97% of recorded deep-sea dives had been performed by only five countries: the U.S., Japan, New Zealand, France, and Germany.
- Observation Means: Visual Imaging from manned submersibles, Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs), Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), Tow Cameras tethered to Ships etc.
- Geomorphological features like ridges and canyons saw a disproportionate amount of exploration, compared to abyssal plains, which dominate the seafloor.
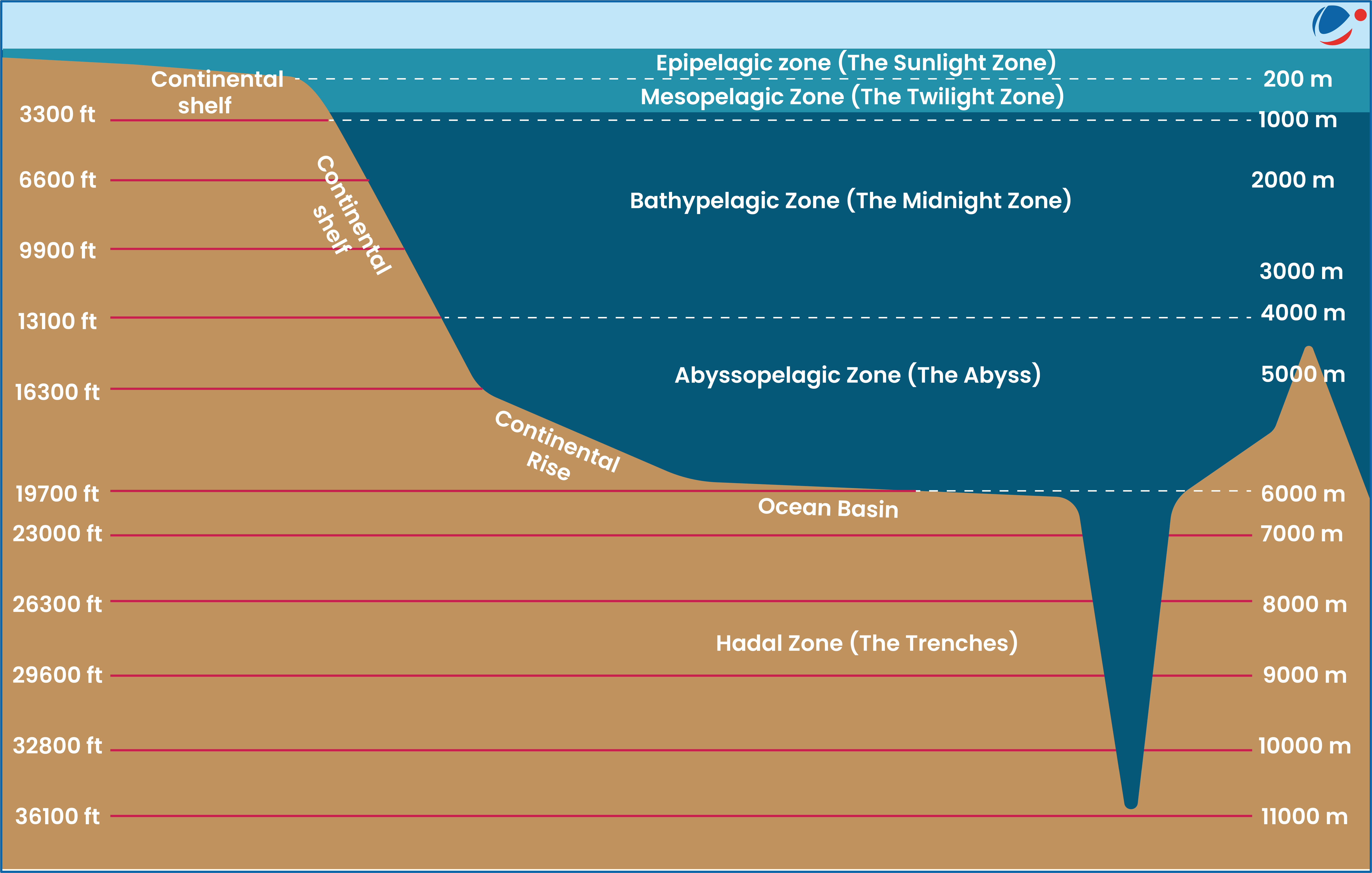
About Deep Ocean
- Deep Ocean is generally defined as sea and seabed below the depth at which light starts to decrease rapidly, typically around 200 meters (where Twilight Zone starts).
- Conditions: Deep ocean is cold – with an average temperature of only 4°C and is subject to extreme pressure, from about 40 to over 110 times the pressure of Earth’s atmosphere.
- Biodiversity: Squid, krill, jellies, and fish are super abundant in Mesopelagic Zone (200m-1000m) with about 90% of world’s fish (by weight).
- Hydrothermal Vents: Openings in the Earth’s Crust on the ocean floor, which releases geothermally heated mineral-rich water, that is used by microorganisms to provide energy and nutrients through chemosynthesis.
- Significance of Exploration: Sources of energy (oil, gas, methane hydrate, ocean currents), promising source for new antibiotic and anti-cancer drugs, presence of polymetallic nodules, understanding, predicting and mitigating climate change etc.