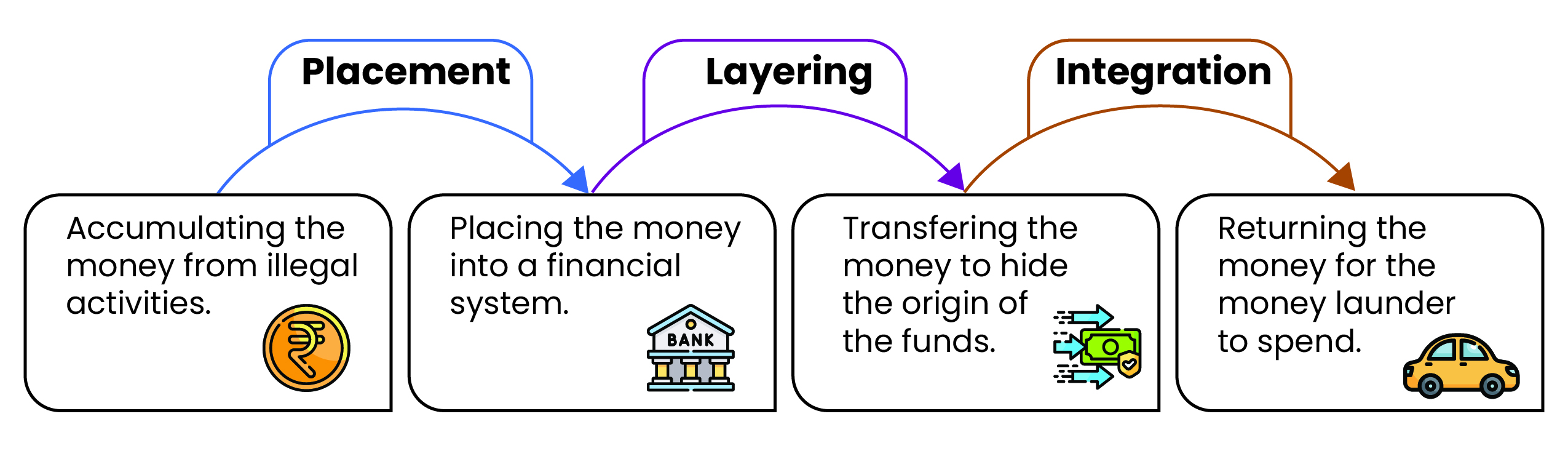
- It is the processing of criminal proceeds to disguise their illegal origin. It involves three stages-Placement, Layering, and Integration (See infographic).
Key Achievements of India’s MER
- Mitigation of Risks arising from ML/TF, and from the proceeds of laundering such as corruption, fraud, and organized crime.
- Transition from a cash-based to a digital economy.
- JAM Trinity (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) leading to significant increase in financial inclusion and digital transactions thereby making transactions more traceable.
Recommendations
- Strengthen the supervision and implementation of preventive measures in non-financial sectors.
- Address delays relating to concluding ML and TF prosecutions.
- Measures aimed at preventing the non-profit sector from being abused for TF should be based on risk based approach.






