Why in the News?
Indian Railway Minister announced the development of the world's most powerful hydrogen fuel-run train engine with 1,200 horsepower.
More about the news
- Only four countries (Germany (1st), France, Sweden, and China) in the world have hydrogen-powered trains, capable of producing around 500 to 600 horsepower.
- All hydrogen powered rail vehicles, whether large or small, are categorized as 'hydrail,' whether the fuel is used for the traction motors, auxiliary systems, or both.
- They have considerable advantage over electric trains: Electric trains require expensive and complex infrastructure, including overhead gantries to carry power cables and power substations, which is not required in hydrail.
About India's Indigenous Hydrogen Train
- Designed by: Research, Design, and Standard Organization (RDSO) in Lucknow.
- Manufactured by: Integral Coach Factory, Chennai manufacturing coaches for the train.
- Background: The Ministry of Railways, Government of India, announced the "Hydrogen for Heritage" project in 2023.
- Union Budget 2023–24: Announced and allotted funds for developing 35 hydrogen fuel cell trains.
- As part of this venture, existing Diesel-Electric Multiple Unit (DEMU) rakes will be retrofitted with green hydrogen fuel cells.
- Trial Route: Jind-Sonipat in Haryana.
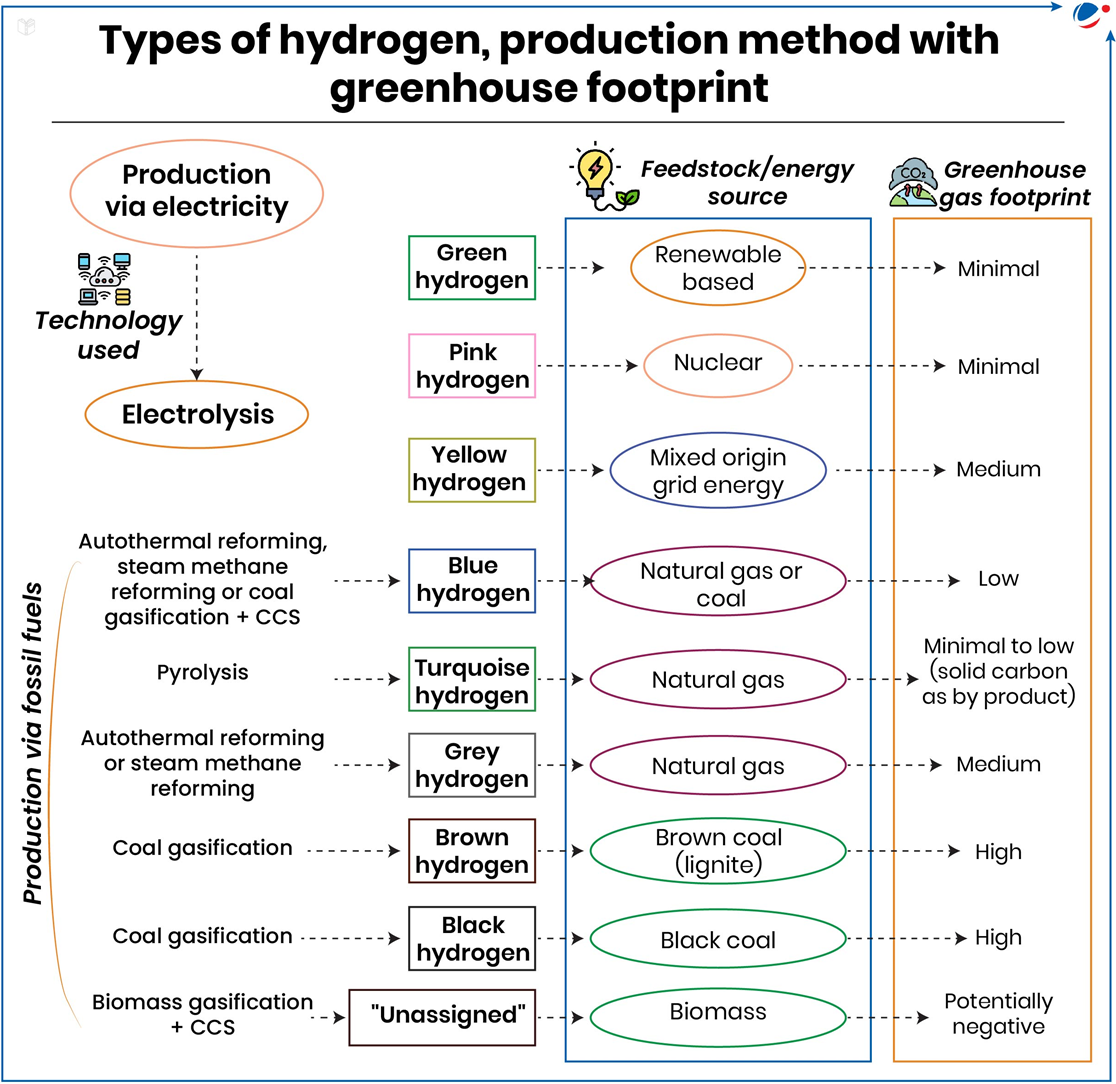
About Hydrogen and its ecosystem
- Hydrogen is the simplest and most abundant element in the universe, consisting of just one proton and one electron.
- Molecular Structure: Diatomic, meaning it contains two atoms.
- Chemical Properties: Highly reactive and combines with almost all elements to form binary compounds called hydrides, can undergo oxidation as well as reduction can lose an electron to form H+ (proton) or gain an electron to form Hˉ (hydride ion).
- Known for forming acids when combined with non-metals like chlorine, sulfur etc.
- Isotopes: Protium, Deuterium, Tritium.
Global initiatives for Hydrogen production
- World Bank's 10 GW Clean Hydrogen Initiative: Promoting clean hydrogen as a low-carbon energy source using renewable energy, in emerging markets and developing countries.
- The Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM): International clean energy leadership platform to drive international collaboration on policies to accelerate the commercial deployment of hydrogen fuels.
- The Clean Energy Ministerial Hydrogen Initiative (CEM H2I): Coordinated by The International Energy Agency (IEA), developed according to the CEM framework document. India is member.
- Global Programme for Hydrogen in Industry (GPHI): In 2021, UNIDO launched (GPHI) to support developing countries and transition economies in overcoming various challenges that hinder hydrogen development.
India's initiatives for Hydrogen production
- National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM): To make India a Global Hub for production, usage and export of Green Hydrogen and its derivatives and green hydrogen production target of 5 million metric tonnes per annum by 2030.
- The Green Hydrogen standard for India: Define emission thresholds for 'Green' classification, was notified on 19th August, 2023.
- Guidelines for Pilot Projects for utilizing Green Hydrogen in the Shipping and Steel Sector: For retrofitting existing ships to run on Green Hydrogen and relevant facilities on ports.
Challenges in adoption of hydrogen as fuel
- Cost of Raw Materials: Precious metals such as platinum and iridium are typically required as catalysts in fuel cells and some types of water electrolyze, which means that the initial cost can be high.
- Hydrogen Extraction: Hydrogen does not exist on its own naturally so needs to be extracted from water or separated from carbon fossil fuels. Both of these processes require a significant amount of energy.
- Need of specific infrastructure for the green hydrogen production and requirement of advanced technology.
- Highly Flammable: Hydrogen gas burns in air at concentrations ranging from 4 to 75%. It brings understandable safety concerns.
- Hydrogen Storage: Complex process, as storing hydrogen as a liquid or at high pressure requires energy-intensive processes, such as liquefaction at cryogenic temperatures or compression to high pressures.
Way forward
- Government Support and Incentives: Continue providing financial incentives and programs to give investors the confidence needed for rapid private investment in the sector.
- Generate Demand for Production: The next step is to generate demand for production and consumption as done in case of Electric vehicles through schemes like PM E-DRIVE Scheme.
- Scale up Renewable Energy Capacity: Green hydrogen production necessitates significant renewable energy capacity. The mission aims for an associated renewable energy capacity addition of about 125 GW.
- Global collaborations: Such as in September 2023, India signed an MoU with Saudi Arabia for cooperation in the field of Green Hydrogen & Ammonia to set up capacities.








